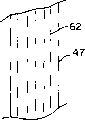CN1272165C - 弹性丝束粘合的层压制品 - Google Patents
弹性丝束粘合的层压制品 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1272165C CN1272165C CNB028249135A CN02824913A CN1272165C CN 1272165 C CN1272165 C CN 1272165C CN B028249135 A CNB028249135 A CN B028249135A CN 02824913 A CN02824913 A CN 02824913A CN 1272165 C CN1272165 C CN 1272165C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- elastic laminate
- paper web
- fiber
- laminate according
- fibre
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/49—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers
- A61F13/496—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers in the form of pants or briefs
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/15577—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing
- A61F13/15585—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing of babies' napkins, e.g. diapers
- A61F13/15593—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing of babies' napkins, e.g. diapers having elastic ribbons fixed thereto; Devices for applying the ribbons
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/49—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers
- A61F13/49007—Form-fitting, self-adjusting disposable diapers
- A61F13/49009—Form-fitting, self-adjusting disposable diapers with elastic means
- A61F13/49014—Form-fitting, self-adjusting disposable diapers with elastic means the elastic means is located at the side panels
- A61F13/49015—Form-fitting, self-adjusting disposable diapers with elastic means the elastic means is located at the side panels the elastic means being elastic panels
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/49—Absorbent articles specially adapted to be worn around the waist, e.g. diapers
- A61F13/49007—Form-fitting, self-adjusting disposable diapers
- A61F13/49009—Form-fitting, self-adjusting disposable diapers with elastic means
- A61F13/4902—Form-fitting, self-adjusting disposable diapers with elastic means characterised by the elastic material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B27/00—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin
- B32B27/02—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin in the form of fibres or filaments
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B5/00—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts
- B32B5/02—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by structural features of a fibrous or filamentary layer
- B32B5/04—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by structural features of a fibrous or filamentary layer characterised by a layer being specifically extensible by reason of its structure or arrangement, e.g. by reason of the chemical nature of the fibres or filaments
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B5/00—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts
- B32B5/22—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by the presence of two or more layers which are next to each other and are fibrous, filamentary, formed of particles or foamed
- B32B5/24—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by the presence of two or more layers which are next to each other and are fibrous, filamentary, formed of particles or foamed one layer being a fibrous or filamentary layer
- B32B5/26—Layered products characterised by the non- homogeneity or physical structure, i.e. comprising a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foam layer; Layered products characterised by having a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts characterised by the presence of two or more layers which are next to each other and are fibrous, filamentary, formed of particles or foamed one layer being a fibrous or filamentary layer another layer next to it also being fibrous or filamentary
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H1/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres
- D04H1/40—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties
- D04H1/54—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving
- D04H1/559—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of staple fibres or like relatively short fibres from fleeces or layers composed of fibres without existing or potential cohesive properties by welding together the fibres, e.g. by partially melting or dissolving the fibres being within layered webs
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/24628—Nonplanar uniform thickness material
- Y10T428/24636—Embodying mechanically interengaged strand[s], strand-portion[s] or strand-like strip[s] [e.g., weave, knit, etc.]
- Y10T428/24645—Embodying mechanically interengaged strand[s], strand-portion[s] or strand-like strip[s] [e.g., weave, knit, etc.] with folds in parallel planes
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/249921—Web or sheet containing structurally defined element or component
- Y10T428/249924—Noninterengaged fiber-containing paper-free web or sheet which is not of specified porosity
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/249921—Web or sheet containing structurally defined element or component
- Y10T428/249924—Noninterengaged fiber-containing paper-free web or sheet which is not of specified porosity
- Y10T428/249933—Fiber embedded in or on the surface of a natural or synthetic rubber matrix
- Y10T428/249939—Two or more layers
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/249921—Web or sheet containing structurally defined element or component
- Y10T428/249924—Noninterengaged fiber-containing paper-free web or sheet which is not of specified porosity
