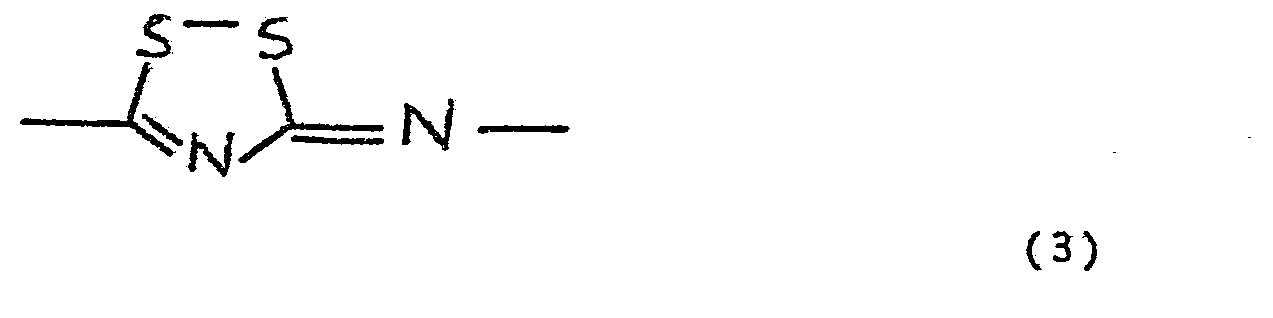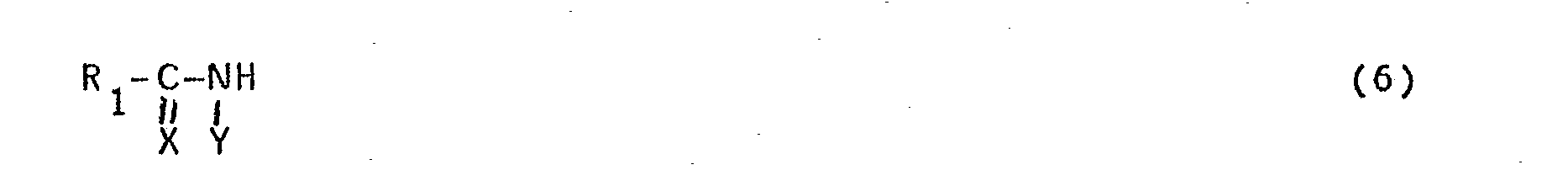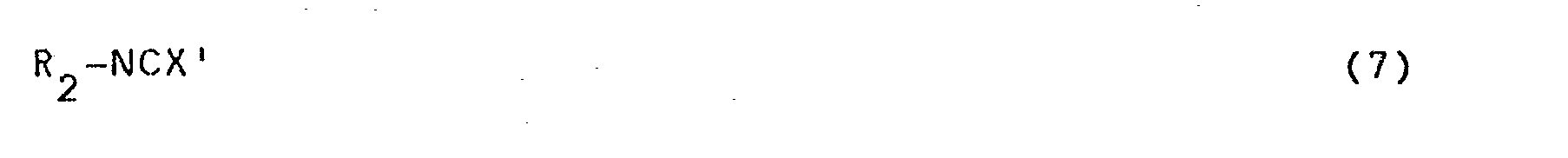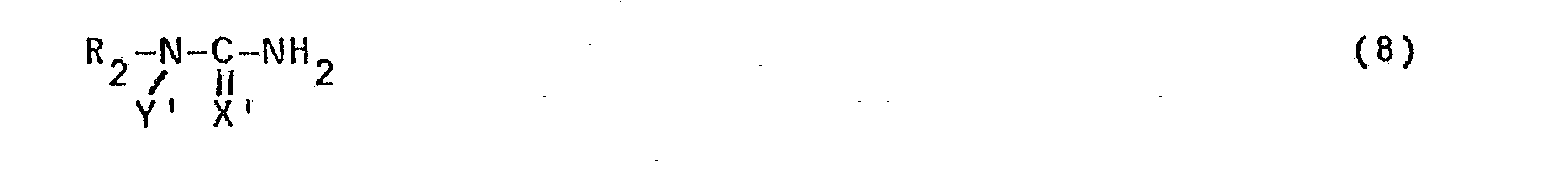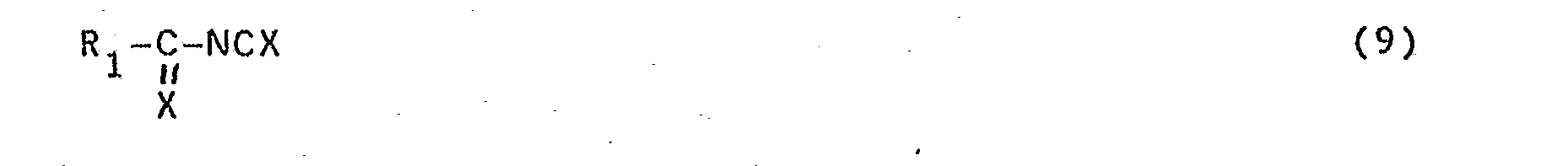EP0193249A2 - Benzoyl urea derivatives having ati-tumor activity - Google Patents
Benzoyl urea derivatives having ati-tumor activity Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0193249A2 EP0193249A2 EP86200300A EP86200300A EP0193249A2 EP 0193249 A2 EP0193249 A2 EP 0193249A2 EP 86200300 A EP86200300 A EP 86200300A EP 86200300 A EP86200300 A EP 86200300A EP 0193249 A2 EP0193249 A2 EP 0193249A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- group
- atoms
- formula
- urea
- halogen
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D213/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D213/24—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D213/28—Radicals substituted by singly-bound oxygen or sulphur atoms
- C07D213/30—Oxygen atoms
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C275/00—Derivatives of urea, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups, the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups
- C07C275/46—Derivatives of urea, i.e. compounds containing any of the groups, the nitrogen atoms not being part of nitro or nitroso groups containing any of the groups, X being a hetero atom, Y being any atom, e.g. acylureas
- C07C275/48—Y being a hydrogen or a carbon atom
- C07C275/54—Y being a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring, e.g. benzoylureas
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C317/00—Sulfones; Sulfoxides
- C07C317/44—Sulfones; Sulfoxides having sulfone or sulfoxide groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C323/00—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups
- C07C323/50—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton
- C07C323/62—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton
- C07C323/63—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton the carbon skeleton being further substituted by nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D213/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D213/60—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D213/72—Nitrogen atoms
- C07D213/75—Amino or imino radicals, acylated by carboxylic or carbonic acids, or by sulfur or nitrogen analogues thereof, e.g. carbamates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D213/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D213/60—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D213/78—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms, with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals
- C07D213/81—Amides; Imides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D213/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D213/60—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D213/78—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms, with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals
- C07D213/81—Amides; Imides
- C07D213/82—Amides; Imides in position 3
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D213/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/89—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D237/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings
- C07D237/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D237/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D237/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D237/20—Nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D237/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings
- C07D237/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D237/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D237/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D237/22—Nitrogen and oxygen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D237/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings
- C07D237/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D237/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D237/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazine or hydrogenated 1,2-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D237/24—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D239/24—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D239/28—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D239/32—One oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen atom
- C07D239/42—One nitrogen atom
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/70—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D239/72—Quinazolines; Hydrogenated quinazolines
- C07D239/86—Quinazolines; Hydrogenated quinazolines with hetero atoms directly attached in position 4
- C07D239/94—Nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/70—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D239/72—Quinazolines; Hydrogenated quinazolines
- C07D239/95—Quinazolines; Hydrogenated quinazolines with hetero atoms directly attached in positions 2 and 4
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D241/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings
- C07D241/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D241/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D241/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D241/20—Nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D241/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings
- C07D241/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D241/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D241/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,4-diazine or hydrogenated 1,4-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D241/24—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D261/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-oxazole or hydrogenated 1,2-oxazole rings
- C07D261/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-oxazole or hydrogenated 1,2-oxazole rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D261/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-oxazole or hydrogenated 1,2-oxazole rings not condensed with other rings having two or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D261/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-oxazole or hydrogenated 1,2-oxazole rings not condensed with other rings having two or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D261/14—Nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D275/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,2-thiazole rings
- C07D275/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,2-thiazole rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D275/03—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,2-thiazole rings not condensed with other rings with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D277/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings
- C07D277/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D277/20—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D277/32—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D277/38—Nitrogen atoms
- C07D277/44—Acylated amino or imino radicals
- C07D277/48—Acylated amino or imino radicals by radicals derived from carbonic acid, or sulfur or nitrogen analogues thereof, e.g. carbonylguanidines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D277/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings
- C07D277/60—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D277/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings
- C07D277/60—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-thiazole or hydrogenated 1,3-thiazole rings condensed with carbocyclic rings or ring systems
- C07D277/62—Benzothiazoles
- C07D277/68—Benzothiazoles with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached in position 2
- C07D277/82—Nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D285/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing rings having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D275/00 - C07D283/00
- C07D285/01—Five-membered rings
- C07D285/02—Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated thiadiazoles
- C07D285/04—Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated thiadiazoles not condensed with other rings
- C07D285/06—1,2,3-Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated 1,2,3-thiadiazoles
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D285/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing rings having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D275/00 - C07D283/00
- C07D285/01—Five-membered rings
- C07D285/02—Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated thiadiazoles
- C07D285/04—Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated thiadiazoles not condensed with other rings
- C07D285/08—1,2,4-Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated 1,2,4-thiadiazoles
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D285/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing rings having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D275/00 - C07D283/00
- C07D285/01—Five-membered rings
- C07D285/02—Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated thiadiazoles
- C07D285/04—Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated thiadiazoles not condensed with other rings
- C07D285/12—1,3,4-Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated 1,3,4-thiadiazoles
- C07D285/125—1,3,4-Thiadiazoles; Hydrogenated 1,3,4-thiadiazoles with oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen atoms, directly attached to ring carbon atoms, the nitrogen atoms not forming part of a nitro radical
- C07D285/135—Nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D307/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D307/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings
- C07D307/34—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D307/56—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D307/68—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D333/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D333/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings
- C07D333/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings not substituted on the ring sulphur atom
- C07D333/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings not substituted on the ring sulphur atom with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to the ring carbon atoms
- C07D333/24—Radicals substituted by carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D333/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D333/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings
- C07D333/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings not substituted on the ring sulphur atom
- C07D333/26—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings not substituted on the ring sulphur atom with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D333/38—Carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals
Definitions
- the invention relates to new benzoyl urea derivatives having antitumor activity, to the preparation of such compounds, and to compositions which comprise at least one of the new compounds as the active substance.