- Y10T428/24994—Fiber embedded in or on the surface of a polymeric matrix
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/249921—Web or sheet containing structurally defined element or component
- Y10T428/249924—Noninterengaged fiber-containing paper-free web or sheet which is not of specified porosity
- Y10T428/24994—Fiber embedded in or on the surface of a polymeric matrix
- Y10T428/249942—Fibers are aligned substantially parallel
- Y10T428/249945—Carbon or carbonaceous fiber
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/29—Coated or structually defined flake, particle, cell, strand, strand portion, rod, filament, macroscopic fiber or mass thereof
- Y10T428/2913—Rod, strand, filament or fiber
- Y10T428/2929—Bicomponent, conjugate, composite or collateral fibers or filaments [i.e., coextruded sheath-core or side-by-side type]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/31504—Composite [nonstructural laminate]
Abstract
一种简化的弹性层压制品由非织造织物形成,而且特别适合于用做训练裤等的侧翼。多个热塑性的弹性的纤维位于第一和第二面层幅面料之间。上述纤维具有弹性芯和粘接剂表面。在两个面层幅面料之间具有弹性纤维,上述面层幅面料砑光在一起,这样通过弹性纤维的接触粘接把上述面层幅面料粘合在一起。
Description
技术领域与背景技术
在用于一次性或有限用途的衣服的弹性层压衣服翼片的领域中,所希望的质量包括轻的重量、良好的皮肤感觉(手感)、外部抗磨性以及良好的柔顺性和粘合强度。通常这样的弹性层压制品可以良好手感的第一面层制成,以一种不刺激皮肤的方式与穿用者的皮肤接触。第二外部的面层用作远离穿用者皮肤的衣服面层的外侧。在这两个面层之间施加有粘接剂和丝束或者弹性材料的幅面料(或网或织物)。
然而这样的弹性层压制品产生的第一个问题是在没有脱粘的情况下上述面层会彼此粘合在一起,以及该弹性层压制品具有拉紧的弹性。当衣服变湿时,例如在遭受全部进入到水中的游泳训练裤中,这尤其成问题。在美学上产生的第二个问题是当更多的粘接剂加入以构成上述层压制品时,由于加入的更多的粘接剂,上述材料变得更重、以及更僵硬,或者具有较低的柔顺性。标准的方法通常需要喷涂整个的一层粘接剂,这就导致美学上的布样性质的降低。再者,由于在制造织物(例如粘接剂的喷涂)时使用了更多的步骤或者更多的材料,从而需要更多的设备和材料,这就导致经济上的损失。
热熔施用粘接剂需要在使用粘接剂时以一种液体的方式施加,以及会存在除了上述问题以外的问题,包括增加的能源消耗、增加的厚度、工艺控制和转化时间。为了粘合,上述面层的熔粘需要热塑性材料的面层幅面料或者弹性丝束或网或者上述两者都加热到至少部分达到它们的熔点。当热熔施用时,这些热熔技术会遇到同样的热连接的问题以及会进一步影响到表面强度和层压强度的问题,以及布样感觉的降低。
这就需要提供经济的、轻重量的、容易制造的具有所需的美学性能的非织造层压制品。
发明内容
根据本发明的一个方面,提供一种弹性层压制品,它包括:第一面层幅面料;第二面层幅面料;多个热塑性的粘性弹性纤维丝束位于第一和第二面织物之间;以及所述纤维丝束具有弹性芯和粘接剂表面,以及通过与所述纤维丝束的粘接剂表面的接触粘接把第一面层幅面料和第二面层幅面料粘合在一起,从而形成弹性层压制品。
本发明还提供一种弹性层压制品,它主要包括:第一幅面料,其构造成位于衣服的内侧;第二幅面料,其构造成位于衣服的外侧;多个热塑性的弹性的纤维位于第一幅面料和第二幅面料之间;以及所述纤维具有弹性芯和粘接剂表面,以及通过与所述纤维丝束的粘接剂表面的接触粘接把第一幅面料和第二幅面料粘合在一起,从而形成弹性层压制品。
在本发明的一方面,本发明通过提供一种由非织造面层和热塑性的弹性的纤维丝束制成的简化的弹性层压制品解决了在技术中存在的上述需要。多个热塑性的粘性弹性纤维丝位于第一和第二面层幅面料之间。纤维具有弹性芯和富含粘接剂的表面。这样该芯就可以自由执行其主要的弹性作用,同时皮或表面可以自由执行其主要的粘性作用,而不存在尝试从一个单一的合成物得到上述两个作用的同时而导致主要作用的不适当地降低。在上述面层幅面料之间具有弹性纤维,上述面层幅面料被砑光在一起,这样通过弹性纤维的接触粘接把上述面层幅面料粘合在一起。这样就不需要用来单独配置粘接剂的额外的材料、机器、或者是步骤。
由于不存在过多的粘接剂,所以层压制品更轻和更加柔顺,同时仍然保持着各层之间的卓越的粘合强度以及所需的外观。进一步,由于丝束的构造可以允许面层在丝束之间保持自由,本发明可以获得额外的蓬松度和柔软性,同时仍然提供丝束对面层的粘合以及面层对面层的粘合的足够的粘性。直到此时,据信没有人想到教导这样的使用有些粘的、或者带粘性的、弹性体丝束的弹性层压制品,因为本领域的普通技术人员会认为这样的粘性丝束在应用的制造条件下难以工作。
适合在本发明中使用的弹性的纤维可以是纺粘(SB)双组分纤维或者是熔喷(MB)双组分纤维,该纤维具有带粘性的皮,或者是搀入粘接剂的单组分纤维,所述粘接剂将集合或者汇聚到或者迁移到纤维的表面。该工艺可以是垂直长丝层压(VFL)工艺,例如用于制作垂直长丝拉伸粘合层压制品(VFSBL),就像在共同未决的申请WO01/87588中披露的那样,其公开日为2001年11月22日,以及名称为TargetedElastic Laminate;或者是水平/连续长丝层压制品(CFL)制造工艺,例如用于制作连续的长丝拉伸粘合层压制品(CFSBL),就像在授予Wright的美国专利5,385,775中披露的那样,其申请日为1995年1月31日;上述所有文献的全文引用在此作为参考。
上述面层可以是非织造层压制品,例如,但并不限于,大约0.1osy到大约4.0osy的非织造织物,一个具体的例子是0.4osy的聚丙烯纺粘非织造幅面料。以及为了使作为成品的层压制品能够提供扩张性和收缩性,上述面层可以是可收缩的或可扩张的,或者两者同时在层压制品所需的弹性方向上或者弹性轴上是可收缩的或可扩张的。
定义
术语“双组分长丝”或者“双组分纤维”指的是由共挤制的至少两种聚合物形成的并且纺在一起而形成的单根纤维,以及在此也指“共轭”或“多组分纤维”。“双组分”并不意味着仅限于两种组分的聚合物,除非另外特别指出。聚合物通常是指实质上排列在横过双组分纤维横截面的独特的区域,并且沿着双组分纤维的长度连续延伸。这样的一种双组分纤维的构造可以是,例如,一种皮/芯排列,其中一种聚合物被另一种聚合物围绕,或者可以是肩并肩排列,或者是肩并肩并肩排列。双组分纤维通常在授予Kaneko等人的美国专利5,108,820、授予Strack等人的美国专利5,336,552以及授予Pike等人的美国专利5,382,400中有所教导。对于两种组分的纤维来说,聚合物存在的比例可以是75/25,50/50,25/75或者任何其它的所需比例。常规的添加剂,例如颜料和表面活性剂可以一起加入到一种聚合物液流中或者两种聚合物液流中,或者施加到长丝的表面。
在此所使用的术语“主要包括”并不排除存在其它材料,这些其它材料不会显著影响一个给定组分或产品的所需特性,这种类型的典型材料可以包括但不限于:颜料,抗氧化剂,稳定剂、表面活性剂、蜡、助流动剂、溶剂、微粒以及用于增加组分可加工性能的材料。
术语“接触粘着力”或者“接触粘着”指的是一种粘性体系,该体系凭据有粘接剂表面粘着而产生粘结,而没有必要用一种以液体状态加入的材料来产生粘结。
“单组分的长丝”指的是仅由一种主要的聚合物形成并且由那种聚合物的单一液流而形成的纤维。但这并不意味着排除那些由一种聚合物形成,但为了染色、粘合性能、抗静电性能、润滑、柔润性、加工性等等而在其中加入了少量添加剂而形成的纤维。
在此所使用的术语“机器方向”或者MD指织物在生产方向中的长度方向。术语“垂直机器方向”或CD指织物的宽度方向,也就是通常垂直于MD的方向。
术语“熔喷纤维”指的是这样形成的纤维,即通过将融化了的热塑材料经过若干细的、通常圆形的模具毛细管挤压,从而形成汇聚到高速、通常热的气体(例如,空气)流中熔化了的丝条或长丝,该气流是熔化了的热塑材料的长丝变细以减少它们的直径,它可以减少至微纤维直径。此后,熔喷纤维由高速气流携带,并且沉积在收集面上,以形成随机散布的熔喷纤维网。例如在授予Butin等人的3,849,241号美国专利中公开了这种方法。熔喷纤维是连续或间断的微纤维,通常平均直径小于10微米,而且当沉积在收集面上时通常不粘。
术语“微纤维”指平均直径不大于约75微米的小直径纤维,例如具有从约1微米至约50微米的纤维,或者更具体地,微纤维通常具有约1微米至30微米的平均直径。另一种经常使用的表示纤维直径的是丹尼尔,丹尼尔定义称每9000米纤维的克数,并且可用纤维直径的微米数的平方乘以密度的克/cc数再乘以0.00707计算。较低的丹尼尔指较细的纤维,而较高的丹尼尔指较粗或者较重的纤维。例如,给定为15微米的聚丙烯纤维的直径,通过将其平方,结果乘以0.89并且乘以0.00707,可以转换成丹尼尔,这样,15微米的聚丙烯纤维就具有约1.42丹尼尔(152×0.89×0.00707=1.415)。在美国以外,测量单位通常用“特”,“特”定义成克/千米纤维。特可用丹尼尔除以9计算。
在此所使用的术语“颈缩”或“颈缩拉伸”是可替换的,它们指的是织物经过牵引,从而在一定条件下扩展,通过将其拉伸和伸长来增加织物的长度,同时减小了织物的宽度或者横向的尺寸。这种可被控制的牵引可以在较低的温度、室温或者较高的温度下进行,并限于在牵引到所需来撕裂织物的伸长时整个尺寸的增加。颈缩过程典型的包括从喂入辊展平一薄片材料,并使其通过一个以一个给定线速度驱动的制动夹辊部件。一个卷取辊或者夹头,以比制动夹辊高的一个线速度运转,牵引织物并且产生来使织物伸长和颈缩的张力。授予Morman的申请日为1990年10月23日的美国专利4,965,122披露了提供一种可逆颈缩的非织造材料的工艺,包括使材料颈缩,接着加热该颈缩材料,接下来冷却。
在此所使用的术语“可颈缩的材料或层”指的是任何可以颈缩的材料,例如非织造材料、纺织或者是编织材料。在此所用术语“颈缩的材料”指的是这样的一种材料,该材料在至少一个尺寸下(例如纵长方向)进行拉伸,减少横向尺寸(例如宽度),这样当牵引力去除时,材料可以被拉回到或者松弛到它的初始宽度。颈缩的材料典型地具有比没有颈缩的材料高的每单位面积的基量。当颈缩的材料回复到它的没有颈缩的初始宽度时,它应该具有与没有颈缩的材料大约相同的基重。这与拉伸一个材料层是有区别的,在拉伸一个材料层时,所述层变薄并且基重被永久性地减少了。
典型地,这样的颈缩非织造织物材料能够被颈缩高达约80%。例如,本发明各方面的颈缩底片30可以由一个被颈缩约10%至约80%的材料来提供,为了具有改善的性能,理想的是从约20%至约60%,更理想的是从约30%至约50%。为了现有公开的目的,术语“颈缩百分比”或者“收缩的百分比”指的是这样确定的一种比例或者百分比,即测量一个可颈缩材料的颈缩前的尺寸和颈缩后的尺寸之间的差值,以及接着除以可颈缩材料颈缩前的尺寸,然后乘以100得到的百分数。颈缩的百分比(径缩百分比)可以根据上面提到的美国专利4,965,122中的描述来确定。
在此所使用的术语“非织造织物”或者“非织造幅面料”指的是具有这样一种结构的造幅面,该结构由将单根纤维或丝束放置于中间形成,但是不是以象在编织织物中的那样的规则或者可辨别的方式进行放置。非织造织物或者幅面料可以由许多工艺来形成,例如,熔喷工艺,纺粘工艺,气流成网工艺以及粘合梳理网工艺。非织造织物的基重通常以每平方码材料的盎司数(osy)或者每平方米的克数(gsm)来表示,而且纤维的直径通常以微米表示。(注意从osy转换到gsm,需要用33.91乘以osy)。
“个人护理制品”或者“个人护理吸收制品”指的是尿布、擦拭片、训练裤、吸收性内衣裤、成人失禁用品、妇女卫生用品、例如绷带的伤口护理产品以及其他类似物。
术语“聚合物”通常包括但不限于,均聚物、共聚物(包括,例如嵌段、接枝、无规和交替共聚物),三元共聚物等及其混合物和改性物。而且,除非特别限制,术语“聚合物”应包括所有可能的分子几何结构。这些结构包括,但并限于全同立构、间同立构和随机对称结构。