- the above-described reactions are preferably carried out in the presence of an organic solvent, for example, an aromatic hydrocarbon, an alkyl halide, a non-cyclic or cyclic dialkyl ether, or acetonitrile, at temperatures between 0°C and the boiling-point of the solvent used.
- an organic solvent for example, an aromatic hydrocarbon, an alkyl halide, a non-cyclic or cyclic dialkyl ether, or acetonitrile
- Compounds of formula (1), wherein Z is the group of formula (3) can be obtained by oxidizing the corresponding dithiourea compounds to be obtained in the above--described manner with, for example, a halogen, for example, bromine or iodine, as a result of which ring closure is effected via the two sulphur atoms.
- This reaction is preferably carried out in a solvent, for example, dichloroethane.
- the compounds can be processed to compositions in the conventional manner.
- a great advantage of the compounds according to the invention as compared with known cytostatics is that they have a low toxicity.
- the antitumor activity of the compounds was determined in a number of in vitro test.
- B16 melanoma cells grow as a "mono]ayer".
- the doubling time of these cells in a cell culture is 12-16 hours.
- "6 multiwell" tissue culture plates having a flat bottom with an area of 8 cm 2 proved to be best suitable.
- the compounds to be examined are vortexed in the presence of glass beads.
- the compound to be tested is then added to the dishes with melanoma Suite in the desired quantity.
- the incubation takes place at 37°C for 20 hours in a C0 2 incubator.
- the incubation is terminated by removing the culture medium with therein the compound to be tested, after which the cells are wahsed once and fresh medium is added.
- Cells were seeded in 24-well cluster plates at a concentration of 10 5 cells/ml of medium. After incubation for 24 hours at 37°C in an air/5% C0 2 atmosphere a suspension of the test compound in 0.5% CMC/saline was added to obtain a final concentration of 50 /ug/ml.
- Adriamycin was used as a positive control. After incubation for 72 hours in the presence of the test compound the cell layers were washed with phosphate bufferend saline and the cells were stained with the vital stain crystal violet. On the stained cell layer a visual assessment was done and the cell-inhibition scored:
- Cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, daunomycin, bleomycin and adriamycin were used with colon WIDR as comparisons.
- Cells were seeded at the appropriate density for each cell line 10 2 -10 5 cells/dishes and incubated at 37°C in an air/5% C0 2 atmosphere. Compounds as solution or suspension in 0.5% CMC/saline were added during seeding or after an overnight pre-incubation period to a final concentration of: 50 / ug/ml.
- the duration of the treatment was about 3 times the cell replication cycle. Afterwards the assays were fixed, stained and scored for the presence of colonies. Colony formation is expressed as the number of colonies present on treated dishes as a percentage of the number of colonies on control dishes.
- the compounds according to the invention have a much stronger activity than the known benzoylurea derivatives having antitumor activity which are described in European Patent application 83201263.7.
- Table F the activity is recorded of a number of known compounds, tested in a concentration which is 10 times as high, i.e. 500 /ug/ml:
- the antitumor activity of the compounds determined in vitro is confirmed by the preliminary results obtained in an in vivo test in mice.
- Example I the compound 1--(4-nitrobenzoyl-3-(2-nitrophenyl)urea was prepared starting from 2-nitroaniline and 4-nitrobenzoylisocyanate. 11 g Of this compound were dissolved in 200 ml of dimethyl formamide and recuced in a Parr apparatus by means of 10 g of Raney nickel at a hydrogen pressure of 2-3 atm. After the reaction the solution was filtered off and evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was recrystallized from a mixture of acetone and isopropanol. Yield 7.1 g (79%) of the title compound. Melting-point 240°C (decomposition).
- 1-(2-Pyridylcarbonyl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)urea was obtained according to the method of Example I. 0.75 g Of this compound was dissolved in 5 ml of acetic acid and 1 ml of hydrogen peroxide (35%). The mixture was heated on a steam bath and 1.5 ml of hydrogen peroxid were added again after 2 and 3 hours. After 4.5 hours on the steam bath the mixture was cooled. The crystalline substance was sucked off and washed with isopropanol. Yield 0.3 g (38%) of the corresponding N-oxide. Melting-point 191°C.
Abstract
Description
- The invention relates to new benzoyl urea derivatives having antitumor activity, to the preparation of such compounds, and to compositions which comprise at least one of the new compounds as the active substance.
- From United States Patent Specification 3,74.8,356 it is known that a group of 1-benzoyl-3-phenyl urea compounds has insecticidal properties. This insecticidal activity is based on a mechanism which has not yet been fully clarified. What is clear is that the insects are killed in that the said urea derivatives inhibit the chitin formation.
- It is known from European Patent Application 83201263.7 (publ. no. 0107214) that a number of 1-benzoyl--3-phenyl urea compounds having insecticidal properties, and metabolites thereof have a cytostatic and tumoricidal activity on tumors in mammals.
- Furthermore it is known from European Patent application 0.025.363 that some N-benzoyl-N'-pyridyloxy phenyl urea compounds also have an antitumor activity.