术语“纺粘纤维”指的是小直径纤维,这种小直径纤维通过是融熔的热塑材料经过喷丝头的许多细的圆形的或者其它形状的毛细管挤压成长丝,然后挤压长丝的直径快速减小而成形,例如参见授予Appel等人的美国专利4,340,563,授予Dorschner等人的美国专利4,692,618,授予Matsuki等人的美国专利3,802,817,授予Kinney的美国专利3,338,992和3,341,394,授予Hartman的美国专利3,502,763,授予Petersen的美国专利3,502,538,授予Dobo等人的美国专利3,542,615。纺粘纤维被骤冷,而且当将纺粘纤维沉积在收集表面上时,通常它不粘。纺粘纤维通常是连续的,并且通常具有比熔喷纤维的平均直径大的平均直径,以及更特别地,通常在约10到30微米之间。
术语“实质上连续的长丝”或者“实质上连续的纤维”指的是这样的长丝或纤维,即这些长丝或纤维通过从喷丝头挤制而制备,包括但不限于纺粘和熔喷纤维,这些长丝或纤维在形成非织造幅面料或者织物之前不从它们的原始长度切断。实质上连续的长丝或纤维的平均长度的范围可以具有从大于约15厘米到大于约1米,以及高达形成的非织造幅面料或织物的长度或者大于上述长度。“实质上连续的长丝”(或纤维)的定义包括在形成非织造幅面料或者织物之前不切断的那些长丝或纤维,但是也包括当非织造幅面料或者织物切断时被随后切断的那些长丝或纤维。
术语“短纤维”指的是天然纤维或者是在形成网之前由所制造的长丝切断的纤维,而且上述纤维具有从0.1到15厘米范围内的平均长度,更通常约为0.2到7厘米。
在此使用的表示程度的词语例如“约”,“实质上”以及类似的词语意思就是“在所述条件下当给定制造之间和材料之间的固有差异时所处的状态或者所处的大概状态”,在此使用是为了防止不合理使用本发明所披露的优点,而且在此所示的精确的或者纯粹的附图是为了帮助理解本发明。
附图说明
现有的伴随附图仅仅是帮助对本发明的各个方面进行解释和理解,并不作为对本发明的限制。没有必要对上述附图进行测量,上述附图并不是对真实物体的精确的摄像,除非另外指明。
图1示出了一种训练裤/游泳裤,它可以使用本发明的弹性层压制品;
图2示出了具有面层的弹性的纤维的替换实施例的横向的横断面;
图3示出了具有面层的弹性的纤维的替换实施例的横向的横断面;
图4示出了具有面层的弹性的纤维的替换实施例的横向方向的横断面;
图5示出了用于制造本发明的弹性层压制品的第一种工艺;
图6示出了用于制造本发明的弹性层压制品的第二种工艺;以及
图7示出了本发明层压制品在纵长方向上或者是在机器方向上进行拉伸顶视平面图。
图8示出了本发明层压制品在纵长方向上或者是在机器方向上未进行拉伸的顶视平面图。
具体实施方式
本发明的某些方面和实施例将在上下文中用一次性吸收制品来描述,而且更具体的指的是具有弹性侧翼的一次训练裤或是游泳衣,上述并不作为限定,而是为了说明本发明。然而很明显,本发明的各方面也可以应用来生产其它的弹性区域以及用来生产其它的衣服或者各种类型的个人护理产品,如妇女护理产品,各种的失禁衣服,医疗服装以及任何其它的一次性衣服,不管它们是吸收性的还是非吸收性的,都需要能够容易制作的弹性区域。典型地,这样的一次性衣服意旨限定用途,并不意旨为了再利用的那些可冲洗的或其它的可清洁的衣服。例如,一次性训练裤在它被穿用者弄脏以后就可以丢弃。
参照图1,衣服20通常限定了一个前腰部分22,一个后腰部分24以及连接前腰部分和后腰部分的裆部26。前腰部分22和后腰部分24包括衣服的在使用中构造成相应的延伸超过前和后腹部区域的常规部分。弹性侧翼28,30分别连接前和后腰部分22,24,在下文还会进一步解释。衣服的裆部26包括衣服的构造成延伸穿过穿用者的在两腿之间的裆部区域的常规部分。
为了提供改善的适配性和为了帮助减少身体排泄物从衣服20中的泄露,衣服的腿部罗口35和腰围边缘37配置有合适的弹性元件,从而具有弹性。例如,如图1所示,衣服20可以包括腿部弹性件36,它构造成控制衣服20的侧边缘的张力,它提供有弹性的腿带,上述腿带可以紧密地配合围绕穿用者的腿部,从而减少泄露和提供改善的舒适性和外观。可以应用弹性件38来使衣服20的腰部边缘37具有弹性,它提供有弹性的腰带。腰部弹性件38构造成帮助位穿用者提供围绕穿用者腰部区域的回弹性以及更加舒适的紧密配合。
参照图1,侧翼28,30也是弹性的,从而为穿用者提供改善的适配性和舒适性。每一侧翼,例如侧翼28包括第一部分42和第二部分44。第一部分42通过任何公知的手段例如超声粘合,粘接剂等与前腰部分22相连接。同样地,第二部分44以类似的方式与后腰部分24相连接。侧翼部分的自由端部不连接到腰部,而是接下来粘合成一个立起的突出的接合线46,从而形成一个侧翼区域49。在此所使用的术语“立起的突出接合线”指的是这样的接合线,即两个独立的基层片材以面对面或者背对背的方式结合在一起,基层的每一片材的外部边缘靠得很近,并且基层的每一片材的外部边缘从成品向外伸出,将接合线布置在交界处,用来抵抗剪切张力。依赖于衣服的应用,连接线36可以是基本上永久性的或者是容易分开的。
参照图2,一种用作侧翼部分的示范性的材料或者层压制品47通过将热塑性弹性粘性纤维48放置在第一非织造面层50和第二非织造面层52之间制造成弹性的、柔软性的以及具有轻的质量,上述面层例如是0.4osy的纺粘非织造幅面料。所述纤维具有弹性芯51以及富含粘性的皮或者外部周界54,上述纤维通过接触粘接粘合到面层或者可扩展的织物50,52上。当然也可以意识到面层材料也可以是除了非织造织物之外的适当的材料。例如纤维可以是具有皮芯结构的双组分纤维,其中芯是从休斯顿kraton Polymers得到的弹性聚合物混合形成的,包含70%重量的KRATONG1730四嵌段共聚物弹性体和30重量的聚乙烯蜡的TX;以及皮是由KRATONG2760的聚合物形成的,其中包含增粘树脂。这样的一种组合物适合于在一金属网丝上或者金属筛上形成纤维,例如象将在下面进一步描述的连续长丝层压制品(CFL)工艺中的那样。中的那样。通过垂直长丝层压制品(VFL)工艺可以获得在皮中的更高水平的增粘剂,将在下面进一步描述,其中纤维形成在具有一层防粘涂层的冷却辊上。
选择性地,参照图3,具有皮/芯结构(未示出)的双组分熔喷纤维(特别适合于VFL工艺)或者具有部分皮/芯结构的纤维56(特别适合于CFL工艺)具有一个弹性的芯聚合物58以及不完全地或者是部分围绕的富含增粘剂或者粘接剂的外部区域60,外部区域60没有必要以360度包绕芯,上述纤维通过接触粘接将面层50和52结合在一起。皮或者外部区域60也可以是弹性体和增粘剂组分的混合物。
作为另外的一个替换实施例,参照图4,例如聚丙烯的基本连续的纺粘纤维的一种单组分纤维62掺入选择性的增粘剂64,上述增粘剂可以迁移到纤维62的表面。这样这种具有选择性迁移增粘剂的单组分纤维就可使省去双组分纤维的生产工艺中的任何特殊需求。这样的长丝和选择性迁移的增粘剂的例子可以包括具有氢化烃树脂增粘剂的聚乙烯纤维。
图5示意性地示出了用于制造前面所述的弹性层压制品的垂直长丝层压制品(VFL)工艺。参照图5,至少一种融熔的弹性体材料通过纺丝孔从模具挤制机70中挤制,成为多根实质上连续的富含粘接剂的弹性长丝72。通过将长丝72经过第一冷却辊冷却和固化。可以是使用几个冷却辊。合适地,冷却辊可以具有从约40°F到约80°F。为了容易地剥离富含粘性的长丝或者纤维72,冷却辊74也可以合适地在表面上具有一层防粘覆盖层(未示出),从而允许在长丝中存在水平比目前的水平金属丝网工艺中的可能的增粘剂水平更高的增粘剂,就象联系图6进行解释的那样。
挤制机70的模头可以相对于第一辊定位,这样连续的长丝可以以一个预定的角度76接触该第一辊74。这种丝束的挤制结构对于将融熔的挤制物沉积到一个旋转的辊或鼓上是特别有利的。一个成角度或者倾斜的取向为长丝的形成提供了一种机会,即长丝从模具形成并且以一个合适的角度到辊的正切点,这就导致了纺丝的改善,更有效的能量传送,以及通常更长的模具寿命。这种结构允许长丝从模具以一个合适的角度形成,并且沿着相对直的路径来接触辊表面的正切点。挤制机70的模具出口与垂直轴(或者是第一个辊的水平轴,依赖于要测量的那个角度)之间的角度可以小到几度或者达到90度。例如,通过将挤制机70径直放到第一辊74的下边缘并且在挤制机上有一个旁侧的模具尖端,可以得到挤制机出口与辊成90度角的情况。并且远离垂直的角度例如约20度、约35度或者约45度的角度也可以使用。发现当使用每英寸具有12个纺丝孔的纺丝板孔密度时,大约45度的角度(如图5中所示)允许体系有效地运转。然而最适宜的角度可以作为下列因素的函数而变化,上述因素是挤制机的出口速度,辊的速度,从模具到辊的垂直距离以及从模具的中心线到辊的顶部固定中心的水平距离。通过应用各种几何形状来导致纺丝有效性的改善和降低长丝的破裂,从而可以得到最佳的性能。
在长丝72冷却和固化之后,它们使用第一系列的拉伸辊78来拉伸或伸长。第一系列的拉伸辊78可以包括一个或者更多的独立的拉伸辊,并且合适地是至少两个拉伸辊80和82,如图5所示。拉伸辊80和82以一个比冷却辊74的旋转速度大的速度旋转,由此拉伸长丝72。
在本发明的一个实施例中,在连续的两个辊中,每一个下面的辊都以一个比前面一个辊的速度大的速度旋转。例如,参见图5,如果冷却辊74以一个速度“x”旋转;拉伸辊80以一个还要大的速度旋转,例如约1.15x;第二个拉伸辊82以一个更大的速度旋转,例如约1.25x到约7x。结果是长丝72可以拉伸到其原始预拉伸长度的约100%到约800%。
在长丝72拉伸之后,它们层压到第一面层材料84上,而且理想的是同时层压到第二面层材料86上。第一面层材料84从辊88展开;并且层压到长丝72的第一侧面上。第二面层材料86从一第二辊90展开,并且层压到长丝72的第二侧面上。在面层材料84、86层压到长丝上之前,它们可以通过额外的辊(未示出)来产生颈缩。接着层压制品通过夹辊92将具有粘接剂表面的弹性纤维通过接触粘接粘合到面层84和86上。可以选择性地使用夹辊92来代替拉伸辊80,82以得到拉伸,或者在使用拉伸辊80,82之外再选择性地使用夹辊92。接下来,层压制品允许松弛,从而允许缩回的弹性体来形成材料中的褶(见图8)。
在本发明的某些方面,通过使用平坦的轧光辊可以将夹辊设计成提供最大的粘合区域。选择性地,有特定图案的辊可以产生特定的益处,例如增加的松密度或者层压制品的拉伸,也可以在不过度影响在面层和丝束之间以及在面层之间和丝束之间的接触粘接强度的地方使用。砑光辊可以加热到低于各种层压组分的熔点之下的温度,或者可以为室温,或者为冷凝的温度。
图6示出了用于制造本发明的另一种弹性层压制品的水平连续的长丝层压制品(CFL)工艺。第一挤制设备102种喂入有弹性体聚合物,或者是从一个或多个料源(未示出)形成的聚合物混合物,并且上述聚合物提供有必要的粘性皮或者选择性迁移的粘接剂。在不同的实施例中,挤制设备102可以被设计成来生产熔喷或者纺粘纤维,以及双组分或单组分纤维。用预先为挤制的工艺,例如改性的熔喷纤维,在前面提到的授予Wright的美国专利5,385,775中有进一步的描述。设备102将长丝104径直挤制在传送体系之上,它可以是绕着辊108顺时针运动的成形金属丝网体系106(也就是传送带)。长丝104可以使用真空泵和/或冷却扇(未示出)来冷却,其中真空泵是通过成形金属丝网来施加的。真空也可以帮助将长丝104保持在输送金属丝网体系上。对于特定的成形金属丝网来说,发现掺入约23%的增粘剂是一个使用的极限。然而,可以预期通过改变成形金属丝网,这个百分数还会增加,上述丝网设计成确保能够处理富含粘性的纤维。增粘剂存在的量可以是从约5%到约40%,并且理想的是从约15%到约25%。
接着长丝104通过张力辊110来拉伸和张紧长丝。理想的是,张力辊110可以提供有一个这样的的表面,该表面与长丝104的粘接剂具有一点亲和力直到没有亲和力。
在长丝104拉伸之后,它们层压到第一面层材料112上,而且理想的是同时层压到第二面层材料114上。第一面层材料112从辊116展开,并且层压到长丝72的第一侧面上。第二面层材料114从一第二辊118展开,并且层压到长丝72的第二侧面上。在面层材料112,114层压到长丝上之前,它们也可以通过额外的辊(未示出)来进行拉伸。接着层压制品通过夹辊120将具有粘接剂表面的弹性纤维的通过接触粘接粘合到面层112和114上。接下来,弹性层压制品122允许松弛,从而在其中形成褶(见图8),以及为了进一步的用途,将上述弹性层压制品收集在收集辊124上。
如在VFL工艺中的那样,通过使用平坦的轧光辊可以将夹辊120设计成提供100%的粘合区域,或者可以提供具有特定图案的粘合区域。辊120可以加热到低于各种层压组分的熔点之下的温度,或者可以为室温,或者为冷凝的温度。
参照图7和8,在图7中显示了一种示范性的处于拉伸或者张紧条件下的弹性层压制品47,其中以部分剖视图显示了弹性的丝束,例如62。图8显示了处于松弛或者不存在张力的条件下的弹性层压制品47,其中通过弹性丝束的收缩在材料47中形成褶126(未示出)。
既然在上文这样描述了一种轻重量的、柔顺性的、容易制造的、具有美学外观的弹性层压制品,但是可以意识到在其上进行一些变型对于本领域的普通技术人员来说是能想到的。因此,本发明意旨仅仅用所附的权利要求来限定本发明的保护范围,而不是由在此提出的示范性的实施例和提到的本发明的各方面来限定的。
Claims (15)
1.一种弹性层压制品,它包括:
a)第一面层幅面料;
b)第二面层幅面料;
c)多个热塑性的粘性弹性纤维丝束位于第一和第二面织物之间;以及
d)所述纤维丝束具有弹性芯和粘接剂表面,以及通过与所述纤维丝束的粘接剂表面的接触粘接把第一面层幅面料和第二面层幅面料粘合在一起,从而形成弹性层压制品。
2.一种弹性层压制品,它主要包括:
a)第一幅面料,其构造成位于衣服的内侧;
b)第二幅面料,其构造成位于衣服的外侧;
c)多个热塑性的弹性的纤维位于第一幅面料和第二幅面料之间;以及
d)所述纤维具有弹性芯和粘接剂表面,以及通过与所述纤维丝束的粘接剂表面的接触粘接把第一幅面料和第二幅面料粘合在一起,从而形成弹性层压制品。
3.根据权利要求2所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述热塑性纤维具有弹性芯,所述弹性芯没有粘接剂。
4.根据权利要求2所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述热塑性纤维具有高于200°F的熔点。
5.根据权利要求4所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述热塑性纤维包括单组分纤维,所述单组分纤维包含热塑性弹性聚合物,所述聚合物在其中具有增粘剂化合物,所述增粘剂在纤维的表面聚集而成为粘接剂。
6.根据权利要求5所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:单组分纤维包括弹性的嵌段共聚物。
7.根据权利要求6所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述增粘剂包括氢化的烃树脂增粘剂。
8.根据权利要求3所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述热塑性纤维包括实质上为皮/芯或者部分为皮/芯结构的双组分纤维,其中纤维的芯部分为没有粘性的弹性体,而皮层部分为粘接剂。
9.根据权利要求8所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述粘接剂是弹性体/增粘剂的混合物。
10.根据权利要求8所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述纤维是纺粘双组分纤维。
11.根据权利要求8所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述纤维是熔喷双组分纤维。
12.根据权利要求2所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述第一幅面料是基重3.391克每平方米和135.64克每平方米之间的非织造幅面料,所述非织造幅面料包括实质上连续的纺粘聚丙烯长丝。
13.根据权利要求2所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述第二幅面料是基重3.391克每平方米和135.64克每平方米之间的非织造幅面料,所述非织造幅面料包括实质上连续的纺粘聚丙烯长丝。
14.根据权利要求2所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述第一幅面料是一种非织造幅面料。
15.根据权利要求2所述的弹性层压制品,其特征在于:所述第二幅面料是一种非织造幅面料。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/034,335 US6902796B2 (en) | 2001-12-28 | 2001-12-28 | Elastic strand bonded laminate |
| US10/034,335 | 2001-12-28 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1604844A CN1604844A (zh) | 2005-04-06 |
| CN1272165C true CN1272165C (zh) | 2006-08-30 |
Family
ID=21875776
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB028249135A Expired - Fee Related CN1272165C (zh) | 2001-12-28 | 2002-11-26 | 弹性丝束粘合的层压制品 |
Country Status (13)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6902796B2 (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP1458562B1 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP4170225B2 (zh) |
| KR (1) | KR100926388B1 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN1272165C (zh) |
| AR (1) | AR038070A1 (zh) |
| AU (1) | AU2002362021B2 (zh) |
| BR (1) | BR0214945A (zh) |
| CO (1) | CO5590944A2 (zh) |
| DE (1) | DE60239291D1 (zh) |
| MX (1) | MXPA04005540A (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2003057469A1 (zh) |
| ZA (1) | ZA200404698B (zh) |
Families Citing this family (55)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATE222739T1 (de) | 1998-05-28 | 2002-09-15 | Procter & Gamble | Hosenähnliche wegwerfwindel mit verbessertem schutz gegen rote flecken und zugehöriges herstellverfahren |
| US20050064186A1 (en) * | 2002-04-05 | 2005-03-24 | Tingdong Lin | Nonwoven web with improved adhesion and reduced dust formation |
| US7347914B2 (en) | 2002-12-13 | 2008-03-25 | Zuiko Corporation | Method for producing an article having an elastic bonded between two webs |
| DE10319754A1 (de) * | 2003-04-30 | 2004-12-02 | Carl Freudenberg Kg | Elastischer Verbundstoff, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| US7892993B2 (en) | 2003-06-19 | 2011-02-22 | Eastman Chemical Company | Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters |
| US20040260034A1 (en) | 2003-06-19 | 2004-12-23 | Haile William Alston | Water-dispersible fibers and fibrous articles |
| US8513147B2 (en) * | 2003-06-19 | 2013-08-20 | Eastman Chemical Company | Nonwovens produced from multicomponent fibers |
| US7601657B2 (en) | 2003-12-31 | 2009-10-13 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Single sided stretch bonded laminates, and methods of making same |
| US20060047260A1 (en) | 2004-09-02 | 2006-03-02 | Gregory Ashton | Absorbent article having a telescoping waist |
| US7612001B2 (en) * | 2004-12-22 | 2009-11-03 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | High performance elastic materials made using styrene block copolymers and mixtures |
| CA2599339C (en) | 2005-03-02 | 2013-05-14 | Sca Hygiene Products Ab | Hygiene pants for single use |
| WO2007008128A1 (en) | 2005-07-14 | 2007-01-18 | Sca Hygiene Products Ab | Absorbent article |
| US7384491B2 (en) * | 2005-09-01 | 2008-06-10 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Apparatus and methods for making crosslinked elastic laminates |
| US8153238B2 (en) * | 2005-12-14 | 2012-04-10 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Stretch bonded laminate including an elastic member containing an adhesive composition |
| US20100291383A1 (en) * | 2006-02-07 | 2010-11-18 | Basf Se | Fiber adhesive |
| EP1983952A4 (en) * | 2006-02-13 | 2011-05-25 | Sca Hygiene Prod Ab | METHOD FOR REINFORCING A BOND BETWEEN BANDS OF MATERIAL AND AN ABSORBENT ARTICLE COMPRISING BANDS OF BONDED MATERIAL |
| US7585382B2 (en) * | 2006-06-30 | 2009-09-08 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Latent elastic nonwoven composite |
| US7582178B2 (en) * | 2006-11-22 | 2009-09-01 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Nonwoven-film composite with latent elasticity |
| US7938921B2 (en) * | 2006-11-22 | 2011-05-10 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Strand composite having latent elasticity |
| JP5188117B2 (ja) * | 2007-07-24 | 2013-04-24 | 花王株式会社 | 弾性フィラメント及びこれを用いた伸縮シート |
| JP4918002B2 (ja) * | 2007-09-07 | 2012-04-18 | 花王株式会社 | 伸縮シート及びその製造方法 |
| US20100075103A1 (en) * | 2006-12-28 | 2010-03-25 | Kao Corporation | Stretch sheet and process of producing the same |