-
- R1 is an aryl group which may be substituted with a) 1-5 halogen atoms, b) 1-3 groups of the formula -0-A, wherein A is a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1-3 C-atoms, and alkanoyl group having 1-6 C-atoms, a carbamoyl group optionally substituted with alkyl having 1-6 C-atoms or with phenyl, c) 1-2 amino groups which may be substituted with an alkanoyl group having 1-3 C-atoms, or with 1 or 2 alkyl groups having 1-3 C-atoms which can form a ring together with the nitrogen atom, d) 1-2 dialkylamino N-oxyde groups, e) 1-2 alkylmercapto groups having 1-3 C-atoms, f) an alkylsulphinyl group or alkylsulphonyl group having 1-3 C-atoms, g) 1 or 2 alkyl groups having 1-6 C-atoms optionally substituted with halogen, h) a nitro group, i) a condensed hetero ring system, or j) a sulfonamide group, or wherein R1 is a heteroaryl group which comprises as hetero atoms an oxygen atom, a sulphur atom and/or 1-3 nitrogen atoms, or the group N→O, which heteroaryl group may be substituted with phenyl, cycloalkyl having 3-10 C-atoms, 1-2 halogen atoms, hydroxyl, nitro, or optionally halogen-substituted alkyl having 1-6 C-atoms, or R1 is a styryl group or aralkyl group, the alkyl group of which comprises 1-3 C-atoms and the aryl group may be substituted with 1-2 halogen atoms, 1-3 groups -0-A wherein A has the above-mentioned meaning, or 1-2 optionally halogen-substituted alkyl groups having 1-18 C-atoms, or a cycloalkyl group having 3-10 C-atoms, or R1 is an amino group optionally substituted with 1 or 2 alkyl groups having 1-6 C-atoms, in which the alkyl group(s) together with the nitrogen atom can form a ring;
- R2 is an aryl group which may be substituted with a) 1-5 halogen atoms, b) 1-3 groups of the formula -O-A wherein A has the above-mentioned meaning, c) 1-2 optionally halogen-substituted alkyl groups having 1-6-C-atoms, d) cycloalkyl having 3-10 C-atoms, e) nitro, f) cyano, g) hydroxycarbonyl, h) alkoxycarbonyl having 1-6 C-atoms, i) alkanoyl having 1-3 C-atoms, j) 1-2 amino groups optionally substituted with 1 or 2 alkyl groups having 1-3 C-atoms, k) the group -C(CF3)2OH, or 1) an alkoxy group having 1-3 C-atoms and optionally substituted with halogen or pyridyl, or R2 is a heteroaryl group which comprises an oxygen atom or a sulphur atom or 1-3 nitrogen atoms and which may be substituted with a) optionally halogen-substituted alkyl having 1-3 C-atoms, b) cycloalkyl having 3-10 C-atoms, c) 1-2 halogen atoms, d) phenyl or e) phenoxy, or R2 is an aralkyl group the alkyl group of which comprises 1-3 C-atoms and the aryl group may be substituted with a) 1-2 halogen atoms, b) 1-3 groups -0-A. wherein A has the above-mentioned meaning, c) 1-2 alkyl groups having 1-3 C-atoms, or R2 is an optionally halogen-substituted alkyl group having 1-6 C-atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 3-10 C-atoms or an amino group optionally substituted with 1 or 2 alkyl groups having 1-3 C-atoms,
- The invention does not relate to those compounds of the above formula (1), in which
- R1 is a group
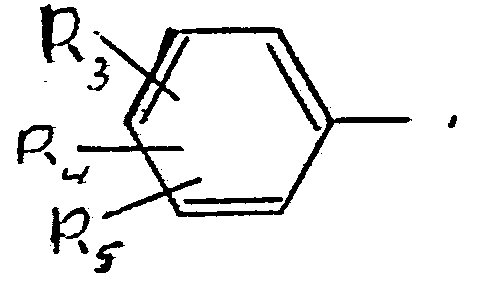
- R3 is a hydrogen atom, a group of the formula -(-O-A)p, wherein A is a hydrogen atom, an alkanoyl group having 1-6 C-atoms, a carbamoyl group optionally substituted with alkyl having 1-6 C-atoms or with phenyl, or an alkyl mercapto group having 1-3 C-atoms,
- R4 is a hydrogen atom or a halogen atom, a nitro group, or an alkyl group optionally substituted with halogen and having 1-6 C-atoms,
- R5 is a hydrogen atom or halogen atom, a nitro group, an alkyl group optionally substited with halogen and having 1-6 C-atoms, an alkoxy group having 1-3 C-atoms, an amino group which may be substituted with 1 or 2 alkyl groups having 1-3 C-atoms,
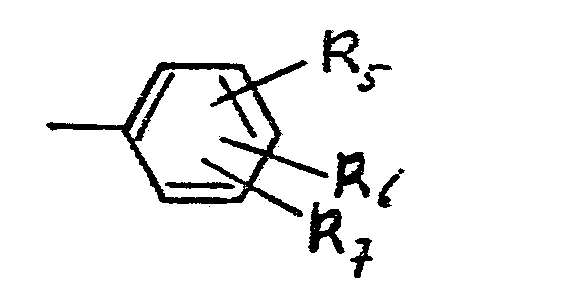
- R6 is a hydrogen atom or a group -(-O-A)q, wherein A is a hydrogen atom, an alkanoyl group having 1-6 C-atoms, a carbamoyl group optionally substituted with alkyl having 1-6 C-atoms or with phenyl, and
- R7 is a hydrogen atom or 1-3 halogen atoms, and p + g has the value 1-6. These compounds are disclosed in non-prepublished European Patent Application 84201221.3.
- Nor does the invention relate to the compounds
- 1) 1-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-chlorophenyl)-urea,
- 2) 1-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(3-hydroxy-4-chlorophenyl)-urea,
- 3) 1-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)urea,
- 4) 1-(2,b-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-trifluoromethylphenyl)urea,
- 5) 1-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-3-(2-hyclroxy-4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl)urea,
- 6) 1-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-trifluoromethylphenyl)urea,
- 7) 1-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)urea,
- 8) 1-(2,b-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-urea,
- 9) 1-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)urea,
- 10) 1-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-3-(4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl)urea,
- 11) 1-(2,b-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(4-cyanophenyl)urea,
- 12) 1-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)-3-[4-(1,1,2,3,3,3-hexafluoro- propoxy)phenyl] urea,
- 13) 1-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(4-cyclohexylphenyl)urea,
- 14) 1-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl)-urea,
- 15) 1-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea,
- 16) 1-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-3-(4--trifluoromethylphenyl)urea,
- 17) 1-(2,6-dichlorobenzoyl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)urea,
- 18) 1-(2,6-dichlorobenzoyl)-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-urea,
- 19) 1-benzoyl-3-(4-chlorophenyl)urea.
- 'The compounds according to the invention can be obtained in a manner known for the synthesis of analogous compounds as described for example in Netherlands Patent Specification 160,809.
- The compounds of formula (1), wherein Z is the group of formula (2), wherein X and X' are an oxygen atom or a sulphur atom and Y is a hydrogen atom, n = 1 and the remaining symbols have the above-mentioned meanings, can be obtained, for example, by reacting a compound of the-formula
- For preparing compounds of formula (1), wherein Z is a group of formula (2) in which Y is an alkyl group having 1-3 C-atoms and optionally substituted with halogen, said group Y can be introduced in a manner known per se by means of an alkylation reaction after completion of the above-described reaction of a compound of formula (4) with a compound of formula (5).
-
- The corresponding compounds wherein Y' is an optionally halogen-substituted alkyl group having 1-3 C-atoms can be obtained by means of an alkylation reaction.
-
- The above-described reactions are preferably carried out in the presence of an organic solvent, for example, an aromatic hydrocarbon, an alkyl halide, a non-cyclic or cyclic dialkyl ether, or acetonitrile, at temperatures between 0°C and the boiling-point of the solvent used.
- Compounds of formula (1), wherein Z is the group of formula (3), can be obtained by oxidizing the corresponding dithiourea compounds to be obtained in the above--described manner with, for example, a halogen, for example, bromine or iodine, as a result of which ring closure is effected via the two sulphur atoms. This reaction is preferably carried out in a solvent, for example, dichloroethane.
- The compounds can be processed to compositions in the conventional manner.
- A great advantage of the compounds according to the invention as compared with known cytostatics is that they have a low toxicity.
- The antitumor activity of the compounds was determined in a number of in vitro test.
- B16 melanoma cells grow as a "mono]ayer". The doubling time of these cells in a cell culture is 12-16 hours. For carrying out the test, "6 multiwell" tissue culture plates having a flat bottom with an area of 8 cm2 proved to be best suitable.
- On day 0, a quantity of 1.3 x 10 B16 melanoma cells is introduced in each cell culture dish.
- On day 1 the compounds to be examined are vortexed in the presence of glass beads. The compound to be tested is then added to the dishes with melanoma celles in the desired quantity. The incubation takes place at 37°C for 20 hours in a C02 incubator. The incubation is terminated by removing the culture medium with therein the compound to be tested, after which the cells are wahsed once and fresh medium is added.
- Forty-eight hours after the beginning of the incubation the quantity of cells in each dish is measured by means of a microcell Coulter Counter. The results thus obtained are expressed by indicating the activity of the compounds by 1+, 2+, 3+, 4+ or 5+ having the following meanings:
- 1+: cell growth is inhibited by 1-20% with respect to the control test
- 2+: cell growth is inhibited by 21-40% with respect to the control test
- 3+: cell growth is inhibited by 41-60% with respect to the control test
- 4+: cell growth is inhibited by 61-80% with respect to the control test
- 5+: cell growth is inhibited by 81-100% with respect to the control test.
- 'A number of representative compounds according to the invention were tested for cytotoxicity in a number of human tumor cell lines. The following cell lines have been used: bladder T24, malanoma IGR37, mammary MCF7, osteo- sarcoma A204, colon WIDR, HT29 and SW116 (P.P. Dendy and B.T. Hill, Human Tumour Drug, Sensititivty testing in vitro, Academic Press 1983; H.B. Lamberts et al., Oncology 40, 301-304, (1983); A.A. van der Huizen, Aziridinyl cy- clophosphazenes, synthesis, structure and cytostatic activity, thesis (1984), Groningen, the Netherlands).