| US7910795B2 (en) * | 2007-03-09 | 2011-03-22 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Absorbent article containing a crosslinked elastic film |
| JP4884274B2 (ja) * | 2007-03-28 | 2012-02-29 | 花王株式会社 | 伸縮シート |
| JP5604041B2 (ja) * | 2007-12-10 | 2014-10-08 | 花王株式会社 | 伸縮性複合シート |
| CA2813544A1 (en) | 2008-01-24 | 2009-07-30 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Extrusion bonded laminates for absorbent articles |
| US8062453B2 (en) * | 2008-04-02 | 2011-11-22 | Bae Systems Land & Armaments, L.P. | Method for quasi-instantaneous polymerization of filament wound composite materials |
| US8709191B2 (en) | 2008-05-15 | 2014-04-29 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Latent elastic composite formed from a multi-layered film |
| JP5011220B2 (ja) * | 2008-06-26 | 2012-08-29 | 花王株式会社 | 伸縮シート |
| US10161063B2 (en) | 2008-09-30 | 2018-12-25 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Polyolefin-based elastic meltblown fabrics |
| US8664129B2 (en) | 2008-11-14 | 2014-03-04 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Extensible nonwoven facing layer for elastic multilayer fabrics |
| US9498932B2 (en) | 2008-09-30 | 2016-11-22 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Multi-layered meltblown composite and methods for making same |
| US9168718B2 (en) | 2009-04-21 | 2015-10-27 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Method for producing temperature resistant nonwovens |
| CN102333644B (zh) * | 2009-02-27 | 2015-07-22 | 埃克森美孚化学专利公司 | 多层非织造原位层压体及其制备方法 |
| RU2011139492A (ru) * | 2009-04-08 | 2013-05-20 | Дзе Проктер Энд Гэмбл Компани | Растягивающиеся ламинаты из нетканого полотна (нетканых полотен) и эластичной плёнки |
| US8512519B2 (en) | 2009-04-24 | 2013-08-20 | Eastman Chemical Company | Sulfopolyesters for paper strength and process |
| US20100297914A1 (en) * | 2009-05-21 | 2010-11-25 | Jacky Cheung | Laminated all elastomeric fabric and bar made thereof |
| JP5674303B2 (ja) | 2009-11-06 | 2015-02-25 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 使い捨て着用物品 |
| US8668975B2 (en) | 2009-11-24 | 2014-03-11 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Fabric with discrete elastic and plastic regions and method for making same |
| US8506544B2 (en) | 2010-06-21 | 2013-08-13 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Disposable absorbent pant with efficient design and convenient single-section side stretch panels |
| US20120183861A1 (en) | 2010-10-21 | 2012-07-19 | Eastman Chemical Company | Sulfopolyester binders |
| US8840757B2 (en) | 2012-01-31 | 2014-09-23 | Eastman Chemical Company | Processes to produce short cut microfibers |
| US10272655B2 (en) | 2012-10-02 | 2019-04-30 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Film with alternating stripes and strands and apparatus and method for making the same |
| US9944043B2 (en) | 2012-10-02 | 2018-04-17 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Laminates and methods of making the same |
| BR112015015014B1 (pt) * | 2012-12-21 | 2021-02-09 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | laminado elástico e processo para a fabricação de laminado elástico |
| US20140248471A1 (en) | 2013-03-01 | 2014-09-04 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Film with Layered Segments and Apparatus and Method for Making the Same |
| US9303357B2 (en) | 2013-04-19 | 2016-04-05 | Eastman Chemical Company | Paper and nonwoven articles comprising synthetic microfiber binders |
| US20150037557A1 (en) | 2013-07-31 | 2015-02-05 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Sustainable Polymer Films |
| US9598802B2 (en) | 2013-12-17 | 2017-03-21 | Eastman Chemical Company | Ultrafiltration process for producing a sulfopolyester concentrate |
| US9605126B2 (en) | 2013-12-17 | 2017-03-28 | Eastman Chemical Company | Ultrafiltration process for the recovery of concentrated sulfopolyester dispersion |
| BR112017028056B1 (pt) | 2015-06-26 | 2022-03-15 | Hunter Douglas Inc | Cobertura para uma abertura arquitetônica e método de fabricação de um tecido para o uso como uma palheta da cobertura |
| BR112020007021A2 (pt) * | 2017-10-31 | 2020-10-06 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | material elástico |
| US11684522B2 (en) | 2017-10-31 | 2023-06-27 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Elastic laminates with curved elastics and methods for manufacturing |
| MY189963A (en) * | 2019-03-15 | 2022-03-22 | Fibertex Personal Care As | Elastic nonwoven fabric sheets and methods for making the same |
| IT202000015871A1 (it) * | 2020-07-01 | 2022-01-01 | Fameccanica Data Spa | Procedimento e apparecchiatura per la produzione di laminati elastici |
Family Cites Families (120)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2206761A (en) * | 1938-10-17 | 1940-07-02 | Bergstein Robert Morris | Machine and method for package closure |
| US2266761A (en) * | 1940-04-16 | 1941-12-23 | American Reenforced Paper Co | Fibrous sheet |
| NL70708C (zh) * | 1941-03-01 | |||
| US2483405A (en) * | 1943-11-20 | 1949-10-04 | American Viscose Corp | Fibrous products and textiles produced therewith |
| US2464301A (en) * | 1943-12-18 | 1949-03-15 | American Viscose Corp | Textile fibrous product |
| BE534424A (zh) * | 1953-12-24 | |||
| NL213342A (zh) * | 1955-12-29 | |||
| US3338992A (en) | 1959-12-15 | 1967-08-29 | Du Pont | Process for forming non-woven filamentary structures from fiber-forming synthetic organic polymers |
| US3186893A (en) * | 1961-06-08 | 1965-06-01 | Plastic Textile Access Ltd | Laminated materials including plastic netting |
| US3502763A (en) | 1962-02-03 | 1970-03-24 | Freudenberg Carl Kg | Process of producing non-woven fabric fleece |
| DE1282590C2 (de) * | 1963-10-25 | 1975-02-13 | Lutravil Spinnvlies GmbH & Co., 8750 Kaiserslautern | Vorrichtung zur herstellung von wirrvliesen aus endlosen polymeren fasern |
| US3391048A (en) * | 1964-01-10 | 1968-07-02 | Eastman Kodak Co | Entangled nonwoven web product from parallel laid filamentary tows |
| US3502538A (en) | 1964-08-17 | 1970-03-24 | Du Pont | Bonded nonwoven sheets with a defined distribution of bond strengths |
| US3449187A (en) * | 1964-12-08 | 1969-06-10 | Bobkowicz E | Method and apparatus for making nonwoven fabrics |
| US3468748A (en) * | 1965-04-14 | 1969-09-23 | Johnson & Johnson | Nonwoven fabric with machine direction elasticity |
| US3371668A (en) * | 1965-04-14 | 1968-03-05 | Johnson & Johnson | Sanitary napkin |
| US3489148A (en) * | 1966-12-20 | 1970-01-13 | Procter & Gamble | Topsheet for disposable diapers |
| US3341394A (en) | 1966-12-21 | 1967-09-12 | Du Pont | Sheets of randomly distributed continuous filaments |
| US3575782A (en) * | 1967-05-19 | 1971-04-20 | Minnesota Mining & Mfg | Elastic shirred web product |
| US3542615A (en) | 1967-06-16 | 1970-11-24 | Monsanto Co | Process for producing a nylon non-woven fabric |
| US3978185A (en) * | 1968-12-23 | 1976-08-31 | Exxon Research And Engineering Company | Melt blowing process |
| US3849241A (en) | 1968-12-23 | 1974-11-19 | Exxon Research Engineering Co | Non-woven mats by melt blowing |
| US3616129A (en) * | 1969-04-07 | 1971-10-26 | Kimberly Clark Co | Longitudinally stretchable nonwoven material |
| US3669823A (en) * | 1969-06-04 | 1972-06-13 | Curlator Corp | Non-woven web |
| US3917448A (en) * | 1969-07-14 | 1975-11-04 | Rondo Machine Corp | Random fiber webs and method of making same |
| US3676242A (en) * | 1969-08-13 | 1972-07-11 | Exxon Research Engineering Co | Method of making a nonwoven polymer laminate |
| DE2048006B2 (de) | 1969-10-01 | 1980-10-30 | Asahi Kasei Kogyo K.K., Osaka (Japan) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung einer breiten Vliesbahn |
| DE1950669C3 (de) | 1969-10-08 | 1982-05-13 | Metallgesellschaft Ag, 6000 Frankfurt | Verfahren zur Vliesherstellung |
| US4148676A (en) * | 1969-11-12 | 1979-04-10 | Bjorksten Research Laboratories, Inc. | Non-woven articles made from continuous filaments coated in high density fog with high turbulence |
| US3673026A (en) * | 1970-01-12 | 1972-06-27 | Int Paper Co | Method for the manufacture of laminated fabrics |
| US3836416A (en) * | 1970-01-29 | 1974-09-17 | Alta Ind | Non woven thermoplastic fabric |
| US3629047A (en) * | 1970-02-02 | 1971-12-21 | Hercules Inc | Nonwoven fabric |
| US3904465A (en) * | 1970-02-20 | 1975-09-09 | Mobil Oil Corp | Process and apparatus for the manufacture of embossed film laminations |
| US3689342A (en) * | 1970-12-08 | 1972-09-05 | Celanese Corp | Method for producing spray-spun nonwoven sheets |
| US3752613A (en) * | 1970-12-08 | 1973-08-14 | Celanese Corp | Apparatus for producing spray spun nonwoven sheets |
| US3857144A (en) * | 1971-07-02 | 1974-12-31 | Mobil Oil Corp | Method of embossing limp plastic sheet material |
| US3773590A (en) * | 1971-07-16 | 1973-11-20 | Exxon Co | Method of forming ribbed battery separators |
| US3890184A (en) * | 1971-07-16 | 1975-06-17 | Exxon Research Engineering Co | Method of making extruded rib battery separators |
| US3932328A (en) * | 1971-11-02 | 1976-01-13 | Johnson & Johnson | Hot melt adhesive composition and tape |
| US3806289A (en) * | 1972-04-05 | 1974-04-23 | Kimberly Clark Co | Apparatus for producing strong and highly opaque random fibrous webs |
| GB1445982A (en) * | 1972-08-11 | 1976-08-11 | Beghin Say Sa | Net and method of producing same |
| US3949128A (en) * | 1972-08-22 | 1976-04-06 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Product and process for producing a stretchable nonwoven material from a spot bonded continuous filament web |
| JPS5212830B2 (zh) | 1972-11-25 | 1977-04-09 | ||
| US4189338A (en) | 1972-11-25 | 1980-02-19 | Chisso Corporation | Method of forming autogenously bonded non-woven fabric comprising bi-component fibers |
| US3838692A (en) * | 1972-11-27 | 1974-10-01 | Johnson & Johnson | Hydrophobic sheet with hydrophilic passages |
| US3912567A (en) * | 1973-05-14 | 1975-10-14 | Kimberly Clark Co | Stabilized nonwoven web and method of preparation |
| US3979050A (en) * | 1973-09-21 | 1976-09-07 | Union Carbide Corporation | Multi-ply film articles |
| US3860003B2 (en) * | 1973-11-21 | 1990-06-19 | Contractable side portions for disposable diaper | |
| US3949130A (en) * | 1974-01-04 | 1976-04-06 | Tuff Spun Products, Inc. | Spun bonded fabric, and articles made therefrom |
| US4100324A (en) | 1974-03-26 | 1978-07-11 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Nonwoven fabric and method of producing same |
| US4028292A (en) * | 1974-05-23 | 1977-06-07 | Johnson & Johnson | Hot melt adhesive |
| US3973063A (en) * | 1974-11-21 | 1976-08-03 | Mobil Oil Corporation | Spot blocked thermoplastic film laminate |
| US4038346A (en) * | 1975-03-31 | 1977-07-26 | The Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company | Tackifier composition and rubber mixture |
| US4107364A (en) * | 1975-06-06 | 1978-08-15 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Random laid bonded continuous filament cloth |
| US4209563A (en) * | 1975-06-06 | 1980-06-24 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method for making random laid bonded continuous filament cloth |
| US4211807A (en) * | 1975-08-08 | 1980-07-08 | Polymer Processing Research Institute Ltd. | Reinforced non-woven fabrics and method of making same |