- Cells were seeded in 24-well cluster plates at a concentration of 105 cells/ml of medium. After incubation for 24 hours at 37°C in an air/5% C02 atmosphere a suspension of the test compound in 0.5% CMC/saline was added to obtain a final concentration of 50 /ug/ml.
- Adriamycin was used as a positive control. After incubation for 72 hours in the presence of the test compound the cell layers were washed with phosphate bufferend saline and the cells were stained with the vital stain crystal violet. On the stained cell layer a visual assessment was done and the cell-inhibition scored:
- 4 approximately 100% cell growth inhibition
- 3 approximately 75% cell growth inhibition
- 2 approximately 50% cell growth inhibition
- 1 approximately 25% cell growth inhibition
- 0 no cell growth inhibition
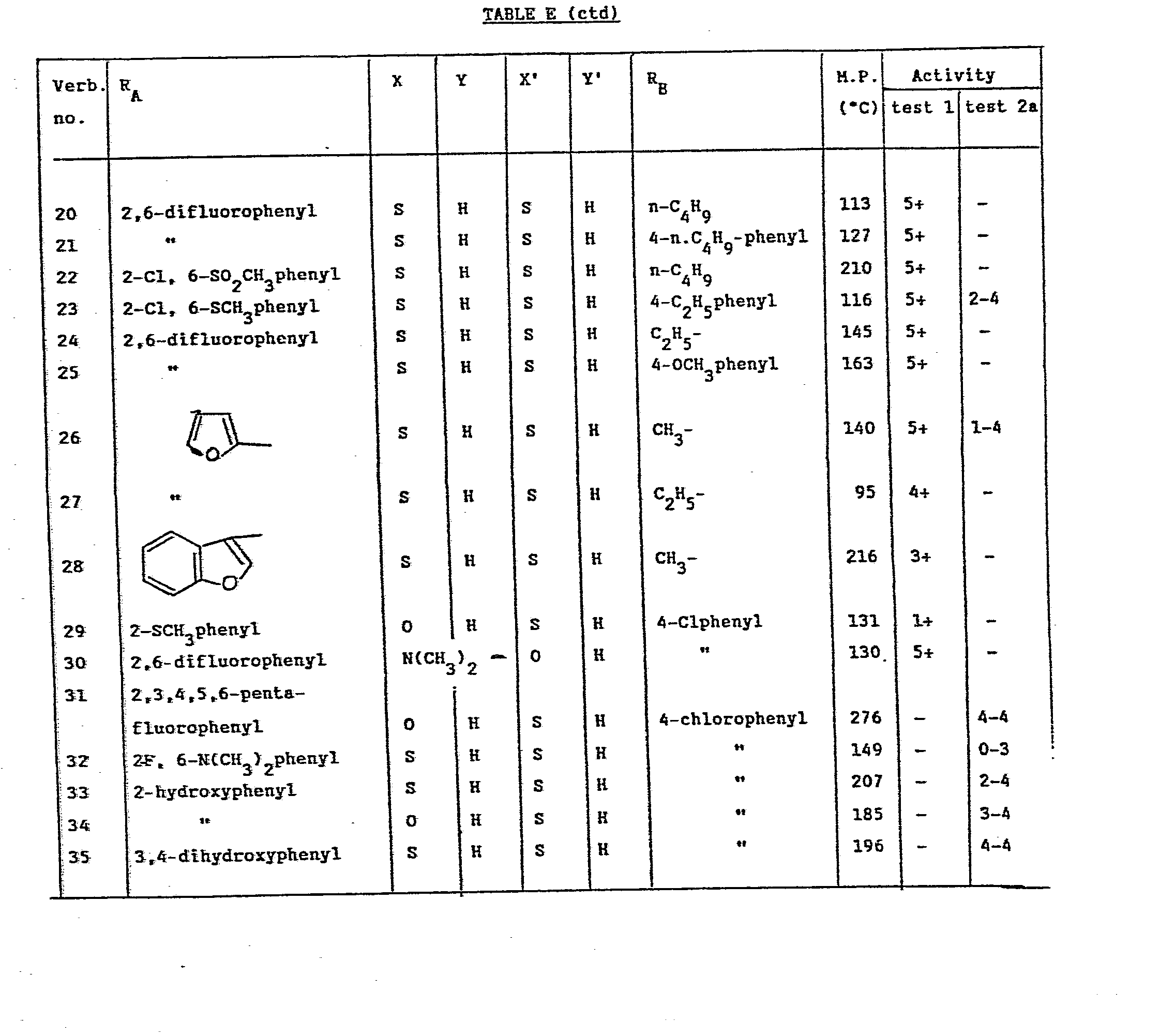
- The variation of the activity against the different cell lines has been indicated in tables A-E.
- Also a number of compounds was tested in this clonogenic assay (R. Ludwig et al, Cancer Chemother. Phar- macol. 12, 135-141, (1984); W.I. Scaefer, and K. Friend, Cancer Letters, 1, 259-262, (1976); P.P. Dendy, and B.T. Hill, Human Tumour Drug, Sensitivity testing in vitro, Academic Press 1983), using the following cell lines: mammary MCF7, and HTB26, colon WIDR and HTB38, lung HT853, melanoma HTB66, and uterine HTB114.
- Cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, daunomycin, bleomycin and adriamycin were used with colon WIDR as comparisons.
- Cells were seeded at the appropriate density for each cell line 102-105 cells/dishes and incubated at 37°C in an air/5% C02 atmosphere. Compounds as solution or suspension in 0.5% CMC/saline were added during seeding or after an overnight pre-incubation period to a final concentration of: 50 /ug/ml.
- The duration of the treatment was about 3 times the cell replication cycle. Afterwards the assays were fixed, stained and scored for the presence of colonies. Colony formation is expressed as the number of colonies present on treated dishes as a percentage of the number of colonies on control dishes.
-
- As stated hereinbefore, the compounds according to the invention have a much stronger activity than the known benzoylurea derivatives having antitumor activity which are described in European Patent application 83201263.7. In Table F below, the activity is recorded of a number of known compounds, tested in a concentration which is 10 times as high, i.e. 500 /ug/ml:
- The antitumor activity of the compounds determined in vitro is confirmed by the preliminary results obtained in an in vivo test in mice.
- The preparation of the compounds will be described in greater detail with reference to the ensuing specific examples.
- To a solution of 0.92 g of pentafluoroaniline in 25 ml of dry ether an equivalent quantity (1.2 g) of pentaflu- orobenzoyl-isocyanate was added at room temperature. After stirring for 2 hours the formed precipitate was sucked off. Yield 1.4 g (70%) of the above--mentioned compound. Melting-point 202°C.
- In the manner described in Example I the compound 1--(4-nitrobenzoyl-3-(2-nitrophenyl)urea was prepared starting from 2-nitroaniline and 4-nitrobenzoylisocyanate. 11 g Of this compound were dissolved in 200 ml of dimethyl formamide and recuced in a Parr apparatus by means of 10 g of Raney nickel at a hydrogen pressure of 2-3 atm. After the reaction the solution was filtered off and evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was recrystallized from a mixture of acetone and isopropanol. Yield 7.1 g (79%) of the title compound. Melting-point 240°C (decomposition).
- solution of 1.4 g of cyclohexane carboxamide and 2.1 g of 3,4-dimethoxyphenylisocyanate in 20 ml of dry xylene was refluxed for 16 hours. After cooling to room temperature the formed precipitate was filtered off and wahsed with hexane. Yield 3.3 g (91%) of 1-cyclohexylcarbonyl-3--(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)urea having a melting-point of 174°C.
- 2.0 g Of the compounds thus obtained were dissolved in 30 ml of dichloromethane. The solution was cooled to -60°C under an atmosphere of nitrogen. A solution of 10 ml of boron tribromide in 25 ml of dichloromethane was added dropwise. Stirring for 16 hours at room temperature was then carried out. The reaction mixture was cooled to -50°C and decomposed with methanol/water. After extracting with dichloromethane, drying, evaporating and recrystallizing from acetone/isopropyl ether, 1.3 g (72%) of the title compound were obtained. Melting-point 203°C.
- 1-(2-Pyridylcarbonyl)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)urea was obtained according to the method of Example I. 0.75 g Of this compound was dissolved in 5 ml of acetic acid and 1 ml of hydrogen peroxide (35%). The mixture was heated on a steam bath and 1.5 ml of hydrogen peroxid were added again after 2 and 3 hours. After 4.5 hours on the steam bath the mixture was cooled. The crystalline substance was sucked off and washed with isopropanol. Yield 0.3 g (38%) of the corresponding N-oxide. Melting-point 191°C.
- 1.0 g Of 2,6-difluoro-N,N-dimethylbenzamidine.HCl was dissolved in 15 ml of dimethyl formamide. 0.6 ml Of triethylamine and 0.73 g of 4-chlorophenyl isocyanate were added. After stirring at room temperature for 24 hours, the reaction mixture was poured in water and extracted with dichloromethane. In this manner 1.24 g (81%) of compound No. 30 from Table E were obtained with a melting-point of 130°C.
- 3.3 g Of 2methoxythiobenzamide and 1.7 g of ethylisothio- cyanate were dissolved in 50 ml of acetonitrile. After cooling in ice water, 0.9 g of 55% sodium hydride in oil were added to the mixture. Stirring at room temperature for 3 hours, filtering, acidifying with acetic acid, adding water and sucking off was carried out. After recrystallization from isopropanol, 2.7 g (53%) of 1-(2-methoxy- thiobenzoyl)-3-ethylthiourea were obtained. Melting-point 77°C.
- 1.3 g Of 1-(2-chlorothiobenzoyl)-3-methylthiourea were dissolved in 25 ml of dichloroethane. A solution of 0.27 ml of bromine in 10 ml of dichloroethane was added dropwise. After stirring for 30 minutes the formed precipitate was filtered off and suspended in acetonitrile. 1.3 ml Of triethylamine were added. After stirring for 1 hour, adding water, filtering off and recrystallizing from isopropanol, 0.4 g (31%) of compound no. 2 from Table D was obtained. Melting-point 206°C.
- 4.3 g Of 2-chloro-6-benzyloxybenzoylisocyanate were dissolved in 15 ml of acetonitrile. 2.55 g Of 4-chlorophe- nylurea were added to this solution. The mixture was refluxed for 1.5 hours. After cooling, sucking off the solid and washing with ether, 4.4 g (64%) of 1-(2-chloro-5-ben- zyloxybenzoyl)-5-(4-chlorophenyl)biurete were obtained with a melting-point of 166°C.
- 1.0 g Of this compound was dissolved in 5 ml of 45% HBr/glacial acetic acid. The mixture was heated at 55°C for 1 hour. After cooling, pouring in water, filtering off the solid and recrystallizing from acetone/acetonitrile, 0.68 g (85%) of 1-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzoyl)-5-(4-chlorophenyl) biurete was obtained. Melting-point 210°C.
- To a cooled solution of 0.8 g of 1-(2-fluoro-6-methoxybenzoyl)-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)urea in a casius--tube 1,5 ml of dimethylamine is added. After 8-12 hours at 100°C, the cooled contents of the tube is pourred in ice-water and the precipitate is collected and washed with water. Yield: 0.6 g of 1-(2-dimethylamino-6-methoxybenzoyl)-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)urea having a melting-point of 200°C.
is a group of the formula
which belong to a group of compounds known from the above--mentioned European Patent Application 83201263.7 (publ. no. 0107214). In comparison with these known compounds, the new compounds have a much stronger antitumor activity.
Claims (10)
and with the exclusion of the compounds:
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| NL8500572 | 1985-03-01 | ||
| NL8500572 | 1985-03-01 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0193249A2 true EP0193249A2 (en) | 1986-09-03 |
| EP0193249A3 EP0193249A3 (en) | 1988-03-16 |
Family
ID=19845602
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP86200300A Withdrawn EP0193249A3 (en) | 1985-03-01 | 1986-02-27 | Benzoyl urea derivatives having ati-tumor activity |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0193249A3 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPS61218569A (en) |
| AU (1) | AU601145B2 (en) |
| DK (1) | DK88186A (en) |
| ES (1) | ES8801896A1 (en) |
| GR (1) | GR860542B (en) |
| IE (1) | IE860511L (en) |
| PH (1) | PH23163A (en) |
| ZA (1) | ZA861446B (en) |
Cited By (36)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0324521A2 (en) * | 1988-01-11 | 1989-07-19 | Duphar International Research B.V | Method of treating haematologic diseases and pharmaceutical compositions to be used therefor |
| EP0333659A2 (en) * | 1988-03-18 | 1989-09-20 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Substituted thioureum derivatives |
| EP0336888A1 (en) * | 1988-03-18 | 1989-10-11 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Pest control agent |
| EP0369453A2 (en) * | 1988-11-18 | 1990-05-23 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | AGE-formation inhibitory agents |
| EP0375069A1 (en) * | 1988-12-21 | 1990-06-27 | Shell Internationale Researchmaatschappij B.V. | Benzamide compounds, their preparation and their use as pesticides |
| US4987135A (en) * | 1988-03-31 | 1991-01-22 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha Ltd. | Substituted benzene derivatives, processes for their production and antitumor compositions containing them |
| EP0413977A2 (en) * | 1989-07-28 | 1991-02-27 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd. | Substituted benzoylurea compounds or their salts, processes for their production and antitumour compositions containing them |
| EP0467613A1 (en) * | 1990-07-17 | 1992-01-22 | Eli Lilly And Company | Antitumor compositions and methods of treatment |
| US5166180A (en) * | 1988-01-11 | 1992-11-24 | Duphar International Research B.V. | Method of treating hematologic diseases and pharmaceutical composition to be used therefor |
| US5302608A (en) * | 1988-11-18 | 1994-04-12 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Age formation inhibitors |
| WO2000054759A2 (en) * | 1999-03-15 | 2000-09-21 | Tularik Inc. | Lxr modulators |
| US6624166B1 (en) * | 1993-06-08 | 2003-09-23 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Pyridazines as interleukin-1β converting enzyme inhibitors |
| WO2003084922A1 (en) * | 2002-04-11 | 2003-10-16 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | Acyl-4-carboxyphenylurea derivatives, method for production and use thereof |
| DE10225635C1 (en) * | 2002-06-07 | 2003-12-24 | Aventis Pharma Gmbh | N-benzoylureido-cinnamic acid derivatives, process for their preparation and their use |
| WO2003105843A1 (en) * | 2002-06-13 | 2003-12-24 | Kinetek Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of using isothiazole derivatives to treat cancer or inflammation |
| WO2004007455A1 (en) * | 2002-07-12 | 2004-01-22 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | Heterocyclically substituted benzoylureas, method for their production and their use as medicaments |
| WO2004033416A2 (en) * | 2002-10-04 | 2004-04-22 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | Carboxyalkoxy-substituted acyl-carboxyphenyl-urea derivatives, production method and use thereof as medicine |
| US7049341B2 (en) | 2002-06-07 | 2006-05-23 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | N-benzoylureidocinnamic acid derivatives, processes for preparing them and their use |
| US7071358B2 (en) | 2002-01-30 | 2006-07-04 | Amgen Inc. | Arylsulfonamidobenzylic compounds |
| US7078404B2 (en) | 2002-04-11 | 2006-07-18 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Acyl-3-carboxyphenylurea derivatives, processes for preparing them and their use |
| US7112606B2 (en) | 2002-01-30 | 2006-09-26 | Amgen Inc. | Heterocyclic arylsulfonamidobenzylic compounds |
| US7223796B2 (en) | 2002-04-11 | 2007-05-29 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Acyl-4-carboxyphenylurea derivatives, processes for preparing them and their use |
| WO2008029096A2 (en) * | 2006-09-04 | 2008-03-13 | University Court Of The University Of Dundee | P53 activating benzoyl urea and benzoyl thiourea compounds |
| US7470699B2 (en) | 2003-07-11 | 2008-12-30 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Trisubstituted aryl and heteroaryl derivatives as modulators of metabolism and the prophylaxis and treatment of disorders related thereto |
| US7781459B2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2010-08-24 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Carboxyalkoxy-substituted acyl-carboxyphenylurea derivatives and their use as medicaments |
| US7812159B2 (en) | 2005-01-10 | 2010-10-12 | Arena Pharamaceuticals, Inc. | Processes for preparing aromatic ethers |
| CN101973959A (en) * | 2010-06-12 | 2011-02-16 | 利尔化学股份有限公司 | 4-methyl-1,2,3-thiadiazole-5-formyl urea compounds and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN102225918A (en) * | 2010-06-12 | 2011-10-26 | 利尔化学股份有限公司 | 1,2,3-thiadiazole formyl urea compounds as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| US8293751B2 (en) | 2003-01-14 | 2012-10-23 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 1,2,3-trisubstituted aryl and heteroaryl derivatives as modulators of metabolism and the prophylaxis and treatment of disorders related thereto such as diabetes and hyperglycemia |
| US8362248B2 (en) | 2005-01-10 | 2013-01-29 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Substituted pyridinyl and pyrimidinyl derivatives as modulators of metabolism and the treatment of disorders related thereto |
| US9365508B2 (en) | 2009-06-09 | 2016-06-14 | University Court Of The University Of St Andrews | Aroyl thiourea derivatives |
| US10894787B2 (en) | 2010-09-22 | 2021-01-19 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Modulators of the GPR119 receptor and the treatment of disorders related thereto |
| WO2021034187A1 (en) | 2019-08-19 | 2021-02-25 | Akkolens International B.V. | Accommodative intraocular lens combination with independent fixed and variable power lens sections |
| US11007175B2 (en) | 2015-01-06 | 2021-05-18 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of treating conditions related to the S1P1 receptor |
| NL2027301A (en) | 2020-01-13 | 2021-08-17 | Akkolens Int B V | Mechanical means for accommodative intraocular lens |
| US11884626B2 (en) | 2015-06-22 | 2024-01-30 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Crystalline L-arginine salt of (R)-2-(7-(4-cyclopentyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyloxy)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrocyclo-penta [b]indol-3-yl)acetic acid(Compound1) for use in S1P1 receptor-associated disorders |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0223741A3 (en) * | 1985-11-22 | 1988-05-25 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Benzoyl ureas, process for their preparation and their use in combating pests |
| DE3545569A1 (en) * | 1985-12-21 | 1987-06-25 | Hoechst Ag | NEW PYRIDINE DERIVATIVES, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF, CONTAINERS THEREOF AND THEIR USE AS A PEST CONTROL |
| DE10302452B4 (en) * | 2003-01-23 | 2005-02-24 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | Carbonylamino-substituted acyl-phenyl-urea derivatives, processes for their preparation and their use |
| WO2006113650A1 (en) * | 2005-04-18 | 2006-10-26 | Khan Saeed R | Design and synthesis of novel tubulin polymerization inhibitors: bonzoylphenyluria (bpu) sulfur analogs |
| CN110563700A (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2019-12-13 | 德西费拉制药有限责任公司 | N-acyl-N' - (pyridin-2-yl) ureas and analogs exhibiting anti-cancer and anti-proliferative activity |
Citations (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB986811A (en) * | 1961-01-23 | 1965-03-24 | Parke Davis & Co | Salts of substituted 1,2-dihydro-s-triazines |
| NL7105350A (en) * | 1971-04-21 | 1972-10-24 | Substd benzoyl and thiobenzoyl ureas and thioureas - insecticides | |
| US3860648A (en) * | 1970-03-02 | 1975-01-14 | Rorer Inc William H | 1-(p-trifluoromethoxyphenyl)-biguanide |
| US4148902A (en) * | 1977-05-13 | 1979-04-10 | The Dow Chemical Company | N-[(optionally substituted phenylamino)carbonyl] pyridine carboxamides and insecticidal use thereof |
| US4160037A (en) * | 1977-09-30 | 1979-07-03 | The Upjohn Company | Compounds, compositions and methods of combatting pest employing thioureas |
| US4160834A (en) * | 1977-03-09 | 1979-07-10 | Eli Lilly And Company | 1-(Substituted benzoyl)-3-(substituted pyrazinyl)ureas |
| DE2926480A1 (en) * | 1978-07-06 | 1980-01-24 | Duphar Int Res | NEW UREA AND THIOURA COMPOUNDS, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THE NEW CONNECTIONS AND INSECTICIDE PREPARATIONS BASED ON THESE COMPOUNDS |
| EP0008768A1 (en) * | 1978-09-11 | 1980-03-19 | BASF Aktiengesellschaft | Aroyl ureas, process for their preparation and their use in insecticidal and acaricidal compositions |
| EP0009762A1 (en) * | 1978-10-07 | 1980-04-16 | Bayer Ag | Substituted N-benzoyl-N'-tert.-alcoxycarbonylphenyl(thio)ureas, methods for their preparation and their use as insecticides |
| EP0025363A1 (en) * | 1979-09-11 | 1981-03-18 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha Ltd. | N-Benzoyl N'-pyridyloxy phenyl ureas, a process for their production and pharmaceutical and insecticidal compositions containing the same |
| EP0035084A1 (en) * | 1980-03-05 | 1981-09-09 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Substituted N-fluorphenyl-N'-halogen benzoyl ureas, process for their prepration, compositions containing them and their use in combating pests |
| EP0042732A1 (en) * | 1980-06-19 | 1981-12-30 | Eli Lilly And Company | 1-benzoyl-3-substituted ureas and thioureas, their preparation, insecticidal formulations containing them and their use as insecticides |
| JPS57109721A (en) * | 1980-12-27 | 1982-07-08 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha Ltd | Carcinostatic agent |
| EP0056124A2 (en) * | 1981-01-14 | 1982-07-21 | BASF Aktiengesellschaft | N-Benzoyl N' phenylureas, preparation and use thereof as insecticides |
| EP0060071A1 (en) * | 1981-03-03 | 1982-09-15 | Eli Lilly And Company | Improvements in or relating to 1-benzoyl-3-(arylpyridyl)urea compounds |
| EP0107214A2 (en) * | 1982-09-02 | 1984-05-02 | Duphar International Research B.V | Pharmaceutical compositions containing benzoyl-phenyl ureas with anti-tumour activity |
| EP0116728A1 (en) * | 1983-01-24 | 1984-08-29 | Duphar International Research B.V | Composition active against mites, whitefly and thrips, pharmaceutical composition, and new benzoylureau compounds |
| EP0116729A2 (en) * | 1983-01-24 | 1984-08-29 | Duphar International Research B.V | Benzoylurea compounds and pesticidal compositions comprisingsame |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5959617A (en) * | 1982-09-02 | 1984-04-05 | デユフアル・インテルナチオナル・レセ−ルフ・ベ−・ヴエ− | Anticancer medicine composition |
| ATE43788T1 (en) * | 1983-09-01 | 1989-06-15 | Duphar Int Res | BENZOYL UREAS WITH ANTITUMORAL ACTIVITIES. |
-
1986
- 1986-02-26 IE IE860511A patent/IE860511L/en unknown
- 1986-02-26 GR GR860542A patent/GR860542B/en unknown
- 1986-02-26 DK DK88186A patent/DK88186A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1986-02-26 ES ES552432A patent/ES8801896A1/en not_active Expired
- 1986-02-26 AU AU54108/86A patent/AU601145B2/en not_active Ceased
- 1986-02-26 ZA ZA861446A patent/ZA861446B/en unknown
- 1986-02-27 PH PH33457A patent/PH23163A/en unknown
- 1986-02-27 EP EP86200300A patent/EP0193249A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1986-03-01 JP JP61042838A patent/JPS61218569A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB986811A (en) * | 1961-01-23 | 1965-03-24 | Parke Davis & Co | Salts of substituted 1,2-dihydro-s-triazines |
| US3860648A (en) * | 1970-03-02 | 1975-01-14 | Rorer Inc William H | 1-(p-trifluoromethoxyphenyl)-biguanide |
| NL7105350A (en) * | 1971-04-21 | 1972-10-24 | Substd benzoyl and thiobenzoyl ureas and thioureas - insecticides | |
| US4160834A (en) * | 1977-03-09 | 1979-07-10 | Eli Lilly And Company | 1-(Substituted benzoyl)-3-(substituted pyrazinyl)ureas |
| US4148902A (en) * | 1977-05-13 | 1979-04-10 | The Dow Chemical Company | N-[(optionally substituted phenylamino)carbonyl] pyridine carboxamides and insecticidal use thereof |
| US4160037A (en) * | 1977-09-30 | 1979-07-03 | The Upjohn Company | Compounds, compositions and methods of combatting pest employing thioureas |
| DE2926480A1 (en) * | 1978-07-06 | 1980-01-24 | Duphar Int Res | NEW UREA AND THIOURA COMPOUNDS, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THE NEW CONNECTIONS AND INSECTICIDE PREPARATIONS BASED ON THESE COMPOUNDS |
| EP0008768A1 (en) * | 1978-09-11 | 1980-03-19 | BASF Aktiengesellschaft | Aroyl ureas, process for their preparation and their use in insecticidal and acaricidal compositions |
| EP0009762A1 (en) * | 1978-10-07 | 1980-04-16 | Bayer Ag | Substituted N-benzoyl-N'-tert.-alcoxycarbonylphenyl(thio)ureas, methods for their preparation and their use as insecticides |
| EP0025363A1 (en) * | 1979-09-11 | 1981-03-18 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha Ltd. | N-Benzoyl N'-pyridyloxy phenyl ureas, a process for their production and pharmaceutical and insecticidal compositions containing the same |
| EP0035084A1 (en) * | 1980-03-05 | 1981-09-09 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Substituted N-fluorphenyl-N'-halogen benzoyl ureas, process for their prepration, compositions containing them and their use in combating pests |
| EP0042732A1 (en) * | 1980-06-19 | 1981-12-30 | Eli Lilly And Company | 1-benzoyl-3-substituted ureas and thioureas, their preparation, insecticidal formulations containing them and their use as insecticides |
| JPS57109721A (en) * | 1980-12-27 | 1982-07-08 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha Ltd | Carcinostatic agent |
| EP0056124A2 (en) * | 1981-01-14 | 1982-07-21 | BASF Aktiengesellschaft | N-Benzoyl N' phenylureas, preparation and use thereof as insecticides |
| EP0060071A1 (en) * | 1981-03-03 | 1982-09-15 | Eli Lilly And Company | Improvements in or relating to 1-benzoyl-3-(arylpyridyl)urea compounds |
| EP0107214A2 (en) * | 1982-09-02 | 1984-05-02 | Duphar International Research B.V | Pharmaceutical compositions containing benzoyl-phenyl ureas with anti-tumour activity |
| EP0116728A1 (en) * | 1983-01-24 | 1984-08-29 | Duphar International Research B.V | Composition active against mites, whitefly and thrips, pharmaceutical composition, and new benzoylureau compounds |
| EP0116729A2 (en) * | 1983-01-24 | 1984-08-29 | Duphar International Research B.V | Benzoylurea compounds and pesticidal compositions comprisingsame |
Non-Patent Citations (7)
| Title |
|---|
| CHEMICAL ABSTRACTS, vol. 94, no. 23, 8th June 1981, page 652, abstract no. 192334q, Columbus, Ohio, US; R. RAI et al.: "A novel route to the synthesis of 3-(arylimino)-5-substituted-1,2,4-dithiazoles. Part I: Oxidative debenzylation and cyclization of S-benzyliso-N-(arylthiocarbamoyl)thioacetamides"; & J.INDIAN.CHEM.SOC. 1980, 57(12), 1166-9 * |
| CHEMICAL ABSTRACTS, vol. 96, no. 13, 29th March 1982, page 700, abstract no. 104147b, Columbus, Ohio, US; Yu.L. YAGUPOL'SKII et al.: "1,4-diaryl-1,3-diaza-1,3-butadiene derivatives"; & ZH.ORG.KHIM. 1981, 17(8), 1720-5 * |
| CHEMICAL ABSTRACTS, vol. 98, no. 13, 28th March 1983, page 67, abstract no. 101190r, Columbus, Ohio, US; & JP-A-57 109 721 (ISHIHARA SANGYO KAISHA) 08-07-1982 * |
| JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURAL AND FOOD CHEMISTRY, vol. 21, no. 6, November/December 1973, pages 993-998, Washington, DC, US; K. WELLINGA et al.: "Synthesis and laboratory evaluation of 1-(2,6-disubstituted benzoyl)-3-phenylureas a new class of insecticides. II. Influence of the acyl moiety on insecticidal activity" * |
| JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURAL AND FOOD CHEMISTRY, vol. 24, no. 1, January/February 1976, pages 134-136, Washington, DC, US; C.C. YU et al.: "Synthesis and insecticidal activity of substituted 1-phenyl-3-benzoylureas and 1-phenyl-3-benzoyl-2-thioureaus" * |
| JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURAL AND FOOD CHEMISTRY, vol. 26, no. 1, January/February 1978, pages 164-166, Washington, DC, US; A.B. MILO et al.: "Heterocyclic analogues of diflubenzuron and growth and reproduction inhibitors of the fall armyworm and housfly" * |
| MONATSHEFTE FUR CHEMIE, vol. 108, pages 367-379, 1977, Springer-Verlag, Vienna, AT; W. STADLBAUER et al.: "Zur Synthese 3,5,6-substituierter s-Triazin-2,4-dione" * |
Cited By (58)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0324521A2 (en) * | 1988-01-11 | 1989-07-19 | Duphar International Research B.V | Method of treating haematologic diseases and pharmaceutical compositions to be used therefor |
| US5166180A (en) * | 1988-01-11 | 1992-11-24 | Duphar International Research B.V. | Method of treating hematologic diseases and pharmaceutical composition to be used therefor |
| EP0324521A3 (en) * | 1988-01-11 | 1991-11-27 | Duphar International Research B.V | Method of treating haematologic diseases and pharmaceutical compositions to be used therefor |
| EP0333659A2 (en) * | 1988-03-18 | 1989-09-20 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Substituted thioureum derivatives |
| EP0336888A1 (en) * | 1988-03-18 | 1989-10-11 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Pest control agent |
| EP0333659A3 (en) * | 1988-03-18 | 1990-12-05 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Substituted thioureum derivatives |
| US4987135A (en) * | 1988-03-31 | 1991-01-22 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha Ltd. | Substituted benzene derivatives, processes for their production and antitumor compositions containing them |
| EP0369453A3 (en) * | 1988-11-18 | 1990-10-24 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Age-formation inhibitory agents |
| US5302608A (en) * | 1988-11-18 | 1994-04-12 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Age formation inhibitors |
| EP0369453A2 (en) * | 1988-11-18 | 1990-05-23 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | AGE-formation inhibitory agents |
| US5155135A (en) * | 1988-12-21 | 1992-10-13 | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij, B.V. | Benzamide compounds, their preparation and their use as pesticides |
| EP0375069A1 (en) * | 1988-12-21 | 1990-06-27 | Shell Internationale Researchmaatschappij B.V. | Benzamide compounds, their preparation and their use as pesticides |
| EP0413977A3 (en) * | 1989-07-28 | 1991-03-20 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd. | Substituted benzoylurea compounds or their salts, processes for their production and antitumour compositions containing them |
| EP0413977A2 (en) * | 1989-07-28 | 1991-02-27 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd. | Substituted benzoylurea compounds or their salts, processes for their production and antitumour compositions containing them |
| US5102884A (en) * | 1989-07-28 | 1992-04-07 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha Ltd. | Substituted benzoylurea compounds or their salts, processes for their production and antitumour compositions containing them |
| EP0467613A1 (en) * | 1990-07-17 | 1992-01-22 | Eli Lilly And Company | Antitumor compositions and methods of treatment |
| US6624166B1 (en) * | 1993-06-08 | 2003-09-23 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Pyridazines as interleukin-1β converting enzyme inhibitors |
| US6995261B2 (en) | 1993-06-08 | 2006-02-07 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | 4-pyridazinecarboxamides and esters as interleukin-1β converting enzyme inhibitors |
| WO2000054759A2 (en) * | 1999-03-15 | 2000-09-21 | Tularik Inc. | Lxr modulators |
| WO2000054759A3 (en) * | 1999-03-15 | 2001-02-15 | Tularik Inc | Lxr modulators |
| US6316503B1 (en) | 1999-03-15 | 2001-11-13 | Tularik Inc. | LXR modulators |
| US7071358B2 (en) | 2002-01-30 | 2006-07-04 | Amgen Inc. | Arylsulfonamidobenzylic compounds |
| US7112606B2 (en) | 2002-01-30 | 2006-09-26 | Amgen Inc. | Heterocyclic arylsulfonamidobenzylic compounds |
| US7326812B2 (en) | 2002-01-30 | 2008-02-05 | Amgen Inc. | Arylsulfonamidobenzylic compounds |
| US7473703B2 (en) | 2002-01-30 | 2009-01-06 | Amgen Inc. | Heterocyclic arylsulfonamidobenzylic compounds |
| WO2003084922A1 (en) * | 2002-04-11 | 2003-10-16 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | Acyl-4-carboxyphenylurea derivatives, method for production and use thereof |
| US7223796B2 (en) | 2002-04-11 | 2007-05-29 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Acyl-4-carboxyphenylurea derivatives, processes for preparing them and their use |
| DE10215907A1 (en) * | 2002-04-11 | 2003-11-06 | Aventis Pharma Gmbh | Acyl-4-carboxyphenyl-urea derivatives, processes for their preparation and their use |
| US7078404B2 (en) | 2002-04-11 | 2006-07-18 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Acyl-3-carboxyphenylurea derivatives, processes for preparing them and their use |
| DE10225635C1 (en) * | 2002-06-07 | 2003-12-24 | Aventis Pharma Gmbh | N-benzoylureido-cinnamic acid derivatives, process for their preparation and their use |
| US7049341B2 (en) | 2002-06-07 | 2006-05-23 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | N-benzoylureidocinnamic acid derivatives, processes for preparing them and their use |
| WO2003105843A1 (en) * | 2002-06-13 | 2003-12-24 | Kinetek Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of using isothiazole derivatives to treat cancer or inflammation |
| WO2004007455A1 (en) * | 2002-07-12 | 2004-01-22 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | Heterocyclically substituted benzoylureas, method for their production and their use as medicaments |
| US7138414B2 (en) | 2002-07-12 | 2006-11-21 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Heterocyclically substituted benzoylureas, process for their preparation and their use as pharmaceuticals |
| CN1304371C (en) * | 2002-07-12 | 2007-03-14 | 塞诺菲-安万特德国有限公司 | Heterocyclically substituted benzoylureas, process for their preparation and their use as pharmaceuticals |
| US7781459B2 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2010-08-24 | Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland Gmbh | Carboxyalkoxy-substituted acyl-carboxyphenylurea derivatives and their use as medicaments |
| WO2004033416A3 (en) * | 2002-10-04 | 2004-05-13 | Aventis Pharma Gmbh | Carboxyalkoxy-substituted acyl-carboxyphenyl-urea derivatives, production method and use thereof as medicine |
| WO2004033416A2 (en) * | 2002-10-04 | 2004-04-22 | Aventis Pharma Deutschland Gmbh | Carboxyalkoxy-substituted acyl-carboxyphenyl-urea derivatives, production method and use thereof as medicine |
| US8293751B2 (en) | 2003-01-14 | 2012-10-23 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 1,2,3-trisubstituted aryl and heteroaryl derivatives as modulators of metabolism and the prophylaxis and treatment of disorders related thereto such as diabetes and hyperglycemia |
| US7838525B2 (en) | 2003-07-11 | 2010-11-23 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Trisubstituted aryl and heteroaryl derivatives as modulators of metabolism and the prophylaxis and treatment of disorders related thereto |
| US7470699B2 (en) | 2003-07-11 | 2008-12-30 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Trisubstituted aryl and heteroaryl derivatives as modulators of metabolism and the prophylaxis and treatment of disorders related thereto |
| US8362248B2 (en) | 2005-01-10 | 2013-01-29 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Substituted pyridinyl and pyrimidinyl derivatives as modulators of metabolism and the treatment of disorders related thereto |
| US7812159B2 (en) | 2005-01-10 | 2010-10-12 | Arena Pharamaceuticals, Inc. | Processes for preparing aromatic ethers |
| US9120765B2 (en) | 2006-09-04 | 2015-09-01 | University Court Of The University Of Dundee | P53 activating compounds |
| WO2008029096A3 (en) * | 2006-09-04 | 2008-04-24 | Univ Dundee | P53 activating benzoyl urea and benzoyl thiourea compounds |
| WO2008029096A2 (en) * | 2006-09-04 | 2008-03-13 | University Court Of The University Of Dundee | P53 activating benzoyl urea and benzoyl thiourea compounds |
| US8501991B2 (en) | 2006-09-04 | 2013-08-06 | University Court Of The University Of Dundee | P53 activating compounds |
| US9365508B2 (en) | 2009-06-09 | 2016-06-14 | University Court Of The University Of St Andrews | Aroyl thiourea derivatives |
| CN101973959B (en) * | 2010-06-12 | 2016-06-01 | 利尔化学股份有限公司 | 4-methyl isophthalic acid, 2,3-thiadiazoles-5-benzoyl urea compounds and its production and use |
| CN102225918B (en) * | 2010-06-12 | 2016-04-20 | 利尔化学股份有限公司 | One class 1,2,3-thiadiazole formoxyl ureide compound and its production and use |
| CN102225918A (en) * | 2010-06-12 | 2011-10-26 | 利尔化学股份有限公司 | 1,2,3-thiadiazole formyl urea compounds as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN101973959A (en) * | 2010-06-12 | 2011-02-16 | 利尔化学股份有限公司 | 4-methyl-1,2,3-thiadiazole-5-formyl urea compounds and preparation method and application thereof |
| US10894787B2 (en) | 2010-09-22 | 2021-01-19 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Modulators of the GPR119 receptor and the treatment of disorders related thereto |
| US11007175B2 (en) | 2015-01-06 | 2021-05-18 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods of treating conditions related to the S1P1 receptor |
| US11884626B2 (en) | 2015-06-22 | 2024-01-30 | Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Crystalline L-arginine salt of (R)-2-(7-(4-cyclopentyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyloxy)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrocyclo-penta [b]indol-3-yl)acetic acid(Compound1) for use in S1P1 receptor-associated disorders |
| WO2021034187A1 (en) | 2019-08-19 | 2021-02-25 | Akkolens International B.V. | Accommodative intraocular lens combination with independent fixed and variable power lens sections |
| DE112020003939T5 (en) | 2019-08-19 | 2022-05-19 | Akkolens International B.V. | Accommodative intraocular lens combination with independent fixed and variable power lens parts |
| NL2027301A (en) | 2020-01-13 | 2021-08-17 | Akkolens Int B V | Mechanical means for accommodative intraocular lens |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| IE860511L (en) | 1986-09-01 |
| DK88186A (en) | 1986-09-02 |
| ES8801896A1 (en) | 1988-03-01 |
| AU601145B2 (en) | 1990-09-06 |
| PH23163A (en) | 1989-05-19 |
| ES552432A0 (en) | 1988-03-01 |
| DK88186D0 (en) | 1986-02-26 |
| AU5410886A (en) | 1986-09-04 |
| ZA861446B (en) | 1986-10-29 |
| EP0193249A3 (en) | 1988-03-16 |
| JPS61218569A (en) | 1986-09-29 |
| GR860542B (en) | 1986-06-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0193249A2 (en) | Benzoyl urea derivatives having ati-tumor activity | |
| EP0136745B1 (en) | Benzoyl urea derivatives having anti-tumor activity | |
| RU2121997C1 (en) | 7-amino-1h-indole derivatives | |
| EP4112606A1 (en) | Aromatic compound and use thereof in preparing antineoplastic drugs | |
| JP4510372B2 (en) | Acylphenylurea derivatives, processes for their preparation and their use as medicaments | |
| RU2515983C2 (en) | Novel compounds of reverse turn mimetics, method of their manufacturing and application | |
| AU7326396A (en) | Hydroxylamine derivatives useful for enhancing the molecular chaperon production and the preparation thereof | |
| US4684747A (en) | N,N'-bis(sulfonyl)hydrazines having antineoplastic activity | |
| US5571845A (en) | Nitroaniline derivatives and their use as anti-tumour agents | |
| CN109438323B (en) | Gossypol-7-N heteroisatin Schiff base compounds with anti-tumor activity and synthesis method thereof | |
| CA1255299A (en) | Guanidinothiazole derivatives containing alkylene bridges, a process for their preparation and their use as medicaments | |
| JPS5951537B2 (en) | Method for producing novel α-aminooxycarboxylic acid hydrazide derivative | |
| US4377687A (en) | Analogs of 1-(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitroso-3-(cycloheyl)-urea substituted by heterocyclic rings or alkyl radicals | |
| US5929082A (en) | Potassium ion channel blockers | |
| Shyam et al. | 1, 2-Bis (sulfonyl) hydrazines. 3. Effects of structural modification on antineoplastic activity | |
| CN109516926B (en) | Preparation and application of piperlonguminine derivative | |
| US4892887A (en) | N,N'-bis(sulfonyl)hydrazines having antineoplastic activity | |
| CN111560029A (en) | Preparation method of triazolobenzothiazole derivative | |
| DK162841B (en) | N- (3-NITRO-4-QUINOLYL) -4-CARBOXAMIDINES, PROCEDURES FOR PREPARING IT AND PHARMACEUTICAL PREPARATIONS CONTAINING SUCH COMPOUNDS | |
| CN109575050B (en) | Gossypol-7-N heteroisatin Schiff base compounds with anti-tumor activity and synthesis method thereof | |
| Ishmetova et al. | Synthesis and tuberculostatic activity of amine-substituted 1, 2, 4, 5-tetrazines and pyridazines | |
| KR860000103B1 (en) | Process for preparing 3'-substituted-5'-(2-amino-4-pyridyl)-1',2'4'-triazoles | |
| KR20050044712A (en) | 1,3-diarylprop-2-en-1-ones, compositions containing same and use thereof | |
| RU2127259C1 (en) | Derivatives of sulfonylurea or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, a method of their synthesis and a pharmaceutical composition based on derivatives of sulfonylurea showing antitumor activity | |
| US3907889A (en) | Chelocardin derivatives |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19880831 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19900131 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19900811 |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: BROUWER, MARIUS S. Inventor name: VAN HES, ROELOF |