| US4013816A (en) * | 1975-11-20 | 1977-03-22 | Draper Products, Inc. | Stretchable spun-bonded polyolefin web |
| US4340558A (en) * | 1976-05-05 | 1982-07-20 | Colgate-Palmolive Company | Scrim reinforced plastic film |
| US4080348A (en) * | 1976-05-18 | 1978-03-21 | Johnson & Johnson | Tacky adhesive |
| US4285998A (en) * | 1976-07-26 | 1981-08-25 | Conwed Corporation | Reinforced thermoplastic film sheet |
| US4090385A (en) * | 1977-01-26 | 1978-05-23 | Bird Machine Company, Inc. | Material treating apparatus |
| US4248652A (en) * | 1978-03-30 | 1981-02-03 | Inmont Corporation | Method of making leatherlike materials (A) |
| JPS6056825B2 (ja) * | 1978-05-01 | 1985-12-12 | 東亜燃料工業株式会社 | 不織布の製造法 |
| US4259220A (en) | 1978-12-06 | 1981-03-31 | H. B. Fuller Company | Hot melt adhesive for elastic banding |
| US4241123A (en) * | 1978-11-14 | 1980-12-23 | Shih Seng C | Non-woven netting |
| US4543099A (en) | 1978-12-06 | 1985-09-24 | H. B. Fuller Company | Method for imparting elastic properties to a flexible substrate |
| US4418123A (en) | 1978-12-06 | 1983-11-29 | H. B. Fuller Company | Extrudable self-adhering elastic and method of employing same |
| DE2924539C2 (de) * | 1979-06-19 | 1983-01-13 | Fa. Carl Freudenberg, 6940 Weinheim | Spinnvlies aus Polyolefin-Filamenten und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| SE425942C (sv) * | 1979-07-02 | 1985-05-14 | Moelnlycke Ab | Engangsbloja |
| US4438167A (en) * | 1979-10-15 | 1984-03-20 | Biax Fiberfilm Corporation | Novel porous fabric |
| US4405397A (en) * | 1979-10-16 | 1983-09-20 | Riegel Textile Corporation | Process for manufacturing elastic leg disposable diapers |
| US4239578A (en) * | 1979-10-16 | 1980-12-16 | Riegel Textile Corporation | Apparatus for inserting elastic strips during the manufacture of elastic leg disposable diapers |
| US4323534A (en) * | 1979-12-17 | 1982-04-06 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Extrusion process for thermoplastic resin composition for fabric fibers with exceptional strength and good elasticity |
| US4303571A (en) * | 1980-01-17 | 1981-12-01 | Exxon Research & Engineering Co. | Film-forming thermoplastic elastomeric polymer compositions |
| US4333782A (en) * | 1980-02-11 | 1982-06-08 | Johnson & Johnson Baby Products Company | Method of making laminated structures having gathered and ungathered marginal portions |
| US4300562A (en) * | 1980-02-11 | 1981-11-17 | Johnson & Johnson Baby Products Company | Laminated structures having gathered marginal portions |
| ZA811895B (en) * | 1980-04-07 | 1982-04-28 | Univ California | Expression of hormone genomic clones |
| US4340563A (en) | 1980-05-05 | 1982-07-20 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Method for forming nonwoven webs |
| US4310594A (en) * | 1980-07-01 | 1982-01-12 | Teijin Limited | Composite sheet structure |
| US4302495A (en) * | 1980-08-14 | 1981-11-24 | Hercules Incorporated | Nonwoven fabric of netting and thermoplastic polymeric microfibers |
| US4413623A (en) * | 1981-02-17 | 1983-11-08 | Johnson & Johnson Baby Products Company | Laminated structures having gathered and ungathered marginal portions and method of manufacturing the same |
| JPS5823951A (ja) | 1981-07-31 | 1983-02-12 | チッソ株式会社 | 嵩高不織布の製造方法 |
| US4507163A (en) * | 1981-08-27 | 1985-03-26 | Johnson & Johnson Baby Products Company | Imparting an inelastic and elastic character to predetermined portions of an elastic web for use in making disposable diapers |
| US4417935A (en) * | 1981-10-13 | 1983-11-29 | Paper Converting Machine Company | Method of diaper manufacture |
| US4402688A (en) * | 1981-10-27 | 1983-09-06 | Colgate-Palmolive | Disposable diaper with contoured elastic |
| JPS58180601A (ja) * | 1982-04-14 | 1983-10-22 | ユニ・チヤ−ム株式会社 | 使い捨ておむつ |
| US4490427A (en) * | 1982-06-14 | 1984-12-25 | Firma Carl Freudenberg | Adhesive webs and their production |
| US4525407A (en) * | 1982-08-27 | 1985-06-25 | Chicopee | Elastic composites |
| US4496417A (en) * | 1982-11-12 | 1985-01-29 | Adolph Coors Company | Control stretch laminating device |
| US4572752A (en) * | 1982-11-12 | 1986-02-25 | Adolph Coors Company | Control stretch laminating device |
| US4586199A (en) * | 1982-12-21 | 1986-05-06 | Molnlycke Ab | Elastic pants |
| US4440819A (en) * | 1982-12-27 | 1984-04-03 | Hughes Aircraft Company | Interconnection of unidirectional fiber arrays with random fiber networks |
| USD284036S (en) * | 1983-03-01 | 1986-06-03 | Molnlycke Aktiebolag | Diaper pants |
| JPS59199856A (ja) * | 1983-04-25 | 1984-11-13 | 東レ株式会社 | 不織シ−ト及びその製造方法 |
| US4500316A (en) * | 1983-06-01 | 1985-02-19 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Disposable garment |
| US4618384A (en) | 1983-09-09 | 1986-10-21 | Sabee Reinhardt N | Method for applying an elastic band to diapers |
| US4552795A (en) * | 1983-12-27 | 1985-11-12 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Co. | Inelastic, heat-elasticizable sheet material |
| US4640859A (en) * | 1983-12-27 | 1987-02-03 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Inelastic, heat-elasticizable sheet material for diapers |
| US4661389A (en) * | 1984-03-27 | 1987-04-28 | Leucadia, Inc. | Multiple-layer reinforced laminate |
| US4555811A (en) * | 1984-06-13 | 1985-12-03 | Chicopee | Extensible microfine fiber laminate |
| US4522863A (en) * | 1984-06-21 | 1985-06-11 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Soft nonwoven laminate bonded by adhesive on reinforcing scrim |
| US4657793A (en) * | 1984-07-16 | 1987-04-14 | Ethicon, Inc. | Fibrous structures |
| US4548859A (en) * | 1984-10-12 | 1985-10-22 | The Boeing Company | Breather material and method of coating fabric with silicone rubber |
| US4657802A (en) * | 1985-07-30 | 1987-04-14 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Composite nonwoven elastic web |
| US4652487A (en) * | 1985-07-30 | 1987-03-24 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Gathered fibrous nonwoven elastic web |
| US4606964A (en) | 1985-11-22 | 1986-08-19 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Bulked web composite and method of making the same |
| US4644045A (en) * | 1986-03-14 | 1987-02-17 | Crown Zellerbach Corporation | Method of making spunbonded webs from linear low density polyethylene |
| US4863779A (en) * | 1986-03-24 | 1989-09-05 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Composite elastomeric material |
| US4968313A (en) * | 1987-04-27 | 1990-11-06 | Sabee Reinhardt N | Diaper with waist band elastic |
| US5895382A (en) * | 1993-04-26 | 1999-04-20 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Foreshortened containment flaps in a disposable absorbent article |
| US6417122B1 (en) * | 1994-11-23 | 2002-07-09 | Bba Nonwovens Simpsonville, Inc. | Multicomponent fibers and fabrics made using the same |
| US5804286A (en) * | 1995-11-22 | 1998-09-08 | Fiberweb North America, Inc. | Extensible composite nonwoven fabrics |
| US6417121B1 (en) * | 1994-11-23 | 2002-07-09 | Bba Nonwovens Simpsonville, Inc. | Multicomponent fibers and fabrics made using the same |
| US5733822A (en) * | 1995-08-11 | 1998-03-31 | Fiberweb North America, Inc. | Composite nonwoven fabrics |
| US5952252A (en) * | 1996-02-20 | 1999-09-14 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Fully elastic nonwoven fabric laminate |
| JP3784131B2 (ja) * | 1997-04-11 | 2006-06-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 使い捨て着用物品 |
| US5883028A (en) * | 1997-05-30 | 1999-03-16 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Breathable elastic film/nonwoven laminate |
| US6221483B1 (en) * | 1998-09-10 | 2001-04-24 | Avery Dennison Corporation | Reversibly extensible film |
| DE19983828T5 (de) * | 1998-12-19 | 2004-07-08 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc., Neenah | Multikomponenten-Feinfaser-Bahnen und Laminate davon |
| US6475600B1 (en) * | 1998-12-23 | 2002-11-05 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Composite material having stretch and recovery including a layer of an elastic material and a transversely extensible and retractable necked laminate of non-elastic sheet layers |
-
2001
- 2001-12-28 US US10/034,335 patent/US6902796B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2002
- 2002-11-26 DE DE60239291T patent/DE60239291D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-11-26 WO PCT/US2002/037798 patent/WO2003057469A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2002-11-26 KR KR1020047009102A patent/KR100926388B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-11-26 JP JP2003557809A patent/JP4170225B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2002-11-26 MX MXPA04005540A patent/MXPA04005540A/es active IP Right Grant
- 2002-11-26 CN CNB028249135A patent/CN1272165C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2002-11-26 BR BR0214945-1A patent/BR0214945A/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2002-11-26 AU AU2002362021A patent/AU2002362021B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2002-11-26 EP EP02797146A patent/EP1458562B1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2002-12-26 AR ARP020105100A patent/AR038070A1/es active IP Right Grant
-
2004
- 2004-06-09 CO CO04054287A patent/CO5590944A2/es not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2004-06-14 ZA ZA2004/04698A patent/ZA200404698B/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP4170225B2 (ja) | 2008-10-22 |
| AU2002362021B2 (en) | 2007-06-28 |
| EP1458562A1 (en) | 2004-09-22 |
| EP1458562B1 (en) | 2011-02-23 |
| DE60239291D1 (de) | 2011-04-07 |
| WO2003057469A1 (en) | 2003-07-17 |
| KR100926388B1 (ko) | 2009-11-11 |
| ZA200404698B (en) | 2005-08-31 |
| MXPA04005540A (es) | 2004-09-10 |
| AR038070A1 (es) | 2004-12-22 |
| CN1604844A (zh) | 2005-04-06 |
| CO5590944A2 (es) | 2005-12-30 |
| BR0214945A (pt) | 2004-12-14 |
| US6902796B2 (en) | 2005-06-07 |
| AU2002362021A1 (en) | 2003-07-24 |
| JP2005514232A (ja) | 2005-05-19 |
| KR20040068228A (ko) | 2004-07-30 |
| US20030124331A1 (en) | 2003-07-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1272165C (zh) | 弹性丝束粘合的层压制品 | |
| AU667557B2 (en) | Nonwoven fabric made with multicomponent polymeric strands including a blend of polyolefin and elastomeric thermoplastic material | |
| EP0693585B1 (en) | Knit like nonwoven fabric composite | |
| KR100309231B1 (ko) | 부텐 중합체를 포함하는 다성분 중합체 스트랜드및그로제조한부직포및제품 | |
| CN1318205C (zh) | 相对重量具有增强的阻隔性能的无纺阻隔织物 | |
| EP1102880B1 (en) | Elastic nonwoven fabric prepared from bi-component filaments | |
| AU668973B2 (en) | Nonwoven fabric made with multicomponent polymeric strands including a blend of polyolefin and ethylene alkyl acrylate copolymer | |
| US6723669B1 (en) | Fine multicomponent fiber webs and laminates thereof | |
| CA2147523C (en) | Slit elastic fibrous nonwoven laminates | |
| MXPA06008389A (es) | Tramas de tela no tejida extensibles y suaves que contienen fibras con velocidad de flujo de fusion alta. | |
| CN101151407A (zh) | 从复合长丝制造弹性和/或水可降解性织物的方法 | |
| WO2000037723A2 (en) | Fine multicomponent fiber webs and laminates thereof | |
| CN1681462A (zh) | 非织造毛圈材料以及有关方法和产品 | |
| JP2001503110A (ja) | 長繊維不織布及びこれを用いた吸収性物品 | |
| KR20210035864A (ko) | 폴리프로필렌 스펀본드를 위한 개선된 연성 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |
Granted publication date: 20060830 Termination date: 20161126 |
|
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |