WO2009132843A1 - Controllable hospital bed - Google Patents
Controllable hospital bed Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2009132843A1 WO2009132843A1 PCT/EP2009/003114 EP2009003114W WO2009132843A1 WO 2009132843 A1 WO2009132843 A1 WO 2009132843A1 EP 2009003114 W EP2009003114 W EP 2009003114W WO 2009132843 A1 WO2009132843 A1 WO 2009132843A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- hospital bed
- controllable
- bed
- functions
- patient
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61G—TRANSPORT, PERSONAL CONVEYANCES, OR ACCOMMODATION SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PATIENTS OR DISABLED PERSONS; OPERATING TABLES OR CHAIRS; CHAIRS FOR DENTISTRY; FUNERAL DEVICES
- A61G7/00—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons
- A61G7/002—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons having adjustable mattress frame
- A61G7/018—Control or drive mechanisms
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61G—TRANSPORT, PERSONAL CONVEYANCES, OR ACCOMMODATION SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PATIENTS OR DISABLED PERSONS; OPERATING TABLES OR CHAIRS; CHAIRS FOR DENTISTRY; FUNERAL DEVICES
- A61G7/00—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons
- A61G7/002—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons having adjustable mattress frame
- A61G7/008—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons having adjustable mattress frame tiltable around longitudinal axis, e.g. for rolling
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61G—TRANSPORT, PERSONAL CONVEYANCES, OR ACCOMMODATION SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PATIENTS OR DISABLED PERSONS; OPERATING TABLES OR CHAIRS; CHAIRS FOR DENTISTRY; FUNERAL DEVICES
- A61G7/00—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons
- A61G7/002—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons having adjustable mattress frame
- A61G7/015—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons having adjustable mattress frame divided into different adjustable sections, e.g. for Gatch position
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61G—TRANSPORT, PERSONAL CONVEYANCES, OR ACCOMMODATION SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PATIENTS OR DISABLED PERSONS; OPERATING TABLES OR CHAIRS; CHAIRS FOR DENTISTRY; FUNERAL DEVICES
- A61G7/00—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons
- A61G7/05—Parts, details or accessories of beds
- A61G7/057—Arrangements for preventing bed-sores or for supporting patients with burns, e.g. mattresses specially adapted therefor
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61G—TRANSPORT, PERSONAL CONVEYANCES, OR ACCOMMODATION SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PATIENTS OR DISABLED PERSONS; OPERATING TABLES OR CHAIRS; CHAIRS FOR DENTISTRY; FUNERAL DEVICES
- A61G2210/00—Devices for specific treatment or diagnosis
- A61G2210/50—Devices for specific treatment or diagnosis for radiography
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61G—TRANSPORT, PERSONAL CONVEYANCES, OR ACCOMMODATION SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PATIENTS OR DISABLED PERSONS; OPERATING TABLES OR CHAIRS; CHAIRS FOR DENTISTRY; FUNERAL DEVICES
- A61G2210/00—Devices for specific treatment or diagnosis
- A61G2210/70—Devices for specific treatment or diagnosis for cooling
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61G—TRANSPORT, PERSONAL CONVEYANCES, OR ACCOMMODATION SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PATIENTS OR DISABLED PERSONS; OPERATING TABLES OR CHAIRS; CHAIRS FOR DENTISTRY; FUNERAL DEVICES
- A61G2210/00—Devices for specific treatment or diagnosis
- A61G2210/90—Devices for specific treatment or diagnosis for heating
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61G—TRANSPORT, PERSONAL CONVEYANCES, OR ACCOMMODATION SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PATIENTS OR DISABLED PERSONS; OPERATING TABLES OR CHAIRS; CHAIRS FOR DENTISTRY; FUNERAL DEVICES
- A61G7/00—Beds specially adapted for nursing; Devices for lifting patients or disabled persons
- A61G7/0005—Means for bathing bedridden persons
Definitions
- the invention relates to a controllable hospital bed, a method for controlling a controllable hospital bed and a computer program product which implements a control for a controllable hospital bed.
- DE 100 01 687 A1 discloses a hospital bed for decubitus prophylaxis. It is exploited that moving the bed frame in different positions reduces the probability of a decubitus.
- the bed frame is mounted on four hydraulically actuated working cylinders. With these cylinders, the bed frame is movable to reduce the likelihood of pressure sores.
- a controllable hospital bed comprising a bed frame, which has movable parts, at least one drive unit for moving the movable parts and / or for driving the movable parts in certain positions, at least one control unit for controlling the at least one drive unit and at least one storage unit for storing a plurality of particular positions and functions, the determined positions comprising a shock position, a cardiac position, a cerebral position, a sitting position, a back position, a resuscitation position, and / or a horizontal position, the functions including continuously moving extremities and / or a trunk, a vibration function, a pressure ulcer prophylaxis function, a selection of different positions by means of a quick and direct adjustment and / or a weight control function, wherein the control unit comprises a Meh provides the number of specific items and functions for selection.
- a bed frame is understood to be a frame which, for example, holds a mattress but may also comprise other devices which are provided, for example, for holding the extremities of a patient.
- the bed frame on movable parts.
- Such a movable part may for example be a movable headrest.
- the movable parts of the bed frame can be moved by drive units and / or moved into certain positions.
- the drive unit or the drive units can be designed electrically and / or hydraulically.
- a bed frame can have joints in the area of the knee and in the hip area and thus divide the bed frame into three movable parts. Moving the lower part by a certain angle and moving the upper part by a certain angle can move the bed from a lying position to a sitting position.
- Such a defined setting of the movable parts can be stored as a specific position, here for example the sitting position.
- a bed frame according to a predetermined movement profile can be moved.
- Such a movement profile can be defined by predetermined positions and times at which the bedstead moves to the predetermined position.
- Such a definition of pressure ulcer prophylaxis function can also be stored.
- a control unit can then move the drive units in such a way that the controllable hospital bed moves to a defined position or performs a defined function.
- the control unit accesses a memory unit on which a plurality of positions and functions can be stored. Through a user interface, the control unit provides a user with a plurality of specific positions and functions.
- the control unit is preferably an electronic controller.
- the controllable bed can also provide other functions, such as a weight control function.
- a weight control function With this weight control function, the weight of a patient who is on the controllable bedside can be measured. Then, a corresponding sensor supplies the measured weight information to a central control unit.
- the measured weight is stored by the control unit, for example, or forwarded to a screen display. It is also conceivable to record a weight measurement series and thus to determine the weight development of the to reproduce patients.
- the shock position describes a position in which the legs of a patient are higher than the trunk and the trunk is higher than the head.
- the arms preferably have slightly upwards.
- Specific movements or specific movement patterns for the extremities as well as the time duration or temporal sequence of the movement patterns for the extremities may be defined for the control unit, or the corresponding movement patterns and time periods may be input to the control unit. The latter allows an individual setting of the motion functions.
- the movements of the trunk and neck are adjustable with respect to a movement pattern and the associated movement time.
- the time duration of the respective movements including start time and end time of a movement pattern can also be set.
- a movement pattern can be specified more precisely, for example, by specifying a maximum flexion of a joint.
- the controllable hospital bed has a thermosystem for regulating a body temperature.
- the thermal system can be controlled for example via the control unit.
- the control unit can then be informed via a communication interface of individual settings or standard settings that are necessary for the regulation of the body temperature of a patient.
- the thermosystem may, for example, also comprise a thermoprobe which can be applied rectally to a patient for measurement of body temperature.
- the measurement of body temperature is then provided to the control unit which controls the thermosystem. On this way, a body temperature control loop has been created.
- the temperature of the thermo system can also be set manually.
- the positions and / or the functions are individually configurable.
- the positions are defined, for example, by the position of the various moving parts. So that the drive units can drive the moving parts into the defined positions, the control unit accesses a storage unit in which the corresponding positions are stored. It may now make sense, for example, depending on the size of the patient or other peculiarities of the patient to change the definition of the position. Similarly, it may be useful to add more defined positions. Changing and adding the positions are described here by configuring the positions. Likewise, definitions of the functions can be changed or new functions can be added. Both are in the term "Configure functions" included.
- the controllable hospital bed has at least one communication interface.
- This communication interface can be used to forward recorded measured values, such as the weight of the patient, to a computer unit at different times.
- the communication interface may be, for example, a USB interface or an interface for a printer.
- the drive units are individually controllable. This makes it possible, for example, that the moving parts in any position that is desired by the user, can be driven.
- control unit provides a timing function.
- a timing function for example, functions can be performed only at certain times of the day, or after a certain time functions can be turned off automatically.
- materials are used in a fuselage area of the controllable hospital bed which essentially do not impair an X-ray measurement.
- a method for controlling a hospital bed comprises at least one of the following steps:
- the control functions may mean, for example, measuring the weight of a patient or checking a fixation.
- the configuration of functions or the configuration of functions can be done by having certain positions already stored in a memory that the controller can access. It may also mean that certain positions or functions are entered by a user, for example, a patient or a hospital employee, in the control unit and stored by this on a memory.
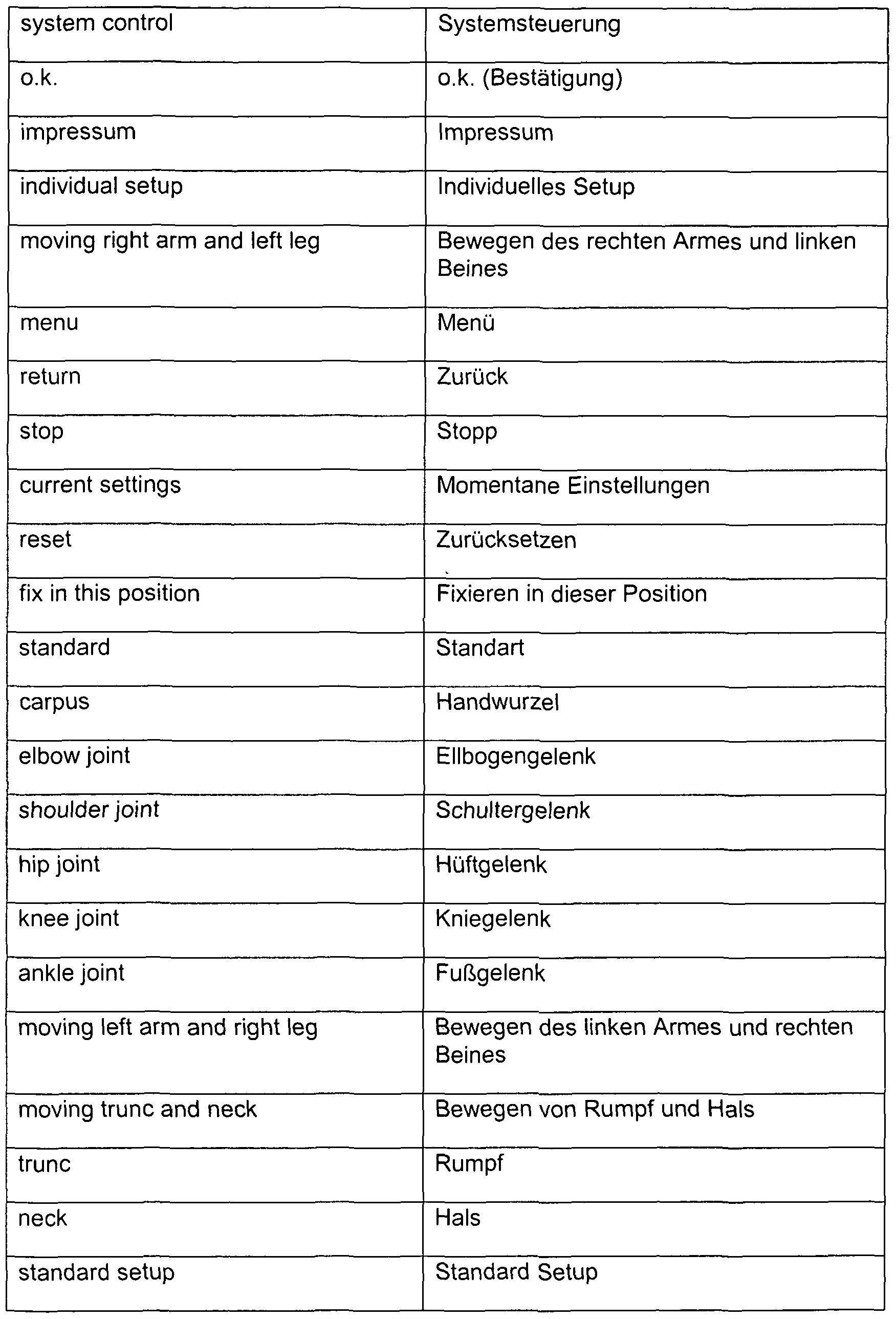
- a control unit 4 can be operated via a touch screen 7.
- the control unit 4 can access a memory unit 5.
- the control unit 4 can control a drive unit 3.
- the drive unit 3 is used to move moving parts of a bed frame 2.
- Measuring units 9 are provided on the bed frame, which supply measured values to the control unit 4. Measured values can be, for example, weight measurements.
- the drive unit 3 Based on the loaded data control unit 4 the drive unit 3 so that the parts of the bedstead drive in the predefined and selected position. Likewise, a position can be selected via the touch screen.
- the data of the selected function is loaded on the storage unit 5 by the controller. According to the loaded data, the drive units are controlled so that the bed frame 2 or the controllable hospital bed 1 performs the desired function.
- the measured values of the measuring unit 9 in the control unit 4 can be processed. A result of this processing is output, for example, via the communication interface 8 to a computer or a printer.
- Fig. 2 shows a touch screen 7 which is used as the user interface of the controllable hospital bed. It has functionalities by touching a correspondingly marked part of a contact surface
- the touch surface has a selection area for a movement device 11, for a vibration device 12, for current settings 13, for pressure ulcer prophylaxis 14, for an acoustic system 29, for a thermosystem 30 and for a system control 16 to a loss of a fixation displayed in an alarm area 15
- These selection areas are used to select a dwell function.
- Further selection areas are a selection area for an emergency stop 17, for a shock position 18, for a heart position 19, for a cerebral position 20, for a sitting position 21, for a jerk position 22, for a resuscitation function 23 and for a horizontal position.
- the movable parts are a first movable part 36 for moving a head and trunk area of a patient 35 and a second movable part 31, a third movable part 32, a fourth movable part 33 and a fifth movable part 34
- the movable parts 31 to 34 serve to move the four extremities of the patient
- the five illustrated movable parts can be moved by drive units
- certain functions can be performed and movement patterns are performed.
- bending of the right elbow can be achieved by a certain angle
- Decubitus element 42 which has chambered air cushion, is arranged Em Thermosystem 43 is arranged laterally on the anti-decubitus element.
- a waterproof mattress pad 44 serves to prevent liquids from getting from a mattress to the thermal system 3 or the anti-decubitus element.
- a telescoping arm system 5 adjusts dimensions of the bed so that the bed can accommodate different patient sizes.
- a cassette holder is slidably disposed below the first movable part 30 for moving a head and trunk area. This cassette holder is used to record x-rays of the lungs or abdomen.
- FIGS. 5 to 62 show screen shots of the system according to the invention.
- the feature "bedside” thus reflects (i) that medical-therapeutic purposes are in the foreground and (ii) that the treatment of a medical patient requires an individual presetting of the sickbed by medical professionals, and not automatically or as in WO 2006/061834 A2 and (iii) that this adjustment is to be carried out by a healthcare professional In WO 2006/061834 A2, the person lying in bed (the user there) can only himself from a large number of predetermined exercises , Positions and functions call him appear appropriate to increase his wellness state.
- the subject matter of claim 1, on the other hand, is directed to the special medical requirements of a controllable hospital bed, which assisted with the therapy and medical treatment of the patient.
- a task of the medical bed is to help maintain vital signs and prevent (or at least reduce) storage damage that may otherwise occur as a result of the patient's immobile storage.
- the controllable hospital bed ensures a largely natural status of essential body functions to ensure even in the situation of the coma, the essential body functions are those that are used day after day and without which no normal life would be possible.
- the controllable hospital bed not only allows the application of numerous therapeutic and rehabilitative functions on the patient, but also allows their programmed time sequence in a rhythm comparable to the natural processes. This means, for example, adhering to a day / night rhythm of movement, taking into account sleep and rest periods, recovery phases after (passive) physical exertion and thus avoiding overloading and observing resting periods after meals.
- the use of the controllable hospital bed takes into account the natural rhythm of life and the natural, subconscious or hidden reactions in everyday life.
- controllable hospital bed provides a number of possible sensor modules for tactile, olfactory or acoustic stimuli.
- DE 196 03 318 A1 does not disclose that positions and / or functions are individually configurable. Rather, it is explicitly determined that only predetermined bed positions and bed type-specific operating modes can be retrieved by means of the nurse control box. The stored data are thus bed type-specific, but not patient-specific. Likewise, there is no safeguarding of the change in setting, which ensures that only the settings prescribed by the medical staff are taken into account and that potentially harmful functions of the sickbed are not called up by the patient or by third parties for accidental or intentional manipulative adjustments. The system of DE 196 03 318 A1 is therefore also not suitable for a Komapatien- to be used. The positions and functions disclosed in DE 196 03 318 A1 are not suitable for promoting and maintaining the essential vital functions of a coma patient therapeutically and in rehabilitation.
- DE 83 04 560 U1 An individualization of the control program, which is configurable by a physician, is not disclosed in DE 83 04 560 U1.
- DE 83 04 560 U1 merely discloses that a control element with multiple or single lever operation can also be operated by a therapist. However, this does not correspond to the embodiment of a controllable hospital bed in which the positions and / or the functions of the (electronic) control unit are individually configurable.
- DE 83 04 560 U1 also lacks the focus on a therapy individually arranged for the support, therapy and rehabilitation of vital functions by a medical specialist for the respective patient who is ever limited in his mobility. Also missing in DE 83 04 560 U1 the special sensors for coma patients.
- the information / software component 2.
- the basis of the system consists of five components, which can be extended or shortened like a telescope. Each component consists of several moving elements like a caterpillar.
- the material is lightweight, for example fiberglass or hard synthetic plastic (a metal is not used for the trunk component to preserve the possibilities of X-rays).
- a maximum body length of 210 centimeters and a maximum body weight of 180 kilograms should be considered.
- Reset means: a new possibility or start of adjustment to adjust the movement.
- Both sliding regulators can be moved separately.
- Stop means: Stop all vibrations.
- “Actual Weight” shows the automatically registered and automatically measured weight value of the patient.
- the comatose patient is reduced in a nonphysiological immobility and a pathological hyposensory state Sensory stimulation and therefore also poor signal processing and reaction, with iatrogenic and disease-related effects interacting.
- Prolonged immobility also means a pathomechanically relevant factor in the development of intestinal atony, from which a bacterial migration of the intestinal wall can result with consecutive sepsis (5).
- the CMICB system is a kinetic therapy system based on a robotic technique that allows continuous passive movement of the four extremities and the trunk and provides sensory tactile and auditory signals.
- the monitor is equipped with
- the main functions of the CMIS are shown on the main monitor and can be activated here:
- thermo system Without feedback setting, the temperature of the thermo system can be controlled manually via the "individual setup" function.
- the following defined bed positions are complemented when activated by voce functions that name the respective functions - such as shock position, emergency stop. Individual or standardized motion functions, vibration effects, acoustic signals and anti-decubitus effects are automatically switched off when the following positions are selected.
- Cerebral position (for example in cranial-brain trauma).
- Weight measurement Digital and graphical representation, "select patients weight”: Initial weight of the patient.
- the bed consists of 5 movable modules (Fig.3):
- Each component consists of several movable bowl-shaped individual elements made of lightweight, durable and easy-to-clean material. For example, fiberglass is considered. Metallic substances are not suitable for X-ray imaging.
- shell of ultralight material e.g., fiberglass
- the unit of telescopic tube and hinge system and shell elements is mounted on a base module that the bed easily movable resp. mobile and can be controlled by computerized height.
- a standard-sized cassette holder, slidable is installed under the thorax module.
- radiographs of the abdomen (abdominal cavity) there is an analogous support at the level of the abdominal module.
- Additional brackets are used to insert a shell in the head area for hair washing and a toilet bin.
- the light and at the same time mechanically strong materials used in the bed system ensure easy maneuvering of the bed for transport. Laterally mounted rails make this possible Attachment of infusion pumps and at the head of a mobile oxygen device.
- An integrated scale allows daily, computer-aided weight documentation
- the receipt resp. the stabilization of vital functions has priority in every case.
- the extent of the movements in terms of time duration and extent of movement depends on the underlying diseases, the cardiovascular reactions, the respiratory situation and the requirements for an operation (for example, required immobilization of a limb after osteosynthesis of a fracture).
- CMICB Continuous moving intensive care bed
- the bed has a fail-safe computer module with an ergonomically easy-to-use input and output panel.
- the computer unit controls the corresponding movement and signaling functions of the bed.
- control information - eg data from the bed, weight measurements and result data on the movements performed - are returned to this computer unit.
- a connection to the other computer units is provided to surveillance monitors which provide the current monitoring data of the intensive care patients, such as blood pressure and heart rate or oxygen saturation to be able to immediately and automatically ensure an immediate stoppage of movement and positioning in an emergency situation in the event of an emergency.
- the data of the CMSI system can be accessed centrally; Alternatively, a printer can be connected to the CMSI computer.
- Basic module of the computer unit is a computer with a hard disk storage capacity for data documentation (for example, a medical record) of all selected basic and individual functions over time.
- the size of the hard disk depends on the volume of the software to be installed and a storage capacity to be calculated for data of the CMSI system in a usage period of 6 months.
- actual weight shows the current weight of the patient, which is automatically graphically and digitally registered via data memory.
- the current date (see FIG. 5) is shown and registered in the footer.
- control elements for tactile stimulation are described explicitly: a distinction is made between a "standard setup” and an “individual setup”.
- the monitor picture shows the control function "thermo system”.
- Thermosystem for the regulation of body temperature for the regulation of body temperature.
- thermoprobe e.g. rectally inserted thermoprobe
- the thermo system regulates the body temperature to the preselected number of degrees.
- thermo system Without feedback setting, the temperature of the thermo system can be controlled manually via the "individual setup" function. See Figure 48
- thermosystem shell of ultralight material (e.g., fiberglass) 2: anti-decubitus element 3: thermosystem
Abstract
The invention relates to a controllable hospital bed which has a plurality of positions and functions. Functions comprise, for example, a bedsore prophylaxis function, a vibration function, extremity movement functions and/or a weight-monitoring function. The positions and functions of the bed are controlled via a control unit and can also be configured. The bed can also have a sensor arrangement which transmits measured data to the control unit. The controllable hospital bed thus provides a multiplicity of functionalities which can relieve the burden on the hospital staff and which serve for the well-being of the patient.
Description
Steuerbares Krankenbett Steerable hospital bed
Die Erfindung betrifft ein steuerbares Krankenbett, ein Verfahren zur Steuerung eines steuerbaren Krankenbetts sowie ein Computerprogrammprodukt, das eine Steuerung für ein steuerbares Krankenbett implementiert.The invention relates to a controllable hospital bed, a method for controlling a controllable hospital bed and a computer program product which implements a control for a controllable hospital bed.
Krankenbetten sind beispielsweise für die stationäre Aufnahme von Patienten in Krankenhäusern bekannt. Ein solches Krankenbett weist ein Bettgestell auf, auf dem sich eine Matratze befindet. Durch mechanisches Verstellen des Bettgestells kann beispielsweise das Kopfteil des Bettes hochgestellt werden, was ein Anlehnen des Oberkörpers ermöglicht. Ebenso kann durch das Bettgestell beispielsweise das Fußteil der Matratze angehoben werden, so dass Blut aus den unteren Extremitäten, den Beinen, leichter Richtung Oberkörper fließen kann. Dies kahn beispielsweise nach einer Verletzung an einem Bein medizinisch sinnvoll sein. Ein solches mechanisches Krankenbett erfordert, dass eine Person, beispielsweise ein Pfleger oder eine Krankenschwester, die Einstellung des Krankenbetts vornimmt. Es ist hier beispielsweise wünschenswert, die Zeit, die das Krankenhauspersonal zur Einstellung eines mechanischen Krankenbettes
benötigt, zu verkürzen. Weiterhin ist es wünschenswert, die Kraftanstrengung, die für die Verstellung nötig ist, zu verringern.For example, hospital beds are known for inpatient hospitalization. Such a hospital bed has a bedstead on which a mattress is located. By mechanical adjustment of the bed frame, for example, the headboard of the bed can be raised, which allows leaning of the upper body. Likewise, for example, the foot part of the mattress can be raised by the bed frame so that blood can flow from the lower extremities, the legs, slightly towards the upper body. This can, for example, be medically useful after an injury to one leg. Such a mechanical bedside requires that a person, such as a carer or a nurse, make the adjustment of the hospital bed. For example, it is desirable here for the time that the hospital staff to hire a mechanical bedside needed to shorten. Furthermore, it is desirable to reduce the effort required for the adjustment.
Schwer kranke Patienten, insbesondere durch Schlaganfall oder Querschnittslähmung gelähmte Patienten, sind häufig in ihrer Beweglichkeit im Krankenbett extrem eingeschränkt. Dass sie überwiegend bewegungslos im Bett liegen hat zur Folge, dass sich die Auflagepunkte ihres Körpers auf der Oberfläche des Bettes nicht ändern. Für eine Änderung der Auflagepunkte wäre eine äußere Krafteinwirkung durch beispielsweise das Krankenhauspersonal erforderlich. An den Auflagepunkten des Körpers drückt ein Knochen auf die Haut, so dass diese komprimiert wird und so den Blutfluss in diesem Bereich einschränkt bzw. verhindert. Als Folge werden diese Auflagepunkte nicht mehr ausreichend mit Sauerstoff versorgt. Auf diese Art kann es zum Absterben von Gewebeteilen kommen. Dies ist als Dekubitus bekannt. Der Dekubitus kann sich infizieren und kann sogar bei Schwerkranken und somit abwehrgeschwächten Patienten zum Tode führen. Um dem Dekubitus vorzubeugen, müssen entsprechend gefährdete Patienten vom Krankenhauspersonal im Bett bewegt werden, damit sich die Auflageflächen häufiger ändern und so eine kontinuierliche Sauerstoffversorgung aller Gewebeteile gewährleistet ist. Es wäre wünschenswert, eine qualitativ hochwertige Vorsorge zum Vermeiden des Dekubitus automatisch durchzufüh- ren. In DE 100 01 687 A1 ist ein Krankenbett für die Dekubitusprophylaxe offenbart. Dabei wird ausgenutzt, dass ein Bewegen des Bettrahmens in verschiedene Positionen die Auftrittswahrscheinlichkeit eines Dekubitus verringert. Dabei ist der Bettrahmen auf vier hydraulisch beaufschlagbaren Arbeitszylindern gelagert. Mit diesen Zylindern ist der Bettrahmen so bewegbar, dass die Wahrscheinlich- keit des Auftretens eines Dekubitus verringert wird.Seriously ill patients, especially patients with paralysis due to stroke or paraplegia, are often extremely restricted in their mobility in the hospital bed. The fact that they lie mostly motionless in bed has the consequence that the contact points of her body do not change on the surface of the bed. For a change of the support points would be an external force by, for example, the hospital staff required. At the support points of the body, a bone presses on the skin so that it is compressed and thus restricts or prevents the blood flow in this area. As a result, these support points are no longer supplied with sufficient oxygen. This can lead to the death of tissue parts. This is known as pressure ulcers. The pressure ulcer can become infected and can even lead to death in seriously ill and thus immunocompromised patients. In order to prevent decubitus ulcers, patients at risk must be moved by the hospital staff in bed, so that the support surfaces change more frequently and so a continuous oxygenation of all tissue parts is guaranteed. It would be desirable to automatically carry out a high-quality precaution for the prevention of decubitus. DE 100 01 687 A1 discloses a hospital bed for decubitus prophylaxis. It is exploited that moving the bed frame in different positions reduces the probability of a decubitus. The bed frame is mounted on four hydraulically actuated working cylinders. With these cylinders, the bed frame is movable to reduce the likelihood of pressure sores.
Bei der Behandlung komatöser Patienten bildet der Erhalt der Vitalfunktionen einen Schwerpunkt. Der komatöse Patient befindet sich in einem immobilen Zustand und erfährt reduzierte Sinnesreizgebungen. Bewegung stellt jedoch für viele Funktionen des menschlichen Körpers einen grundlegenden Faktor dar. Die Funktionen beziehen sich dabei nicht nur auf die Muskulatur, sondern können beispielsweise auch Organfunktionen einschließen. Länger andauernde Immobili-
tät, wie sie insbesondere bei komatösen Patienten vorliegt, kann zu Arthrose, zu Inaktivitätsosteoporose, zu Veränderungen von Knorpeln und des Band- /Kapselapparates oder zu Muskelatrophie führen. In diesem Zusammenhang stellen Druck, Zug, Biegung und Torsion wichtige mechanische Reize mit struk- turerhaltender Wirkung für den Patienten dar. Weitere Folgen der Immobilität des komatösen Patienten sind beispielsweise die Steigerung des Thromboserisikos sowie der Ödemneigung oder das Verlernen von Bewegungsabläufen. Es wäre wünschenswert die Behandlung von komatösen Patienten durch die Bereitstellung geeigneter technischer Mittel zu verbessern.In the treatment of comatose patients, maintaining vital signs is a priority. The comatose patient is in an immobile state and experiences reduced sensory stimulation. Movement, however, is a fundamental factor in many functions of the human body. The functions are not only related to the musculature, but may also include, for example, organ functions. Longer-term real estate In particular, in patients with comatose disease, osteoarthritis, inactivity osteoporosis, changes in cartilage and the ligament / capsule apparatus, or muscle atrophy can all result. In this context, compression, tension, bending and torsion are important mechanical stimuli with structure-preserving effect for the patient. Further consequences of the immobility of the comatose patient are, for example, the increase in risk of thrombosis as well as the tendency to edema or the elimination of movement. It would be desirable to improve the treatment of comatose patients by providing appropriate engineering means.
Ausgehend von dem genannten Stand der Technik ist es Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung, ein steuerbares Krankenbett bereit zu stellen, dass das Krankenhauspersonal möglichst umfangreich entlasten und unterstützen kann. Insbesondere soll dabei eine Vielzahl von Funktionalitäten bereitgestellt werden.Based on the cited prior art, it is an object of the present invention to provide a controllable hospital bed that can relieve and support the hospital staff as extensively as possible. In particular, a variety of functionalities should be provided.
Die Aufgabe wird erfindungsgemäß gelöst mit einem steuerbaren Krankenbett, umfassend ein Bettgestell, das bewegbare Teile aufweist, mindestens einer Antriebseinheit für das Bewegen der bewegbaren Teile und/oder zum Fahren der bewegbaren Teile in bestimmte Positionen, mindestens eine Steuereinheit zum Steuern der mindestens einen Antriebseinheit und mindestens eine Speichereinheit zur Speicherung einer Vielzahl von bestimmten Positionen und Funktionen, wobei die bestimmten Positionen eine Schockposition, eine Herzposition, eine Zerebralposition, eine Sitzposition, eine Rückenposition, eine Wiederbelebungsposition und/oder eine horizontale Position umfassen, wobei die Funktionen ein kontinuierliches Bewegen von Extremitäten und/oder eines Rumpfes, eine Vibrationsfunktion, eine Druckgeschwürprophylaxefunktion, eine Auswahl von ver- schiedenen Positionen mittels einer schnellen und direkten Einstellung und/oder eine Gewichtskontrollfunktion umfassen, wobei die Steuereinheit eine Mehrzahl der bestimmten Positionen und Funktionen zum Auswählen bereitstellt.The object is achieved with a controllable hospital bed, comprising a bed frame, which has movable parts, at least one drive unit for moving the movable parts and / or for driving the movable parts in certain positions, at least one control unit for controlling the at least one drive unit and at least one storage unit for storing a plurality of particular positions and functions, the determined positions comprising a shock position, a cardiac position, a cerebral position, a sitting position, a back position, a resuscitation position, and / or a horizontal position, the functions including continuously moving extremities and / or a trunk, a vibration function, a pressure ulcer prophylaxis function, a selection of different positions by means of a quick and direct adjustment and / or a weight control function, wherein the control unit comprises a Meh provides the number of specific items and functions for selection.
Als Bettgestell wird ein Gestell verstanden, das beispielsweise eine Matratze hält, aber auch andere Vorrichtungen, die beispielsweise für das Halten von Extremi- täten eines Patienten vorgesehen sind, umfassen kann. Um beispielsweise die
Matratze oder genannte Vorrichtungen bewegen zu können, weist das Bettgestell bewegbare Teile auf. Ein solches bewegbares Teil kann beispielsweise eine bewegbare Kopfstütze sein. Die bewegbaren Teile des Bettgestells können über Antriebseinheiten bewegt werden und/oder in bestimmte Positionen gefahren werden. Die Antriebseinheit bzw. die Antriebseinheiten können elektrisch und/oder hydraulisch ausgestaltet sein. Beispielsweise kann ein Bettgestell Gelenke in dem Bereich des Knies und im Hüftbereich aufweisen und somit das Bettgestell in drei bewegbare Teile aufteilen. Ein Bewegen des unteren Teils um einen bestimmten Winkel sowie ein Bewegen des oberen Teils um einen be- stimmten Winkel kann das Bett aus einer Liegeposition in eine Sitzposition fahren. Eine solche definierte Einstellung der bewegbaren Teile kann als eine bestimmte Position, hier beispielsweise die Sitzposition, gespeichert werden. Um beispielsweise die Dekubitusprophylaxe vorzunehmen kann beispielsweise ein Bettrahmen gemäß einem vorgegebenen Beweg ungsprofil bewegt werden. Ein solches Bewegungsprofil kann durch vorgegebene Positionen sowie Zeitpunkte, zu denen das Bettgestell in die vorgegebene Position fährt, definiert werden. Eine solche Definition einer Druckgeschwürprophylaxefunktion kann ebenfalls gespeichert werden. Eine Steuereinheit kann die Antriebseinheiten dann so bewegen, dass das steuerbare Krankenbett in eine definierte Position fährt oder eine defi- nierte Funktion ausführt. Dabei greift die Steuereinheit auf eine Speichereinheit zurück, auf der eine Vielzahl von Positionen und Funktionen gespeichert sein kann. Über eine Benutzerschnittstelle stellt die Steuereinheit einem Benutzer eine Mehrzahl von bestimmten Positionen und Funktionen bereit. Bei der Steuereinheit handelt es sich vorzugsweise um eine elektronische Steuerung. Zusätz- lieh zu den Positionen und Funktionen, die ein Bewegen von bewegbaren Teilen über Antriebseinheiten nutzen, kann das steuerbare Bett auch weitere Funktionen, wie beispielsweise eine Gewichtskontrollfunktion, bereitstellen. Mit dieser Gewichtskontrollfunktion kann das Gewicht eines Patienten, der sich auf dem steuerbaren Krankenbett befindet, gemessen werden. Dann liefert ein entspre- chender Sensor die gemessene Gewichtsinformation an eine zentrale Steuereinheit. Von der Steuereinheit wird das gemessene Gewicht beispielsweise gespeichert oder zu einer Bildschirmausgabe weitergeleitet. Ebenso ist denkbar, eine Gewichtsmessreihe aufzunehmen und damit die Gewichtsentwicklung des Pa-
tienten wiederzugeben. Die Schockposition beschreibt eine Position, in der die Beine eines Patienten höher als der Rumpf liegen und der Rumpf höher als der Kopf. Die Arme weisen vorzugsweise leicht nach oben. Eine Herzposition beschreibt beispielsweise eine Position, bei der der Winkel zwischen Oberkörper und Oberschenkel größer als 90° ist sowie der Winkel zwischen Oberschenkel und Unterschenkel, an der Kniekehle gemessen, größer als 90° ist. Die Sitzposition unterscheidet sich von der Herzposition insbesondere dadurch, dass der Oberkörper weiter aufgerichtet ist. Die Zerebralposition beschreibt eine Position, in der der Patient im wesentlichen liegt, jedoch die Kniekehle leicht angewinkelt ist und der Oberschenkel gegenüber dem Oberkörper leicht angewinkelt ist. Die horizontale Position beschreibt eine Position, in der der Patient im Wesentlichen ganz ausgestreckt liegt. Die Rückenposition beschreibt eine Position, in der der Patient mit dem Rücken gerade liegt, die Beine angewinkelt sind und die Unterschenkel im Wesentlichen parallel zu dem Rücken liegen. Die Wiederbelebungs- position ist eine Position, in der das Bettgestell den Patienten ausgestreckt auf dem Rücken liegend möglichst tief Richtung Boden fährt. Die Mehrzahl von bestimmten Positionen und Funktionen umfasst mindestens zwei Positionen und mindestens eine Funktion, bevorzugt mindestens vier Positionen und mindestens zwei Funktionen, besonders bevorzugt mindestens 5 Positionen und mindestens 4 Funktionen.A bed frame is understood to be a frame which, for example, holds a mattress but may also comprise other devices which are provided, for example, for holding the extremities of a patient. For example, the To move mattress or said devices, the bed frame on movable parts. Such a movable part may for example be a movable headrest. The movable parts of the bed frame can be moved by drive units and / or moved into certain positions. The drive unit or the drive units can be designed electrically and / or hydraulically. For example, a bed frame can have joints in the area of the knee and in the hip area and thus divide the bed frame into three movable parts. Moving the lower part by a certain angle and moving the upper part by a certain angle can move the bed from a lying position to a sitting position. Such a defined setting of the movable parts can be stored as a specific position, here for example the sitting position. For example, to make decubitus prophylaxis, for example, a bed frame according to a predetermined movement profile can be moved. Such a movement profile can be defined by predetermined positions and times at which the bedstead moves to the predetermined position. Such a definition of pressure ulcer prophylaxis function can also be stored. A control unit can then move the drive units in such a way that the controllable hospital bed moves to a defined position or performs a defined function. In this case, the control unit accesses a memory unit on which a plurality of positions and functions can be stored. Through a user interface, the control unit provides a user with a plurality of specific positions and functions. The control unit is preferably an electronic controller. In addition to the positions and functions that utilize moving parts via drive units, the controllable bed can also provide other functions, such as a weight control function. With this weight control function, the weight of a patient who is on the controllable bedside can be measured. Then, a corresponding sensor supplies the measured weight information to a central control unit. The measured weight is stored by the control unit, for example, or forwarded to a screen display. It is also conceivable to record a weight measurement series and thus to determine the weight development of the to reproduce patients. The shock position describes a position in which the legs of a patient are higher than the trunk and the trunk is higher than the head. The arms preferably have slightly upwards. A cardiac position, for example, describes a position in which the angle between the upper body and thigh is greater than 90 °, and the angle between thigh and lower leg, measured at the popliteal fossa, is greater than 90 °. The sitting position differs from the heart position in particular in that the upper body is further erected. The cerebral position describes a position in which the patient lies substantially, but the popliteal fossa is slightly angled and the thigh is slightly angled relative to the upper body. The horizontal position describes a position in which the patient lies substantially completely outstretched. The back position describes a position in which the patient is lying with his back straight, the legs are angled and the lower legs are substantially parallel to the back. The resuscitation position is a position in which the bedstead extends the patient lying on his back as far as possible to the ground. The plurality of specific positions and functions comprises at least two positions and at least one function, preferably at least four positions and at least two functions, more preferably at least five positions and at least four functions.
Für die Dekubitusprophylaxe kann das steuerbare Krankenbett beispielsweise gekammerte Luftkissen aufweisen, die jeweils mit wechselndem Druck gefüllt werden. Der Druck der gekammerten Luftkissen kann dann über die Steuereinheit gesteuert werden.For decubitus prophylaxis, the controllable hospital bed may have, for example, chambered air cushions which are each filled with alternating pressure. The pressure of the chambered airbags can then be controlled via the control unit.
Die Vibrationsfunktion kann von der Steuerung so eingestellt werden, dass für die rechte Hand, die linke Hand, den rechten Fuß und den linken Fuß ein eigener Vibrationswert eingestellt werden kann. Das steuerbare Krankenbett kann so eingestellt werden, dass einzelne Gelenke wie z. B. das Hüftgelenk, das Kniegelenk, der Ellbogen, das Schultergelenk, um bestimmte Winkel, die einstellbar sind, bewegt werden.
Ein solches steuerbares Krankenbett lässt sich für Therapiezwecke, Diagnosezwecke und Mess- und Kontrollzwecke an dem Patienten einsetzen. Es kann somit den Komfort des Patienten vergrößern, das Krankenhauspersonal entlasten sowie Therapien unterstützen oder durchführen. Beispielsweise kann ein solches steuerbares Krankenbett einem komatösen Patienten sensorische Reize, wie beispielsweise taktile Reize, Bewegungsreize oder akustische Reize zufügen und somit bei der Behandlung von komatösen Patienten unterstützen bzw. die Behandlung verbessern. Spezifische Bewegungen bzw. spezifische Bewegungsmuster für die Extremitäten sowie die Zeitdauer oder zeitliche Abfolge der Bewegungsmuster für die Extremitäten kann für die Steuereinheit definiert sein, oder aber die entsprechenden Bewegungsmuster und Zeitdauern können der Steuereinheit eingegeben werden. Letzteres ermöglicht ein individuelles Einstellen der Bewegungsfunktionen. Ebenso sind die Bewegungen des Rumpfes und des Nackens bezüglich eines Bewegungsmusters und der zugehörigen Bewe- gungszeit einstellbar. Die zeitliche Dauer der jeweiligen Bewegungen einschließlich Anfangszeit und Endzeit eines Bewegungsmusters kann ebenso eingestellt werden. Ein Bewegungsmuster kann beispielsweise durch die Angabe einer maximalen Beugung eines Gelenkes genauer spezifiziert werden. In einer Weiterbildung der Erfindung weist das Bettgestell des steuerbaren Krankenbetts ein erstes bewegbares Teil zum Halten und Bewegen eines Kopf- und Rumpfbereiches eines Patienten und ein zweites, ein drittes, ein viertes und ein fünftes bewegbares Teil zum Halten und Bewegen jeweils einer Extremität des Patienten auf. Mit einem entsprechenden steuerbaren Krankenbett wird eine kontinuierliche passive Bewegung der vier Extremitäten und des Rumpfes ermöglicht. Auf diese Weise können auch taktile Reize vermittelt werden.The vibration function can be adjusted by the controller so that a separate vibration value can be set for the right hand, the left hand, the right foot and the left foot. The controllable hospital bed can be adjusted so that individual joints such. As the hip joint, the knee joint, the elbow, the shoulder joint to certain angles that are adjustable, to be moved. Such a controllable bedside can be used for therapeutic purposes, diagnostic purposes and measurement and control purposes on the patient. It can thus increase the comfort of the patient, relieve the burden on hospital staff and support or carry out therapies. For example, such a steerable bedside can impart sensory stimuli to a comatose patient, such as tactile stimuli, movement stimuli or auditory stimuli, thus assisting or improving the treatment of comatose patients. Specific movements or specific movement patterns for the extremities as well as the time duration or temporal sequence of the movement patterns for the extremities may be defined for the control unit, or the corresponding movement patterns and time periods may be input to the control unit. The latter allows an individual setting of the motion functions. Similarly, the movements of the trunk and neck are adjustable with respect to a movement pattern and the associated movement time. The time duration of the respective movements including start time and end time of a movement pattern can also be set. A movement pattern can be specified more precisely, for example, by specifying a maximum flexion of a joint. In a further development of the invention, the bed frame of the controllable hospital bed has a first movable part for holding and moving a head and trunk area of a patient and a second, a third, a fourth and a fifth movable part for holding and moving in each case a limb of the patient , With a corresponding controllable hospital bed a continuous passive movement of the four extremities and the trunk is made possible. In this way, tactile stimuli can be taught.
In einer Weiterbildung der Erfindung weist das steuerbare Krankenbett mindestens eine Sensoreinheit auf. Die Sensoreinheiten können dazu benutzt werden, Kontrollinformationen wie zum Beispiel Daten des Bettes, Gewichtsmessungen und/oder Ergebnisdaten über durchgeführte Bewegungen an die Steuereinheit zu übertragen. Diese Kontrollinformationen können auch anderen Überwachungseinheiten oder Computereinheiten bereitgestellt werden. Wird beispielsweise von einer Messeinheit oder von einer externen Überwachungseinheit, die beispiels-
weise Blutdruck, Herzfrequenz oder Sauerstoffsättigung misst, ein Notfall festgestellt, so kann dieses Notfallsignal der Steuereinheit übermittelt werden, worauf die Steuerung einen sofortigen Stillstand der Bewegung des Krankenbettes und eine Positionierung des Patienten in Notfalllage durchführt. Beispielsweise kön- nen Extremitäten und/oder der Rumpf mit Klettverschlüssen an beweglichen Teilen des Bettgestells befestigt werden. Dabei weisen die Klettverschlüsse Sensoren auf, die einen mangelhaften Verschluss anzeigen, wenn der Klettver- schluss nicht ordnungsgemäß verschlossen ist. Dieses Sensorsignal wird dann beispielsweise der Steuereinheit bereitgestellt, die daraufhin ein Warnsignal ausgeben kann.In a development of the invention, the controllable hospital bed has at least one sensor unit. The sensor units can be used to transmit control information such as bed data, weight measurements and / or result data to the control unit via performed movements. This control information may also be provided to other monitoring units or computer units. If, for example, a measuring unit or an external monitoring unit, the If blood pressure, heart rate or oxygen saturation is detected, an emergency is detected, then this emergency signal can be transmitted to the control unit, whereupon the control system carries out an immediate standstill of the movement of the patient bed and a positioning of the patient in emergency situation. For example, extremities and / or the torso can be fastened to mobile parts of the bedstead with hook-and-loop fasteners. In this case, the Velcro fasteners on sensors that indicate a faulty closure, if the hook and loop fastener is not properly closed. This sensor signal is then provided to the control unit, for example, which can then output a warning signal.
In einer Weiterbildung der Erfindung weist das steuerbare Krankenbett ein akustisches System zur Ausgabe akustischer Reize auf. Neben taktilen Signalen sind auch akustische Signale zur Reizgebung an einen komatösen Patienten geeignet. Beispielsweise können über die Steuereinheit die zeitliche Dauer von Hör- Signalen sowie die Lautstärke der Hörsignale, die das akustische System abgibt, von der Steuereinheit gesteuert und an der Steuereinheit eingestellt werden. Das akustische System weist beispielsweise einen Kopfhörer und einen Speicher für Tondaten auf. Die Steuereinheit kann dem Kopfhörer beispielsweise über eine drahtlose Verbindung die Tondaten bereitstellen. An der Steuereinheit können dann auch Lautstärkeregelungen sowie Zeitdauereinstellungen vorgenommen werden.In a development of the invention, the controllable hospital bed has an acoustic system for emitting acoustic stimuli. In addition to tactile signals, acoustic signals are also suitable for stimulating a comatose patient. By way of example, the control unit can control the duration of audible signals as well as the volume of audible signals emitted by the audible system by the control unit and adjust it at the control unit. The acoustic system has, for example, a headphone and a memory for sound data. The control unit may provide the headphone with the sound data via a wireless connection, for example. On the control unit can also be made volume controls and time settings.
In einer Weiterbildung der Erfindung weist das steuerbare Krankenbett ein Ther- mosystem zur Regulierung einer Körpertemperatur auf. Das Thermosystem kann beispielsweise über die Steuereinheit gesteuert werden. Der Steuereinheit kön- nen dann über eine Kommunikationsschnittstelle individuelle Einstellungen oder Standardeinstellungen, die für die Regulation der Körpertemperatur eines Patienten notwendig sind, mitgeteilt werden. Das Thermosystem kann beispielsweise auch eine Thermosonde aufweisen, die zur Messung der Körpertemperatur rektal an einem Patienten angelegt werden kann. Die Messung der Körpertemperatur wird dann der Steuereinheit bereitgestellt, die das Thermosystem steuert. Auf
diese Weise ist ein Regelkreis für die Körpertemperatur entstanden. Die Temperatur des Thermosystems kann auch manuell eingestellt werden.In a development of the invention, the controllable hospital bed has a thermosystem for regulating a body temperature. The thermal system can be controlled for example via the control unit. The control unit can then be informed via a communication interface of individual settings or standard settings that are necessary for the regulation of the body temperature of a patient. The thermosystem may, for example, also comprise a thermoprobe which can be applied rectally to a patient for measurement of body temperature. The measurement of body temperature is then provided to the control unit which controls the thermosystem. On this way, a body temperature control loop has been created. The temperature of the thermo system can also be set manually.
In einer Weiterbildung der Erfindung weist das steuerbare Krankenbett mindestens einen Notfall-Stop-Schalter auf. Ein solcher Notfall-Stop-Schalter dient dem Patienten oder beispielsweise dem Krankenhauspersonal, um bei unvorhergesehenen Notfällen das steuerbare Bett sofort abschalten bzw. stoppen zu können. Auf diese Weise wird die Sicherheit eines entsprechenden steuerbaren Bettes erhöht.In a development of the invention, the controllable hospital bed has at least one emergency stop switch. Such an emergency stop switch serves the patient or, for example, the hospital staff in order to be able to switch off or stop the controllable bed immediately in the event of unforeseen emergencies. In this way, the security of a corresponding controllable bed is increased.
Gemäß einer Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen steuerbaren Krankenbettes sind die Positionen und/oder die Funktionen individuell konfigurierbar. Die Positionen sind beispielsweise durch die Lage der verschiedenen beweglichen Teile definiert. Damit die Antriebseinheiten die beweglichen Teile in die definierten Positionen fahren können, greift das Steuergerät auf eine Speichereinheit zu, in der die entsprechenden Positionen gespeichert sind. Es kann nun sinnvoll sein, beispielsweise abhängig von der Größe des Patienten oder anderen Eigenarten des Patienten, die Definition der Position zu verändern. Ebenso kann es sinnvoll sein, weitere definierte Positionen hinzuzufügen. Das Ändern und Hinzufügen der Positionen werden hier durch Konfigurieren der Positionen beschrieben. Ebenso können Definitionen der Funktionen verändert werden oder neue Funktionen hinzugefügt werden. Beides ist im Begriff „Funktionen konfigurieren" enthalten.According to a development of the controllable hospital bed according to the invention, the positions and / or the functions are individually configurable. The positions are defined, for example, by the position of the various moving parts. So that the drive units can drive the moving parts into the defined positions, the control unit accesses a storage unit in which the corresponding positions are stored. It may now make sense, for example, depending on the size of the patient or other peculiarities of the patient to change the definition of the position. Similarly, it may be useful to add more defined positions. Changing and adding the positions are described here by configuring the positions. Likewise, definitions of the functions can be changed or new functions can be added. Both are in the term "Configure functions" included.
In einer Weiterbildung der Erfindung stellt das erfindungsgemäße steuerbare Krankenbett eine Alarmfunktion bereit. Beispielsweise können Körperteile des Patienten oder der Patient selbst an dem steuerbaren Bett fixiert werden. Das Lösen einer Fixierung kann über einen entsprechenden Sensor gemessen wer- den, und dieses Messsignal kann der Steuereinheit bereitgestellt werden. Löst sich die Fixierung ungewollt, so kann die Steuereinheit auf Basis des empfangenen Messsignals einen Alarm auslösen, der diesen Zustand angibt. Weitere Alarmfunktionen können auf dem Prinzip beruhen, dass Kontrollmechanismen oder Messeinheiten Signale an die Steuereinheit liefern, diese Signale von der
Steuereinheit ausgewertet werden und daraufhin ein entsprechender Alarm ausgelöst wird.In a further development of the invention, the controllable hospital bed according to the invention provides an alarm function. For example, body parts of the patient or the patient can be fixed to the controllable bed itself. The release of a fixation can be measured via a corresponding sensor, and this measurement signal can be provided to the control unit. If the fixation dissolves unintentionally, the control unit can trigger an alarm on the basis of the received measurement signal which indicates this state. Other alarm functions may be based on the principle that control mechanisms or measuring units supply signals to the control unit, these signals from the Control unit are evaluated and then a corresponding alarm is triggered.
In einer Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen steuerbaren Krankenbettes ist die Steuereinheit über einen Berührungsbildschirm bedienbar. Grundsätzlich ist jede Benutzerschnittstelle, beispielsweise Maus, Tastatur, Sprachsteuerung usw., für die Steuereinheit denkbar. Insbesondere die Verwendung eines Berührungsbildschirms, der mit einem Berührungsstift bedienbar ist, ist besonders vorteilhaft, da hygienische Anforderungen in einem Krankenhaus gut erfüllt werden können. Die Benutzerschnittstelle kann so ausgestaltet sein, dass für viele der Positionen und Funktionen, deren Definitionen in der Speichereinheit gespeichert sind, mit einer eigenen Schaltfläche einzeln ausgewählt werden können, d. h. ein einzelnes Drücken auf einer Bedienoberfläche genügt, um das steuerbare Bett in eine ausgewählte Position zu fahren bzw. eine ausgewählte Funktion auszuführen.In a further development of the controllable hospital bed according to the invention, the control unit can be operated via a touch screen. In principle, any user interface, for example mouse, keyboard, voice control, etc., is conceivable for the control unit. In particular, the use of a touchscreen operable with a touch pen is particularly advantageous because hygienic requirements can be well met in a hospital. The user interface may be configured such that for many of the positions and functions whose definitions are stored in the memory unit can be individually selected with a separate button, i. H. a single press on a user interface is sufficient to drive the controllable bed to a selected position or to perform a selected function.
In einer Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen steuerbaren Krankenbetts weist das steuerbare Krankenbett mindestens eine Kommunikationsschnittstelle auf. Diese Kommunikationsschnittstelle kann dazu dienen, aufgenommene Messwerte wie beispielsweise das Gewicht des Patienten zu verschiedenen Zeiten an eine Rechnereinheit weiterzuleiten. Bei der Kommunikationsschnittstelle kann es sich beispielsweise um eine USB-Schnittstelle oder um eine Schnittstelle für einen Drucker handeln.In a development of the controllable hospital bed according to the invention, the controllable hospital bed has at least one communication interface. This communication interface can be used to forward recorded measured values, such as the weight of the patient, to a computer unit at different times. The communication interface may be, for example, a USB interface or an interface for a printer.
In einer Weiterbildung der Erfindung sind die Antriebseinheiten individuell steuerbar. Dadurch ist es beispielsweise möglich, dass die beweglichen Teile in jede beliebige Stellung, die vom Nutzer gewünscht ist, gefahren werden können.In a development of the invention, the drive units are individually controllable. This makes it possible, for example, that the moving parts in any position that is desired by the user, can be driven.
In einer Weiterbildung der Erfindung stellt die Steuereinheit eine Timingfunktion bereit. Mittels einer Timingfunktion können beispielsweise Funktionen nur zu bestimmten Tageszeiten durchgeführt werden, oder nach einer gewissen Zeit können Funktionen automatisch abgestellt werden.
In einer Weiterbildung werden in einem Rumpfbereich des steuerbaren Krankenbettes Materialien verwendet, die eine Röntgenmessung im Wesentlichen nicht beeinträchtigen.In a development of the invention, the control unit provides a timing function. By means of a timing function, for example, functions can be performed only at certain times of the day, or after a certain time functions can be turned off automatically. In one development, materials are used in a fuselage area of the controllable hospital bed which essentially do not impair an X-ray measurement.
Insbesondere bei Röntgenmessungen im Rumpfbereich von Menschen, die sich nicht oder nur eingeschränkt bewegen können, ist es wünschenswert, dass für die Röntgenmessung kein Umzug des Patienten von seinem Krankenbett zu einer anderen Liege nötig ist. Durch die Verwendung o. g. Materialien können Röntgenmessungen durchgeführt werden, ohne dass der Patient sein Bett verlassen muss.In particular, in X-ray measurements in the trunk area of people who can not or only partially move, it is desirable that for the X-ray measurement, no move of the patient from his bedside to another couch is needed. By using o. G. Materials can be X-ray measurements performed without the patient having to leave his bed.
Gemäß einem weiteren Aspekt der Erfindung umfasst ein Verfahren zur Steuerung eines erfindungsgemäßen Krankenbetts mindestens einen der folgenden Schritte:According to a further aspect of the invention, a method for controlling a hospital bed according to the invention comprises at least one of the following steps:
Fahren des steuerbaren Krankenbettes in eine ausgewählte Position, nachdem die ausgewählte Position konfiguriert und ausgewählt ist, - Durchführen einer ausgewählten Funktion des steuerbaren Krankenbetts, nachdem die ausgewählte Funktion konfiguriert und ausgewählt ist,Moving the steerable bed to a selected position after the selected position is configured and selected, - performing a selected function of the steerable bed after the selected function is configured and selected;
Durchführen von Kontrollfunktionen und Bereitstellen eines Alarmsignals.Performing control functions and providing an alarm signal.
Die Kontrollfunktionen können beispielweise die Messung des Gewichts eines Patienten oder die Überprüfung einer Fixierung bedeuten. Das Konfigurieren von Positionen bzw. das Konfigurieren von Funktionen kann dadurch geschehen sein, dass bestimmte Positionen bereits in einem Speicher, auf den die Steuerung zugreifen kann, gespeichert sind. Es kann ebenfalls bedeuten, dass bestimmte Positionen oder Funktionen von einem Nutzer, beispielsweise von einem Patienten oder einem Krankenhausmitarbeiter, in die Steuereinheit eingegeben werden und von dieser auf einen Speicher abgelegt werden.The control functions may mean, for example, measuring the weight of a patient or checking a fixation. The configuration of functions or the configuration of functions can be done by having certain positions already stored in a memory that the controller can access. It may also mean that certain positions or functions are entered by a user, for example, a patient or a hospital employee, in the control unit and stored by this on a memory.
Gemäß einem weiteren Aspekt der Erfindung ist in einem Computerprogrammprodukt eine Steuerung für ein erfindungsgemäßes Krankenbett implementiert.
Die Steuereinheit kann beispielsweise als Software in einem Prozessor realisiert sein. Ein solches Computerprogrammprodukt kann beispielsweise über eine Kommunikationsschnittstelle an dem steuerbaren Krankenbett auf einem Prozessor, der zu dem steuerbaren Krankenbett gehört, geladen werden.According to a further aspect of the invention, a controller for a hospital bed according to the invention is implemented in a computer program product. The control unit may, for example, be implemented as software in a processor. Such a computer program product can be loaded, for example, via a communication interface at the controllable hospital bed on a processor which belongs to the controllable hospital bed.
Im folgenden wird die Erfindung anhand von Ausführungsbeispielen mit Bezug auf die Figuren 1 bis 4 näher erläutert.In the following the invention with reference to embodiments with reference to Figures 1 to 4 will be explained in more detail.
Fig. 1 zeigt in schematischer Darstellung ein erfindungsgemäßes steuerbares Krankenbett 1. Eine Steuereinheit 4 ist über einen Berührungsbildschirm 7 bedienbar. Die Steuereinheit 4 kann auf eine Speichereinheit 5 zugreifen. Mit einem Notfallschalter 6 kann das steuerbare Bett 1 jederzeit sofort abgeschaltet werden. Die Steuereinheit 4 kann eine Antriebseinheit 3 steuern. Die Antriebseinheit 3 dient dem Bewegen von beweglichen Teilen eines Bettgestells 2. An dem Bettgestell sind Messeinheiten 9 angebracht, die Messwerte an die Steuereinheit 4 liefern. Messwerte können beispielsweise Gewichtsmessungen sein. Erhält die Steuereinheit 4 über den Berührungsbildschirm 7 den Befehl, das Bett 2 in eine vorgegebene Position zu fahren, beispielweise in eine Sitzposition, dann lädt es die entsprechenden Daten zu der gewünschten Position aus der Speichereinheit 5. Auf Basis der geladenen Daten steuert die Steuereinheit 4 die Antriebseinheit 3 so, dass die Teile des Bettgestells in die vordefinierte und ausgewählte Position fahren. Ebenso kann über den Berührungsbildschirm eine Position ausgewählt werden. Die Daten der ausgewählten Funktion werden von der Steuerung auf der Speichereinheit 5 geladen. Entsprechend den geladenen Daten werden die Antriebseinheiten so gesteuert, dass das Bettgestell 2 bzw. das steuerbare Krankenbett 1 die gewünschte Funktion ausführt. Ebenso können die Messwerte der Messeinheit 9 in der Steuereinheit 4 verarbeitet werden. Ein Ergebnis dieser Verarbeitung wird beispielsweise über die Kommunikationsschnittstelle 8 an einen Rechner oder einen Drucker ausgegeben.1 shows a schematic illustration of an inventive controllable hospital bed 1. A control unit 4 can be operated via a touch screen 7. The control unit 4 can access a memory unit 5. With an emergency switch 6, the controllable bed 1 can be switched off immediately at any time. The control unit 4 can control a drive unit 3. The drive unit 3 is used to move moving parts of a bed frame 2. Measuring units 9 are provided on the bed frame, which supply measured values to the control unit 4. Measured values can be, for example, weight measurements. Receives the control unit 4 via the touch screen 7 command to drive the bed 2 in a predetermined position, for example, in a sitting position, then it loads the corresponding data to the desired position from the memory unit 5. Based on the loaded data control unit 4 the drive unit 3 so that the parts of the bedstead drive in the predefined and selected position. Likewise, a position can be selected via the touch screen. The data of the selected function is loaded on the storage unit 5 by the controller. According to the loaded data, the drive units are controlled so that the bed frame 2 or the controllable hospital bed 1 performs the desired function. Likewise, the measured values of the measuring unit 9 in the control unit 4 can be processed. A result of this processing is output, for example, via the communication interface 8 to a computer or a printer.
Fig. 2 zeigt einen Berührungsbildschirm 7 der als Benutzerschnittstelle des steuerbaren Krankenbetts verwendet wird. Er weist Funktionalitäten auf, die durch Berühren eines entsprechend gekennzeichneten Teils einer Berührfläche
10 ausgewählt werden können Die Beruhrflache weist einen Auswahlbereich für eine Bewegungseinrichtung 11 , für eine Vibrationseinrichtung 12, für aktuelle Einstellungen 13, für eine Druckgeschwurprophylaxe 14, für ein akustisches System 29, für ein Thermosystem 30 und für eine Systemkontrolle 16 auf Ein Verlust einer Fixierung wird in einem Alarmbereich 15 angezeigt Diese Auswahl- bereiche dienen der Auswahl einer Einnchtungsfunktionalitat Weitere Auswahl- bereiche sind ein Auswahlbereich für einen Notfall-Stop 17, für eine Schockposi- tion 18, für eine Herzposition 19, für eine Zerebralposition 20, für eine Sitzpositi- on 21 , für eine Ruckenposition 22, für eine Wiederbelebungsfunktion 23 und für eine horizontale Position Weiterhin ist ein Auswahlbereich für eine Gewichts- messfunktion 25 und ein OK-Bereich 26 vorhanden Ein manuelles Steuern eines steuerbaren Krankenbettes wird über Pfeile 27 und 28 zur Einstellung der Bettposition ermöglicht Durch Beruhren der Auswahlbereiche fuhrt eine Steuerung eines steuerbaren Krankenbetts die ausgewählte Funktionalität aus Wird eine Einnchtungsfunktionalitat gewählt, wird der Beruhrungsbildschirm ein entsprechendes Einπchtungsmenu anzeigen, in dem weitere Eingaben getätigt werden könnenFig. 2 shows a touch screen 7 which is used as the user interface of the controllable hospital bed. It has functionalities by touching a correspondingly marked part of a contact surface The touch surface has a selection area for a movement device 11, for a vibration device 12, for current settings 13, for pressure ulcer prophylaxis 14, for an acoustic system 29, for a thermosystem 30 and for a system control 16 to a loss of a fixation displayed in an alarm area 15 These selection areas are used to select a dwell function. Further selection areas are a selection area for an emergency stop 17, for a shock position 18, for a heart position 19, for a cerebral position 20, for a sitting position 21, for a jerk position 22, for a resuscitation function 23 and for a horizontal position. Furthermore, there is a selection area for a weighting function 25 and an OK area 26. Manual control of a controllable hospital bed is enabled via arrows 27 and 28 for adjusting the bed position By touching the Au When a control panel of a controllable hospital bed executes the selected functionality, if an indoor functionality is selected, the touch screen will display a corresponding menu for entering further entries
Fig 3 zeigt einen Patienten 35, der auf bewegbaren Teilen eines Bettgestells liegt bzw an diesen fixiert ist Bei den bewegbaren Teilen handelt es sich um ein erstes bewegbares Teil 36 zum Bewegen eines Kopf- und Rumpfbereiches eines Patienten 35 und um ein zweites bewegbares Teil 31 , ein drittes bewegbares Teil 32, ein viertes bewegbares Teil 33 und ein fünftes bewegbares Teil 34 Die bewegbaren Teile 31 bis 34 dienen dem Bewegen der vier Extremitäten des Patienten Die fünf dargestellten bewegbaren Teile können über Antriebseinheiten bewegt werden Durch eine geeignete Steuerung der Antπebseinheiten können bestimmte Funktionen und Bewegungsmuster ausgeführt werden So kann beispielsweise durch geeignetes Bewegen des bewegbaren Teils 33 ein Beugen des rechten Ellbogens um einen bestimmten Winkel erreicht werden3 shows a patient 35 lying on or fixed to movable parts of a bed frame. The movable parts are a first movable part 36 for moving a head and trunk area of a patient 35 and a second movable part 31, a third movable part 32, a fourth movable part 33 and a fifth movable part 34 The movable parts 31 to 34 serve to move the four extremities of the patient The five illustrated movable parts can be moved by drive units By suitable control of the anti-taching units certain functions can be performed and movement patterns are performed. Thus, for example, by appropriately moving the movable member 33, bending of the right elbow can be achieved by a certain angle
Fig 4 zeigt schematisch einige Teile des steuerbaren Krankenbetts Das Schema zeigt eine Schale 41 aus ultraleichtem Material, z B Glasfaser, auf der ein Anti-FIG. 4 schematically shows some parts of the controllable hospital bed. The diagram shows a shell 41 made of ultralight material, for example glass fiber, on which an anti-bacterial
Dekubituselement 42, das gekammerte Luftkissen aufweist, angeordnet ist Em
Thermosystem 43 ist seitlich an dem Anti-Dekubituselement angeordnet. Eine wasserdichte Matratzenauflage 44 dient dazu, zu vermeiden, dass Flüssigkeiten von einer Matratze zu dem Thermosystem 3 oder dem Anti-Dekubituselement gelangen. Ein Teleskoparmsystem 5 dient der Einstellung von Abmessungen des Bettes, so dass sich das Bett an verschiedene Patientengrößen anpassen kann. Unterhalb des ersten bewegbaren Teils 30 zum Bewegen eines Kopf- und Rumpfbereiches ist eine Kassettenhalterung verschiebbar angeordnet. Diese Kassettenhalterung dient der Aufnahme von Röntgenaufnahmen der Lunge oder des Bauchraumes.Decubitus element 42, which has chambered air cushion, is arranged Em Thermosystem 43 is arranged laterally on the anti-decubitus element. A waterproof mattress pad 44 serves to prevent liquids from getting from a mattress to the thermal system 3 or the anti-decubitus element. A telescoping arm system 5 adjusts dimensions of the bed so that the bed can accommodate different patient sizes. Below the first movable part 30 for moving a head and trunk area, a cassette holder is slidably disposed. This cassette holder is used to record x-rays of the lungs or abdomen.
Des Weiteren zeigen Figuren 5 bis 62 Screen Shots des erfindungsgemäßen Systems.Furthermore, FIGS. 5 to 62 show screen shots of the system according to the invention.
Im Gegensatz zu Systemen des Standes der Technik bestimmt der Gegenstand des Anspruchs 1 , dass es sich um ein Krankenbett handelt - und nicht wie in WO 2006/061834 A2 um eine Wellness-vorrichtung. Ferner ist gemäß Anspruch 1 definiert, dass die Positionen und die Funktionen individuell konfigurierbar sind. Nutzer des Krankenbetts ist nicht die im Bett liegende Person, sondern das den im Bett liegenden Patienten therapierende medizinische Fachpersonal, das das Krankenbett zur Erfüllung seines medizinischen Auftrags für den Patienten nutzt. Das Merkmal „Krankenbett" reflektiert somit , (i) dass medizinisch-therapeutische Zwecke im Vordergrund stehen und (ii) dass die Behandlung eines medizinischen Patienten einer individuellen Voreinstellung des Krankenbetts durch medizinisches Fachpersonal bedarf, und nicht wie in WO 2006/061834 A2 automatisch oder nach besonderen Vorlieben der im Bett liegenden Person erfolgen kann und (iii) dass diese Einstellung durch medizinisches Fachpersonal vorzu- nehmen ist. In WO 2006/061834 A2 kann die im Bett liegende Person (der dortige Verwender) selbst nur aus einer Vielzahl von vorbestimmten Übungen, Positionen und Funktionen eine ihm geeignet erscheinende aufrufen, um seinen Wellnesszustand zu erhöhen.In contrast to prior art systems, the subject-matter of claim 1 determines that it is a hospital bed - and not, as in WO 2006/061834 A2, a wellness device. It is further defined according to claim 1 that the positions and the functions are individually configurable. The user of the hospital bed is not the person lying in bed, but the medical specialist who treats the bedside patient who uses the bedside for the fulfillment of his medical order for the patient. The feature "bedside" thus reflects (i) that medical-therapeutic purposes are in the foreground and (ii) that the treatment of a medical patient requires an individual presetting of the sickbed by medical professionals, and not automatically or as in WO 2006/061834 A2 and (iii) that this adjustment is to be carried out by a healthcare professional In WO 2006/061834 A2, the person lying in bed (the user there) can only himself from a large number of predetermined exercises , Positions and functions call him appear appropriate to increase his wellness state.
Der Gegenstand des Anspruches 1 hingegen richtet sich an die speziellen medi- zinischen Anforderungen eines steuerbaren Krankenbetts, welches das medizini-
sche Fachpersonal bei der Therapie und bei der medizinischen Behandlung des Patienten unterstützt. Bei vollständig oder im Wesentlichen immobilen Patienten und insbesondere bei Komapatienten ist eine Aufgabe des medizinischen Betts die Unterstützung der Aufrechterhaltung von Vitalfunktionen und der Vermeidung (oder zumindest: der Verminderung) von Lagerungsschäden, die andernfalls infolge der immobilen Lagerung des Patienten eintreten können. So ist das steuerbare Krankenbett gemäß Anspruch 1 insbesondere geeignet, Patienten im künstlichen oder krankheitsbedingten Koma zu unterstützen, indem der Patient nicht starr und bewegungslos im Bett liegt, sondern mit Hilfe des erfindungsge- mäßen steuerbaren Krankenbettes (i) eine optimierte Lagerung, (ii) unterschiedliche Bewegungstherapien, (iii) unterschiedliche sensorische Therapien mit taktilen, olefaktorischen oder akustischn Reizen und (iv) Rehabilitationsmaßnahmen erhalten kann, wobei das medizinische Personal entsprechend entlastet wird. Dadurch werden sämtliche neurologische und moto- rische Funktionen unterstützt und somit auch bei längerer Immobilität eines Patienten sowie im Koma gefördert. Das erfindungsgemäße steuerbare Krankenbett gewährleistet einen möglichst weitgehend natürlichen Status der wesentlichen Körperfunktionen auch in der Situation des Komas zu gewährleisten, wobei die wesentlichen Körperfunktionen diejenigen sind, die Tag für Tag zum Einsatz kommen und ohne die kein normales Leben möglich wäre. Das steuerbare Krankenbett ermöglicht nicht nur die Applikation zahlreicher therapeutischer und rehabilitierender Funktionen am Patienten, sondern erlaubt auch deren programmierten zeitlichen Ablauf in einem den natürlichen Abläufen vergleichbaren Rhythmus. Dies bedeutet zum Beispiel die Einhaltung eines Tag-/Nachtrhythmus von Bewegung unter Berücksichtigung von Schlaf- und Ruhephasen, von Erholungsphasen nach der (passiven) körperlichen Anstrengung und damit die Vermeidung von Überbelastungen und Einhaltung von Ruhephasen nach den Malzeiten. Durch die Verwendung des steuerbaren Krankenbettes werden der natürliche Lebensrhythmus und die naturgemäßen, im alltäglichen Leben unbewusst oder verborgen ablaufenden Reaktionen berücksichtigt.The subject matter of claim 1, on the other hand, is directed to the special medical requirements of a controllable hospital bed, which assisted with the therapy and medical treatment of the patient. In fully or substantially immobile patients, and especially coma patients, a task of the medical bed is to help maintain vital signs and prevent (or at least reduce) storage damage that may otherwise occur as a result of the patient's immobile storage. Thus, the controllable bedside according to claim 1 is particularly suitable to assist patients in artificial or disease-related coma by the patient is not rigid and motionless in bed, but with the aid of the present invention controllable hospital bed (i) optimized storage, (ii) different movement therapies, (iii) different sensory therapies with tactile, olefaktorischen or akustischn stimuli and (iv) rehabilitation measures can be obtained, whereby the medical staff is relieved accordingly. As a result, all neurological and motor functions are supported and thus promoted even with prolonged immobility of a patient and in coma. The controllable hospital bed according to the invention ensures a largely natural status of essential body functions to ensure even in the situation of the coma, the essential body functions are those that are used day after day and without which no normal life would be possible. The controllable hospital bed not only allows the application of numerous therapeutic and rehabilitative functions on the patient, but also allows their programmed time sequence in a rhythm comparable to the natural processes. This means, for example, adhering to a day / night rhythm of movement, taking into account sleep and rest periods, recovery phases after (passive) physical exertion and thus avoiding overloading and observing resting periods after meals. The use of the controllable hospital bed takes into account the natural rhythm of life and the natural, subconscious or hidden reactions in everyday life.
Ähnliches gilt auch für die neurologischen Funktionen des Menschen. Der Komapatient ist nicht allein in der Lage zur Wahrnehmung, Bewegung und komplexem
Verknüpfen neurophysiologischer Funktionen, so dass das steuerbare Krankenbett ihn unterstützt, auch diese passiv zu vermitteln. Dazu stellt das steuerbare Krankenbett eine Reihe von möglichen Sensorikmodulen für taktile, olfaktorische oder akustische Reize zur Verfügung.The same applies to the neurological functions of humans. The coma patient is not alone capable of perception, movement and complex Linking neurophysiological functions, so that the controllable hospital bed supports him, even this passively convey. For this purpose, the controllable hospital bed provides a number of possible sensor modules for tactile, olfactory or acoustic stimuli.
Aufgrund der medizinisch hoch komplexen Zusammenhänge zwischen den unterschiedlichen Körperfunktionen von in ihrer Mobilität eingeschränkten Patienten und insbesondere von Komapatienten, ist eine individualisierte Behandlung der Patienten erforderlich. So ist das System gemäß WO 2006/061834 A2 in keinster Weise geeignet, den komplexen Anforderungen einer medizinischen Behandlung von in ihrer Mobilität eingeschränkten Patienten oder von Komapatienten gerecht zu werden. WO 2006/061834 A2 bezieht sich lediglich auf eine Unterstützung der selbständigen Wellnessbehandlung von älteren oder anderweitig bewegungseingeschränkten Menschen, um sie insbesondere zu motivieren, ihren Körper zu trainieren. Die standardisierten Programme und Funktionen der Entgegenhaltung WO 2006/061834 A2 wären jedoch nicht für die medizinische Behandlung von in ihrer Mobilität eingeschränkten oder gar von Komapatienten geeignet, vielmehr würde eine solche Selbstanwendung automatisierter Vorgänge die Gefahr schwerer medizinischer Schäden nach sich ziehen, da sie ohne jegliche ärztliche Überwachung und Individualisierung auf den Patienten - „automatisch" - ange- wendet werden.Due to the medically highly complex relationships between the different body functions of mobility-impaired patients, and in particular coma patients, an individualized treatment of patients is required. Thus, the system according to WO 2006/061834 A2 is in no way suitable for meeting the complex requirements of medical treatment of patients whose mobility is limited or of coma patients. WO 2006/061834 A2 relates only to support for the independent wellness treatment of elderly or otherwise movement-restricted people, in particular to motivate them to train their body. However, the standardized programs and functions of the document WO 2006/061834 A2 would not be suitable for the medical treatment of mobility impaired or even of coma patients, but such a self-application of automated processes would entail the danger of serious medical damage, since they would be without any medical supervision and individualization to the patient - "automatically" - be used.
Auch Dokument DE 196 03 318 A1 offenbart nicht, dass Positionen und/oder Funktionen individuell konfigurierbar sind. Vielmehr ist explizit bestimmt, dass mittels der Kontrollbox für das Pflegepersonal nur vorbestimmte Bettstellungen und betttypenspezifische Betriebsarten abgerufen werden können. Die abgespei- cherten Daten sind also betttypenspezifisch, nicht jedoch patienten- individuell. Ebenso fehlt eine Absicherung der Einstelländerung, die sicherstellt, dass nur die vom medizinischen Personal vorgegebenen Einstellungen berücksichtigt werden und nicht durch versehentliche oder absichtliche manipulative Einstellungen seitens des Patienten oder von Dritten für den individuellen Patienten möglicher- weise schädliche Funktionen des Krankenbetts aufgerufen werden. Das System der DE 196 03 318 A1 ist folglich ebenfalls nicht geeignet für einen Komapatien-
ten verwendet zu werden. Die in der DE 196 03 318 A1 offenbarten Positionen und Funktionen sind nicht geeignet, um die wesentlichen Vitalfunktionen eines Komapatienten therapeutisch und in der Rehabilitation zu fördern und zu erhalten.Also document DE 196 03 318 A1 does not disclose that positions and / or functions are individually configurable. Rather, it is explicitly determined that only predetermined bed positions and bed type-specific operating modes can be retrieved by means of the nurse control box. The stored data are thus bed type-specific, but not patient-specific. Likewise, there is no safeguarding of the change in setting, which ensures that only the settings prescribed by the medical staff are taken into account and that potentially harmful functions of the sickbed are not called up by the patient or by third parties for accidental or intentional manipulative adjustments. The system of DE 196 03 318 A1 is therefore also not suitable for a Komapatien- to be used. The positions and functions disclosed in DE 196 03 318 A1 are not suitable for promoting and maintaining the essential vital functions of a coma patient therapeutically and in rehabilitation.
Eine Individualisierung des Steuerprogramms, welche durch einen Arzt konfigurierbar ist, ist nicht in DE 83 04 560 U1 offenbart. DE 83 04 560 U1 offenbart lediglich, dass ein Steuerorgan mit Mehrfach-oder Einhebel-bedienung auch durch einen Therapeuten bedient werden kann. Dies entspricht jedoch nicht der Ausgestaltung eines steuerbaren Krankenbettes, in der die Positionen und/oder die Funktionen der (elektronischen) Steuereinheit individuell konfigurierbar sind. Auch bei DE 83 04 560 U1 fehlt die Fokussierung auf eine vom medizinischen Fachpersonal für den je in seiner Mobilität eingeschränkten jeweiligen Patienten individuell angeordnete Therapie zur Unterstützung, Therapie und Rehabilitation von Vitalfunktionen. Ebenfalls fehlt in DE 83 04 560 U1 die spezielle Sensorik für Komapatienten.An individualization of the control program, which is configurable by a physician, is not disclosed in DE 83 04 560 U1. DE 83 04 560 U1 merely discloses that a control element with multiple or single lever operation can also be operated by a therapist. However, this does not correspond to the embodiment of a controllable hospital bed in which the positions and / or the functions of the (electronic) control unit are individually configurable. DE 83 04 560 U1 also lacks the focus on a therapy individually arranged for the support, therapy and rehabilitation of vital functions by a medical specialist for the respective patient who is ever limited in his mobility. Also missing in DE 83 04 560 U1 the special sensors for coma patients.
Im Folgenden werden Ausführungsformen der Erfindung beschrieben:Hereinafter, embodiments of the invention will be described:
Medizinisches RoboterbettsystemMedical robot bed system
Das medizinische Roboterbettsystem besteht aus drei Komponenten:The robotic medical bed system consists of three components:
1. Die Information / Softwarekomponente 2. Die Elektronikkomponente1. The information / software component 2. The electronic component
3. Die Hardware.3. The hardware.
Die Basis des Systems besteht aus fünf Komponenten, welche verlängert oder verkürzt werden können wie ein Teleskop. Jede Komponente besteht aus mehreren beweglichen Elementen wie eine Raupe.The basis of the system consists of five components, which can be extended or shortened like a telescope. Each component consists of several moving elements like a caterpillar.
Das Material hat ein geringes Gewicht, zum Beispiel Glasfaser oder hartes synthetisches Plastik (ein Metall wird für die Rumpfkomponente nicht verwendet, um die Möglichkeiten von Röntgenstrahlen zu bewahren).
Eine maximale Körperlänge von 210 Zentimeter und ein maximales Körpergewicht von 180 Kilogramm sollte berücksichtigt werden.The material is lightweight, for example fiberglass or hard synthetic plastic (a metal is not used for the trunk component to preserve the possibilities of X-rays). A maximum body length of 210 centimeters and a maximum body weight of 180 kilograms should be considered.
Monitormonitor
Ein Touch Screen Monitor mit einem Touchstift (nicht durch einen Finger wegen der klinischen Hygieneannahemen); Fixierung des Stiftes auf der rechten Seite des Monitorgehäuses.A touch screen monitor with a touch pen (not by a finger due to clinical hygiene issues); Fixation of the pin on the right side of the monitor housing.
- Auf einer Seite des Monitorgehäuses: An/Ausschalter- On one side of the monitor housing: On / Off switch
- Anschluss für einen Drucker- Connection for a printer
- USB Anschluss- USB connection
- Leistungsschalter- Circuit breaker
- Hard disc (beispielsweise 20 Megabyte)- Hard disc (for example, 20 megabytes)
- im Allgemeinen: Verändern der Knopffarbe durch Drücken beziehungsweise Aktivieren- in general: change the button color by pressing or activating
- „Zurück" Mittel, um zum vorigen Bild zurückzukehren- "Back" means to return to the previous picture
- „Menü" Mittel, um zurück zu dem Hauptbildschirmbild zu gehen- "menu" means to go back to the main screen
- Die Farbe der Knöpfe und des Monitors kann natürlich verändert werden- The color of the buttons and the monitor can of course be changed
- Im Falle eines Alarmes: Popup und unterschiedliche akustische Geräusche- In case of an alarm: popup and different acoustic sounds
- Sprachfeedback eines gewählten Inhaltes (wie ein Navigationssystem)- Voice feedback of a selected content (like a navigation system)
- Bildschirmschoner- Screensaver
- Animationsintro- Animation intro
Hinzufügen einer „Hilfe" Funktion, wo immer es erforderlich ist.
Siehe Figur 5Add a "help" function wherever it is needed. See Figure 5
„Medizinisches Roboterbettsystem":"Medical Robot Bed System":
Login Name: VerwendernameLogin Name: Username
Sprache: Englisch, Chinesisch, Deutsch, Französisch, Spanisch, Russisch, Griechisch, Türkisch, Polnisch...Language: English, Chinese, German, French, Spanish, Russian, Greek, Turkish, Polish ...
Datum: automatisches Datieren durch Anschalten des Monitors; automatischer Zeit (Funkzeit) im HintergrundDate: automatic dating by turning on the monitor; automatic time (radio time) in the background
HauptmonitorbildMain monitor image
O. K. -Knopf nur fürO. K. button only for
- Notstop- emergency stop
- Schockposition, Herzposition, Zerebralposition, Sitzposition, Rückenposition, Reanimationsposition und Horizontalposition, Gewicht.- Shock position, heart position, cerebral position, sitting position, back position, resuscitation position and horizontal position, weight.
Die Hauptfunktionen des Bettsystems sind auf dem Hauptmonitor gezeigt:The main functions of the bed system are shown on the main monitor:
1. Kontinuierliche Bewegung der Extremitäten und des Rumpfes1. Continuous movement of the extremities and the trunk
2. „Vibration" Funktion zum Verhindern der tiefen Perzeption2. "vibration" function to prevent the deep perception
3. Die Decubitus Prophylaxe: System zum Verhindern einer Decubital Ulcera3. The Decubitus Prevention: System for preventing a decubital ulcer
4. Unterschiedliche Positionen werden mit der Möglichkeit einer schnellen und direkten Einstellung gewählt4. Different positions are selected with the possibility of a quick and direct adjustment
5. Gewichtskontrolle mit der Möglichkeit einer täglichen Dokumentation.5. Weight control with the possibility of daily documentation.
Hinzufügen eines LED Steuerungslichtsystems „An", „Aus", „Standby", „Batterie", „AC power".Add an LED control light system "On", "Off", "Standby", "Battery", "AC power".
Siehe Figuren 51 und 52
„Individuelles Setup" führt zu einem Setup einer definierten GelenkbewegungSee Figures 51 and 52 "Individual Setup" leads to a setup of a defined joint movement
„Standart Setup" - „Information" führt zu den Standard Setup Werten von Bewegungen, - „Aktivierungs" Mitte! zum Aktivieren des Standardbewegungsprogram- mes (alle Gelenke);"Standard Setup" - "Information" leads to the standard setup values of motions, - "Activation" middle! To activate the standard movement program (all joints);
Siehe Figur 53See Figure 53
Die Felder: „Individuelles Setup" und „Information: Standartsetup" ohne eine Drückfunktion: All die anderen Felder mit einer Drückfunktion.The fields: "Individual Setup" and "Information: Standartsetup" without a push function: All the other fields with a push function.
Siehe Figur 6See Figure 6
Navigieren der Anpassungen durch Verwenden des Stiftes.Navigate the adjustments by using the stylus.
„Stop" Mittel: keine Bewegung in den Armen, Beinen oder Rumpf; die Position, die der Arm und so weiter einnehmen werden, ist dann die neutrale Nullposition."Stop" means: no movement in the arms, legs or torso, the position that the arm and so on will take is then the neutral zero position.
„Zurückstell" Mittel: eine neue Möglichkeit oder Start der Anpassung, um die Bewegung einzustellen."Reset" means: a new possibility or start of adjustment to adjust the movement.
„Standard": Die Bewegung folgt automatisch dem Standardprogramm für das ausgewählte Gelenk."Standard": The movement automatically follows the standard program for the selected joint.
„Momentane Einstellung" führt zurück zu dem „Momentane Einstellungs-"Punkt in dem Hauptmenü."Current setting" returns to the "Current setting" item in the main menu.
„Fixierung in dieser Position" Mittel: Bewegungstop in der ausgewählten Setup Gelenkposition."Fixation in this position" Medium: Movement stop in the selected setup joint position.
Beide Gleitregulatoren sind separat bewegbar.Both sliding regulators can be moved separately.
Siehe Figuren 7 bis 13See Figures 7 to 13
Zum Demonstrieren der Gelenkbewegung könnte es beispielsweise durch einen bewegten Menschen ausgefüllt werden (als eine Animationsfigur)To demonstrate the joint movement, for example, it could be filled in by a moving human (as an animated figure)
Siehe Figuren 14 bis 17
„Standard" Mittel als eine Mittelposition (Punkt 5) aller Bereiche.See FIGS. 14 to 17 "Standard" means as a middle position (point 5) of all areas.
„Stop" Mittel: Stop aller Vibrationen."Stop" means: Stop all vibrations.
„Aus" Mittel: Stop der separaten Funktion."Off" means: Stop the separate function.
Siehe Figur 18See Figure 18
„Gewicht": tatsächliches Gewischt"Weight": actual wiped
„Datum": tatsächliches Datum"Date": actual date
Siehe Figur 19See Figure 19
„Standard": alle Bereiche an"Standard": all areas on
Siehe Figur 20See Figure 20
„Datum": Datum eines Verlustes einer Fixierung"Date": Date of loss of a fixation
„Verlust einer Fixierung": Stunde und Minute einer verlorenen Fixierung"Loss of fixation": hour and minute of a lost fixation
„Zurücksetzung": Zeit und Stunde einer Wiederfixierung"Reset": time and hour of re-fixation
Automatisch registrierte Aktionen.Automatically registered actions.
Zufügen all der notwendigen Dateien/Punkte eines Interesses für ein zentrales System; es gibt beispielsweise zwei gezeigte Figuren (siehe Figuren 22 und 23)Adding all the necessary files / points of interest to a central system; for example, there are two figures shown (see FIGS. 22 and 23)
Optional wird die Datei „Standby, Runterfahren, neuer Start" in dem Bild: „Hauptmenü" gezeigt.Optionally the file "Standby, shutdown, new start" is shown in the picture: "Main menu".
Siehe Figuren 21 bis 23See Figures 21 to 23
Die folgenden Positionen werden durch eine Stimme begleitet, welche sagt „Notstop", „Schockposition" und so weiter.The following positions are accompanied by a voice that says "emergency stop", "shock position" and so on.
Im Fall der ausgewählten Positionen:
Automatischer Standard und individuelle Bewegung „Aus"In the case of selected positions: Automatic standard and individual movement "off"
Im Falle von Ausgewählten Positionen:In the case of Selected Positions:
Vibrationsfunktion aus.Vibration function off.
Siehe Figur 24See Figure 24
Automatischer Zeit und Zeitraum einer Notstopregistrierung.Automatic time and period of emergency stop registration.
Siehe Figuren 25 bis 31See Figures 25 to 31
„Register" für eine Information; siehe nächste Ansicht, automatisch registriert. Alarmgeräusch."Register" for information, see next view, automatically registered.
Siehe Figuren 32 und 33See Figures 32 and 33
„ausgewähltes Patientengewicht": Anfangsgewicht."Selected patient weight": initial weight.
„Tatsächliches Gewicht": zeigt den automatisch registrierten und automatisch gemessenen Gewichtswert des Patienten."Actual Weight": shows the automatically registered and automatically measured weight value of the patient.
„Monat": zeigt einen ersten bis zwölften Monat des Jahres, beispielsweise durch Starten der Messung am 2. Februar."Month": shows the first to the twelfth month of the year, for example by starting the measurement on 2 February.
Diagramm „Gewicht": zeigt das Anfangsgewicht in der Mitte des Vektors.Diagram "Weight": shows the initial weight in the middle of the vector.
Durch einen Klick auf das Gewicht in dem Diagramm wird automatisch das Datum gezeigt;Clicking on the weight in the diagram automatically displays the date;
„Hinzufügen eines Diagramms": Hinzufügen eines neuen Diagramms, jedes Diagramm wird gespeichert."Add a Chart": Add a new chart, each chart is saved.
Siehe Figur 34See Figure 34
Und so weiter unbegrenzt.And so on unlimited.
„Gesamtansicht": ein Diagramm, welches die Entwicklung eines Gewichtes während der gesamten Messzeit zeigt.
Siehe Figur 35"Overall view": a diagram showing the development of a weight during the entire measuring time. See Figure 35
Natürlich ist das hier gezeigte Design nur ein Vorschlag.Of course, the design shown here is just a suggestion.
Medizinisches RoboterbettsystemMedical robot bed system
Lebenserhaltung im KomaLife support in a coma
"Continuous moving and sensory mediating intensive care bed System" (CMSI)- eine neue intensivmedizinische Strategie zur adjuvanten Therapie komatöser Patienten"Continuous moving and sensory intensive care bed system" (CMSI) - a new intensive care strategy for the adjuvant treatment of comatose patients
1. Einleitung1 Introduction
Schwerpunkt in der Behandlung komatöser Patienten ist bis heute der Erhalt der Vitalfunktionen. Der Erhalt resp. die Wiederherstellung komplexer nervaler und muskulärer Funktionen findet hingegen kaum Beachtung.The main focus in the treatment of comatose patients is the preservation of vital signs. The receipt resp. the restoration of complex nervous and muscular functions, however, receives little attention.
Der sedierte, relaxierte und kontrolliert beatmete Patient befindet sich in einem weitgehend immobilen sowie hyposensorischen Zustand. Die naturgemäß vor- handenen komplexen Feedback- Mechanismen zwischen motorischen, sensorischen und psychologischen Funktionen als Grundlage der Homöokinesie (2) sind dabei unterbrochen. Passive Bewegungen und taktile resp. Sensorische Reizge- bungen finden lediglich im Rahmen von Positionswechseln bei der Körperpflege, Lagerung und bei der Durchführung prophylaktischer Maßnahmen statt (3,4). Sensorische Reize wirken primär als akustische Phänomene der umgebenden Geräuschkulisse und als taktile Reize durch inkonstante Berührungen von Personen wie der zuständigen Pflegekraft, Physiotherapeutin oder Angehörigen ein, die mit dem Patienten in unmittelbarem Kontakt stehen. Hinzu kommen geringe thermo-, olfaktorische und nozizeptive sowie in nur schwer nachzuweisendem Maße propriozeptive Reize.The sedated, relaxed and controlled ventilated patient is in a largely immobile and hyposensory state. The naturally existing complex feedback mechanisms between motor, sensory and psychological functions as the basis of homeokinesia (2) are interrupted. Passive movements and tactile resp. Sensory stimuli only occur in the context of changes of position during personal hygiene, storage and prophylactic measures (3,4). Sensory stimuli primarily act as acoustic phenomena of the surrounding background noise and as tactile stimuli through incontinent touches of persons such as the responsible caregiver, physiotherapist or relatives who are in direct contact with the patient. In addition, there are low thermo-, olfactory and nociceptive as well as difficult-to-detect proprioceptive stimuli.
Zusammenfassend befindet der komatöse Patient in einer unphysiologischen Immobilität und einem pathologischen hyposensorischen Zustand reduzierter
Sinnesreizgebung und daher auch mangelhafter Signalverarbeitung und reaktion, wobei iatrogene und krankheitsbedingte Effekte zusammenwirken.In summary, the comatose patient is reduced in a nonphysiological immobility and a pathological hyposensory state Sensory stimulation and therefore also poor signal processing and reaction, with iatrogenic and disease-related effects interacting.
Die Folgen der Immobilität des langzeit- beatmeten Intensivpatienten werden bis heute im Allgememen deutlich unterschätzt, sowohl was die Auswirkungen auf den muskuloskelettalen Apparat und die erforderliche rehabilitative Erholungsphase nach Beendigung des Komas als auch was die komplexe Interaktion der somatischen Muskulatur mit den Organfunktionen während des Komas betrifft.The consequences of the immobility of the long-term ventilated intensive care patients are still generally underestimated in terms of both the effects on the musculoskeletal apparatus and the required rehabilitative recovery phase after the coma has ended, as well as the complex interaction of the somatic musculature with the organ functions during the coma ,
Zwischen der somatischen Muskulatur und dem inneren Organstoffwechsel sowie dem Energiemetabolismus existieren verschiedene kooperative Interaktio- nen. Aus eingeschränkten oder fehlenden motorischen Aktivitäten resultiert daher eine Störung der Integration molekularer, zellulärer, physiologischer, organischer und neutraler Mechanismen und damit der Effizienz des Energiemetabolismus und des inneren Organstoffwechsels mit weitreichenden Folgen (3) . Damit bedeutet Bewegen für die Funktionalität des menschlichen Körpers eine grundlegenden und gleichzeitig regulativen Faktor und umgekehrt die Immobilität einen entscheidenden pathomechanistischen Faktor in der Genese komplexer Organstörungen.There are various cooperative interactions between the somatic musculature and the internal organ metabolism as well as the energy metabolism. Limited or absent motor activity therefore results in a disruption of the integration of molecular, cellular, physiological, organic, and neutral mechanisms, and thus the efficiency of energy metabolism and internal organ metabolism, with far-reaching consequences (3). Thus, moving for the functionality of the human body means a fundamental and at the same time regulative factor and, conversely, immobility is a crucial pathomechanistic factor in the genesis of complex organ disorders.
1.1 Folgen der Immobilität auf den muskuloskelettalen Apparat1.1 Consequences of immobility on the musculoskeletal apparatus
Längerdauernde Immobilität führt zurProlonged immobility leads to
Muskelatrophie; Aktin- und Myosinfilamente verlieren ihre Fähigkeit zur Kontraktionmuscular atrophy; Actin and myosin filaments lose their ability to contract
Gelenkkontrakturen mitJoint contractures with
a. Veränderungen am hyalinen Knorpel unda. Changes in hyaline cartilage and
b. Veränderungen am Band- und Kapselapparat mit Verkürzungen und verminderter Zugbelastbarkeit von Sehnen und Bändern
- Inaktivitätsosteoporose mit Reduktion des Knochensalzgehaltes und der Knochenmasse (9)b. Changes to the ligament and capsule apparatus with shortening and reduced tensile strength of tendons and ligaments - Inactivity osteoporosis with reduction of bone salt content and bone mass (9)
undand
- Arthrose.- Arthrosis.
Die Auswirkungen der Immobilität auf den Kapsel-/ Bandapparat ist u.a. für die Kreuzbänder des Kniegelenks untersucht (10). Hiernach muss die verminderte Belastbarkeit der Bänder auf einen Verlust der bandspezifischen parallelen Faserstruktur zurückgeführt werden. Dabei manifestiert sich in den Bindegewebszellen eine Synthesestörung, die mit einem reduzierten Gehalt an Glykosaminog- lykanen, Proteoglykanen oder Kollagen einhergeht. Die Regenerationsfähigkeit der Bänder ist deutlich limitiert.The effects of immobility on the capsular / ligamentous apparatus are i.a. examined for the cruciate ligaments of the knee joint (10). According to this, the reduced load capacity of the bands must be attributed to a loss of the band-specific parallel fiber structure. This manifests itself in the connective tissue cells a synthesis disorder, which is accompanied by a reduced content of Glykosaminog- lykanen, proteoglycans or collagen. The regeneration capacity of the bands is clearly limited.
Druck, Zug, Biegung und Torsion stellen wichtige mechanische Reize mit gestaltbildender oder strukturerhaltender Wirkung dar. Zusätzlich besitzt die Zugoder Druckwirkung der Muskulatur einen entscheidenden Einfluss auf die Erhal- tung des Gleichgewichts zwischen Knochenanbau und Knochenabbau (9). Für den Ausprägungsgrad der Inaktivitätsosteoporose sind das Lebensalter, die Zeitdauer des Bewegungsverlustes sowie der Grad der Bewegungseinschränkung von entscheidender Bedeutung. Eine Inaktivitätsosteoporose tritt bereits nach wenigen Wochen auf, beginnend im Bereich der Spongiosa perifokal der Epiphysenfugen. Die Atrophie des Knochenschaftes mit Reduktion der Dicke der Kompakta wird erst nach einigen Wochen beobachtet. Im Falle bettlägeriger Patienten tritt im Rahmen einer generalisierten Osteoporose ein Verlust an Knochenmasse von 4-5% im Monat auf (9). Muskel- und Knochenatrophien lassen sich auch trotz adäquater parenteraler Ernährung oder enteraler Sondenernäh- rung nicht vermeiden (1 ).Pressure, traction, bending and torsion are important mechanical stimuli with a structuring or structure-preserving effect. In addition, the tensile or compressive effect of the musculature has a decisive influence on the maintenance of the balance between bone cultivation and bone destruction (9). For the degree of inactivity of the inoperative osteoporosis the age, the duration of the movement loss and the degree of movement restriction are of crucial importance. Inactivity osteoporosis occurs after just a few weeks, beginning in the area of the cancellous bone perifocal of the epiphyseal plates. The atrophy of the bone shaft with reduction in the thickness of the compact is observed only after a few weeks. In the case of bedridden patients, generalized osteoporosis causes 4-5% loss of bone mass per month (9). Muscular and bone atrophy can not be avoided despite adequate parenteral nutrition or enteral tube feeding (1).
Nach Noack (11 ) hat die Immobilisation die Entwicklung einer Arthrose zur Folge, die auf Ernährungsstörungen des Knorpels basiert. Die Versorgung des Gelenkknorpels mit Nährstoffen folgt ausschließlich über die Synovialflüssigkeit, wobei die physiologisch wechselnde Druckbelastung des Knorpels im Sinne eines Pumpmechanismus einen entscheidenden Faktor darstellt.
In Abhängigkeit der Dauer und des Ausmaßes der Immobilität werden rehabilita- tive Maßnahmen mit Eingliederung in das Berufs- resp. Alltagsleben erschwert und verlängert, da die Rehabilitation neben den Folgen der Grunderkrankung entscheidend von den sekundären Auswirkungen der Immobilität auf den musku- loskelettalen Apparat bestimmt wird. Besonders bei älteren Menschen führt die Immobilität häufig zu einer späteren Pflegebedürftigkeit, wobei das Risiko bei einer Immobilitätsphase von 4 Wochen um das über βOfache ansteigt (13).According to Noack (11), immobilization results in the development of osteoarthritis, which is based on malnutrition of the cartilage. The supply of the articular cartilage with nutrients follows exclusively via the synovial fluid, wherein the physiologically changing pressure load of the cartilage in the sense of a pumping mechanism is a decisive factor. Depending on the duration and extent of immobility, rehabilitative measures with integration into the occupational resp. Everyday life is aggravated and prolonged because rehabilitation, in addition to the consequences of the underlying disease, is decisively determined by the secondary effects of immobility on the musculoskeletal apparatus. Especially in the elderly, immobility often leads to a later need for care, with the risk increasing more than βO times at a 4-week immobility period (13).
1.2 Weitere somatische Folgen der Immobilität1.2 Other somatic consequences of immobility
- Störungen der neutralen Mobilität- Disorders of neutral mobility
- Zerebral- vermittelten Wahmehmungsstörungen mit Störungen der Koordination durch "Verlernen" von Bewegungsführung und Bewegungsabläufen- Cerebral-mediated impairments of perception with impaired coordination by "unlearning" movement guidance and movement sequences
- Störung der Vasomotorik mit Steigerung des Thromboserisikos sowie- Disorder of the vasomotor with increased thrombosis risk as well
Ödenneigung. Längerdauernde Immobilität führt zur Störung der äußeren Gleitfähigkeit oder der inneren Elastizität der Nerven (1 ).Barren slope. Prolonged immobility leads to a disturbance of the external lubricity or internal elasticity of the nerves (1).
Bereits nach einer Immobilitätsphase von 4 Tagen können signifikante Orientie- rungs- und Koordinationsstörungen von Bewegungsabläufen nachgewiesen werden (6,7,8). Längerdauernde Immobilität bedeutet zudem einen pathomecha- nistisch relevanten Faktor bei der Entstehung der Darmatonie, aus der eine bakterielle Durchwanderung der Darmwand mit konsekutiver Sepsis resultieren kann (5)After just four days of immobility, significant orientation and coordination disturbances of movement can be detected (6,7,8). Prolonged immobility also means a pathomechanically relevant factor in the development of intestinal atony, from which a bacterial migration of the intestinal wall can result with consecutive sepsis (5).
Folgen der HyposensorikConsequences of hyposensorics
Die kurz-, mittel- und langfristigen Folgen des hyposensorischen Zustandes des komatösen Patienten sind unklar. Die physiologische Wahrnehmung als Summe der Schritte Aufnahme, Auswahl, kognitive Verarbeitung und Interpretation von sensorischen Informationen ist in Abhängigkeit der Tiefe des komatösen Zustandes mehr oder weniger vollständig unterbrochen. Die Reaktionsmöglichkeiten des komatösen Patienten beschränken sich auf den Input einer im Vergleich zur
analytischen, differenzierten Funktion des Wachbewusstseins primitiven Bewuss- tseinsebene. Dennoch werden sensorische Reize der umgebenden Welt aufgenommen auch wenn zum Teil nur singuläre Sequenzen von Reizen registriert werden können. Die Wahrnehmung stellt sich dann primär über das größte Sin- nesorgan, die Haut, als unmittelbar und körperbezogen dar (12).The short-, medium- and long-term consequences of the hyposensory state of the comatose patient are unclear. The physiological perception as the sum of the steps of recording, selection, cognitive processing and interpretation of sensory information is more or less completely interrupted depending on the depth of the comatose state. The reaction possibilities of the comatose patient are limited to the input of one compared to analytical, differentiated function of waking consciousness at the primitive level of consciousness. Nevertheless, sensory stimuli of the surrounding world are recorded even if only singular sequences of stimuli can be registered. Perception then presents itself primarily through the largest sense organ, the skin, as being immediate and body-related (12).
2. Continous moving intensive care bed (CMICB)2. Continuous moving intensive care bed (CMICB)
2.1 Technik und Zielsetzungen2.1 Technology and objectives
Bei dem CMICB- System handelt es sich um ein kinetisches Therapie- System auf der Basis einer Roboter- gesteuerten Technik, das eine kontinuierliche passi- ve Bewegung der vier Extremitäten sowie des Rumpfes erlaubt und sensorische taktile und akustische Signale vermittelt.The CMICB system is a kinetic therapy system based on a robotic technique that allows continuous passive movement of the four extremities and the trunk and provides sensory tactile and auditory signals.
Primäres Ziel ist es, Kontrakturen, Muskelatrophien und Thrombosen zu vermeiden und hierdurch eine kürzere Phase der Rehabilitation zu erreichen resp. eine permanente Immobilität zu vermeiden. Die Vermittlung sensorischer Signale im Rahmen einer erweiterten basalen Stimulation hat eine raschere postkomatöse Restitutio neurologisch bedingter Wahrnehmungsstörungen zum Ziel.The primary goal is to avoid contractures, muscle atrophy and thrombosis and thereby achieve a shorter phase of rehabilitation. to avoid a permanent immobility. The mediation of sensory signals in the context of an extended basal stimulation aims at a faster postcomatous restitution of neurological perception disorders.
Das CMICB- System besteht aus 2 Hauptkomponenten: Zum Einen wurde ein computerassistiertes Modul mit spezieller Software zur Steuerung der elektronischen und sensorischen Einzelfunktionen entwickelt, zum Anderen wurde eine Bettmechanik konzipiert, die aus 5 beweglichen Funktionselementen besteht.The CMICB system consists of two main components: on the one hand a computer-assisted module with special software for controlling the electronic and sensory individual functions was developed, on the other hand a bed mechanism was designed, which consists of 5 movable functional elements.
2.1.1 Computermodul2.1.1 Computer module
Mit der Computereinheit verfügt das Bett über ein ausfallsicheres Computermodul mit einem ergonomisch leicht zu bedienenden Ein- und Ausgabepanel. Darüber erfolgen das Systemsetup, die Userverwaltung und die Verwaltung der pa- tientenspezifischen Basisdaten und Bewegungsvorgaben, d.h. alle Parameter der Bewegungs- und Signalfunktionen.With the computer unit, the bed has a fail-safe computer module with an ergonomically easy-to-use input and output panel. The system setup, the user administration and the administration of the pa- rameter-specific basic data and movement instructions, i. E. all parameters of the motion and signal functions.
Über dieses Panel werden nach Auswahl der betreffenden Optionen die Bewegungsabläufe aktiviert bzw. deaktiviert.
Die Computereinheit steuert nach Aktivierung die entsprechenden Bewegungsund signalgebenden Funktionen des Bettes. Dabei laufen auch Kontrollinformationen - z.B. Daten des Bettes, Gewichts- Messungen und Ergebnisdaten über die durchgeführten Bewegungen - an diese Computereinheit zurück. Außerdem ist eine Verbindung zu den anderen Computereinheiten/ Überwachungsmonitoren vorgesehen, die die aktuellen Überwachungsdaten der Intensivpatienten - wie beispielsweise Blutdruck und Herzfrequenz oder Sauerstoffffsättigung- liefern, um im Notfall unverzüglich und automatisch einen sofortigen Stillstand der Bewegung und eine Positionierung in Notfalllage gewährleisten zu können. Zent- ral können die Daten des CMSI- Systems ausgedruckt werden alternativ kann auch ein Drucker an den CMSI- Rechner angeschlossen werden.This panel activates or deactivates the motion sequences when the options are selected. After activation, the computer unit controls the corresponding movement and signaling functions of the bed. Control information - eg data from the bed, weight measurements and result data on the movements performed - are also returned to this computer unit. It also provides connectivity to the other computer units / monitors that provide up-to-date intensive care monitoring data, such as blood pressure and heart rate or oxygen saturation, to promptly and automatically prevent immediate movement and emergency positioning in the event of an emergency. The data of the CMSI system can be printed out centrally. Alternatively, a printer can also be connected to the CMSI computer.
2.1.1.1 Rechner2.1.1.1 Calculator
Grundmodul der Computereinheit ist ein Rechner mit einer Hard disk- Speicherkapazität zur Datendokumentation aller gewählten Grund- und Einzelfunktionen im zeitlichen Verlauf. Die Größe der Festplatte richtet sich nach dem Volumen der zu installierenden Software und einer zu errechnenden Speicherkapazität für Daten des CMSI- Systems in einem Einsatzzeitraum von 6 Monaten. Es sind weiterhin vorhanden:Basic module of the computer unit is a computer with a hard disk storage capacity for data documentation of all selected basic and individual functions over time. The size of the hard disk depends on the volume of the software to be installed and a storage capacity to be calculated for data of the CMSI system in a usage period of 6 months. There are still available:
- Anschluss für Drucker- Connection for printer
- USB- ports (3)- USB ports (3)
Soundkartesound card
- CD- Rom Laufwerk.- CD-ROM drive.
2.1.1.2 Monitor2.1.1.2 Monitor
Der (Fiat-) Monitor der Computereinheit befindet sich als Touch screen monitor mit einem Touch pen im Bereich der fixen Bauteile des Bettsystems. Aus medi-
zin- hygienischen Gründen bietet sich eine Bedienung der Monitorfunktionen mittels Fingerberührung nicht an.The (Fiat) monitor of the computer unit is located as a touch screen monitor with a touch pen in the area of the fixed components of the bed system. From medical For hygienic reasons, operating the monitor functions by means of finger touch is not an option.
Der Monitor ist ausgestattet mitThe monitor is equipped with
An-/AusschalterOn / off switch
- Farbwechsel der Buttons, wenn sie aktiviert werden- Color change of the buttons when activated
Im Falle einer Alarmfunktion: pop up und verschiedene, voneinander zu differenzierende akustische SignaleIn case of an alarm function: pop up and different, differentiated acoustic signals
- Voice feed back bei Wahl einer Funktion (entsprechend eines Navigator Systems)- Voice feedback when selecting a function (according to a navigator system)
- Screen saver- Screen Saver
- Animation intro.- Animation intro.
2.1.2 Software und Funktionen2.1.2 Software and Features
Generelle Funktionen:General functions:
- "return" bedeutet: Zurückgehen auf das letzte Monitorbild- "return" means: going back to the last monitor picture
- "menu" bedeutet: Zurückgehen auf das Hauptmenü.- "menu" means: going back to the main menu.
Siehe Figur 5See Figure 5
Erste Ansicht des SystemsFirst view of the system
Login Name: VerwendernameLogin Name: Username
Sprache: Englisch, Deutsch.Language: English, German.
Datum: DatumDate: Date
Uhrzeit (Funkuhr) auf jedem Monitorbild (unter o.k. Button); ab View 2 zusätzlich das
DatumClock (radio clock) on each monitor picture (under ok button); from View 2 additionally the date
A. Main monitor pictureA. Main monitor picture
o.k.- button only foro.k.- button only for
- emergency stop- emergency stop
shock position, cardiac position, cerebral position, sitting position, back Position, reanimation position and horizontal position, weight.Shock position, cardiac position, cerebral position, sitting position, back position, resuscitation position and horizontal position, weight.
Die Hauptfunktionen des CMIS werden auf dem Hauptmonitor gezeigt und können hier aktiviert werden:The main functions of the CMIS are shown on the main monitor and can be activated here:
1. Movement: Continuous movement der Extremitäten und des Stammes in Standard- oder individueller Auswahl von1. Movement: Continuous movement of the extremities and trunk in standard or individual selection of
a. Wahl der Extremitäta. Choice of extremity
b. Bewegungsumfang in den Gelenken resp. in der Wirbelsäuleb. Range of motion in the joints resp. in the spine
c. zeitlicher Dauer undc. time duration and
d. zeitlichem Ablauf;d. timing;
2. Acustic Signals: Funktion für die basale Stimulation durch Höreindrücke in Standard- oder individueller Auswahl von2. Acustic Signals: Function for the basic stimulation by hearing impressions in standard or individual selection of
a. zeitlicher Dauer der Höreindrückea. Duration of the hearing impressions
b. Lautstärke der Höreindrückeb. Volume of the audio impressions
3. Vibration: Funktion zum Erhalt resp. Restitutio der Tiefensensibilität in Standard- oder individueller Auswahl von3. Vibration: Function for obtaining resp. Restitutio of depth sensitivity in standard or individual selection of
a. Lokalisation
b. zeitlicher Dauer unda. localization b. time duration and
c. Intensität der Vibration.c. Intensity of vibration.
4. Decubitus Prophylaxe: System zur Prävention von Dekubitalulcera in Standard- oder individueller Auswahl von4. Decubitus prophylaxis: system for the prevention of decubital ulcers in standard or individual selection of
a. Lokalisation unda. Localization and
b. zeitlicher Dauer.b. time duration.
5. Thermo System: System zur Regulation der Körpertemperatur in Standardoder individueller Einstellung.5. Thermo System: system for regulating body temperature in standard or individual setting.
6. Current settings: Überblick über die aktuellen Einstellungen des Systems.6. Current settings: Overview of the current settings of the system.
7. System control: Administratorfunktionen etc.7. System control: Administrator functions etc.
8. Wahl verschiedener voreingestellter Positionen mit der Option des raschen direkten Settings in Verbindung spezifischer Funktionen:8. Choice of different preset positions with the option of fast direct setting in combination with specific functions:
a. emergency Stopp (Notfall- Stop der Bettbewegungen)a. emergency stop (emergency stop of bed movements)
b. shock position (Schocklage mit Stop der Anti- Dekubitus- Funktion)b. shock position (shock with stop of anti-decubitus function)
c. cardiac position (Herzlagerung mit Stop der Anti- Dekubitus- Funktion)c. cardiac position (cardiac support with stop of the anti-decubitus function)
d. cerebral position (Lagerung im Falle von Verletzungen und Erkrankungen des Gehirns)d. cerebral position (storage in case of injuries and diseases of the brain)
e. sitting position (sitzende Position, zum Beispiel zur beginnenden Mobilisation mit Stop der Anti- Dekubitus- Funktion)e. sitting position (seated position, for example at the beginning of mobilization with stop of the anti-decubitus function)
f. back position (Schachtellagerung bei Rückenerkrankungen und -Verletzungen)f. back position (box storage for back diseases and injuries)
g. horizontal position (flache Lagerung)G. horizontal position (flat storage)
sowie Notfall- Lagerung
7. reanimation position (Lagerung zur Reanimation mit automatischer Rückenlagerung, Stop der Anti- Dekubitus- Funktion, Tieferstellen des Bettes, Thermo- Regulation mit Hypothermie 25 Grad Celsius)as well as emergency storage 7. resuscitation position (storage for resuscitation with automatic back support, stop of the anti-decubitus function, lowering of the bed, thermo-regulation with hypothermia 25 degrees Celsius)
9. Weight control (Gewichtskontrolle mit täglicher Dokumentation der Messun- gen, graphischer Darstellung des Verlaufs).9. Weight control (weight control with daily documentation of the measurements, graphical representation of the course).
7. up and down bed position (Höher- und Tieferfahren des Bettes)7. up and down bed position (raising and lowering the bed)
Hinzufügen eines LED- controllight System "on", "off, stand by", "battery", "AC power".Add a LED controllight system "on", "off, stand by", "battery", "AC power".
Siehe Figur 2See Figure 2
Main monitor picture.Main monitor picture.
A. Einstellung des MovingsA. Setting the Moving
Siehe Figur 36See Figure 36
Moving setup: Einstellen der Bewegung von Extremitäten und Rumpf mit der Wahl "individuell" und "Standard",Moving setup: adjusting the movement of extremities and trunk with the choice of "individual" and "standard",
"individual setup" führt zum setup zu definierenden Bewegungen sowie zur Einstellung der Bewegungen der Zeitdauer""individual setup" leads to the setup of defined movements and to the adjustment of the movements of the duration "
"Standard setup" - führt zu bereits definierten Einstellungen der Bewegung sowie der Zeitdauer"Standard setup" - leads to already defined settings of the movement as well as the duration
Siehe Figur 37See Figure 37
Moving individual setup: Individuelles Einstellen der BewegungsfunktionenMoving individual setup: Individual adjustment of the movement functions
Siehe Figur 6
Einstellung der Bewegungen in den Gelenken des rechten Armes und des linken Beines. Einstellung des Bewegungsumfanges mittels Pen. Beide Schieberegler für ein Gelenk sind jeweils separat regelbar.See Figure 6 Adjustment of the movements in the joints of the right arm and the left leg. Adjustment of the range of motion by means of a pen. Both sliders for one joint can be adjusted separately.
"stop": keine Bewegung im Arm oder Bein; die Einstellung erfolgt dann automa- tisch in die Neutral O-Position."stop": no movement in the arm or leg; the adjustment then takes place automatically in the neutral O position.
"reset": Rückstellen auf den herstellerseits vorgegebenen Bewegungsumfang;"reset": reset to the range of movement specified by the manufacturer;
"Standard": bei Wahl des Gelenkes und Aktivierung der Standard- Funktion entspricht der Bewegungsumfang in dem gewählten Gelenk den Werten in der Standard- Funktion."Standard": when selecting the joint and activating the standard function, the range of motion in the selected joint corresponds to the values in the standard function.
"current settings": Führt zum Bereich "current setting" im Hauptmenü."current settings": Leads to the "current setting" area in the main menu.
"fix in this position": Bewegungsstop im gewählten setup der Gelenkfunktion."fix in this position": Movement stop in the selected setup of the joint function.
Siehe Figur 7See Figure 7
Einstellung der Bewegungen in den Gelenken des linken Armes und des rechten Beines.Adjustment of the movements in the joints of the left arm and the right leg.
Siehe Figur 8See Figure 8
Einstellung der Bewegungen des Rumpfes sowie des Nackens.Adjustment of the movements of the trunk and the neck.
Siehe Figur 39See Figure 39
Definition der zeitlichen Dauer der Bewegungen.Definition of the duration of the movements.
Die Aktivierung erfolgt mittels Pen durch Anklicken der hellblauen Punktmarkie- rungen der Uhren.The activation takes place by means of a pen by clicking on the light blue dot markings of the clocks.
Siehe Figur 38See Figure 38
Standard- Setup für die Bewegungen der Extremitäten, des Rumpfes sowie des Nackens.
Siehe Figur 54Standard setup for the movements of the extremities, the trunk and the neck. See Figure 54
Definierter Bewegungsumfang in den Gelenken des Arms.Defined range of motion in the joints of the arm.
Siehe Figur 55See Figure 55
Definierter Bewegungsumfang in den Gelenken des Beins.Defined range of motion in the joints of the leg.
Siehe Figur 13See Figure 13
Definierter Bewegungsumfang des Rumpfes sowie des Halses. Die graphische Darstellung der Demonstrationsperson könnte als sich entsprechend der definierten Gradzahlen bewegendes Männchen i.S. einer Animationsgraphik erfolgen.Defined range of motion of the trunk and neck. The graphical representation of the demonstrator could be considered as moving according to the defined number of degrees moving male i.S. an animation graphic done.
Siehe Figur 39See Figure 39
Definierter Zeitrahmen der kontinuierlichen Bewegungen des Rumpfes sowie der Extremitäten.Defined timeframe of the continuous movements of the trunk and extremities.
Berücksichtigt wird hier der Tag/Nachtrhythmus und sowie die Nutrition time.It takes into account the day / night rhythm and the nutrition time.
Siehe Figur 56See Figure 56
Individuelle oder Standard- Einstellung der akustischen Signale zur basalen Stimulation.Individual or standard setting of the acoustic signals for basal stimulation.
Das System besteht aus einem Rekorder und weichen (wireless) Kopfhörern für den Patienten. Nach mündlicher und schriftlicher Anleitung nehmen die Angehörigen des Patienten zu Hause charakteristische Geräuschphänomene entsprechend des Tagesablaufs auf (z.B. morgens Klingeln des Weckers, Zähneputzen, Kaffeemaschine, am Vormittag Geräusche des Arbeitslebens, mittags die Glocke eines nahegelegenen Kirchturms, abends Geräusche aus dem TV wie Z.B. die Intromusik der Tagesschau etc.) sowie seine gern gehörte Musik.The system consists of a recorder and soft (wireless) headphones for the patient. After oral and written instructions take the family members of the patient at home characteristic noise phenomena according to the daily routine (eg in the morning ringing the alarm, brushing teeth, coffee machine, in the morning noises of working life, at noon the bell of a nearby church tower, in the evening noises from the TV such as the Intro music of the Tagesschau etc.) as well as his often heard music.
Der Rechner bietet die Option der Digitalisierung, mittels Soundkarte erfolgt der Datentransfer zum Kopfhörer. Der Rekorder kann auch direkt an die Kopfhörer angeschlossen werden.
Siehe Figur 40The calculator offers the option of digitization, via sound card the data is transferred to the headphones. The recorder can also be connected directly to the headphones. See Figure 40
Individuelle Lautstärkenregelung der akustischen Signale mittels Schieberegler, die durch den Pen bedient werden.Individual volume control of the acoustic signals by means of sliders operated by the pen.
Siehe Figur 41See Figure 41
Individuelle Einstellung der Zeitdauer der akustischen Signale. Zum Aktivieren werden die hellblauen Buttons mittels Pen markiert.Individual adjustment of the duration of the acoustic signals. To activate the light blue buttons are marked by Pen.
B. Einstellung der akustischen SignaleB. Setting the acoustic signals
Siehe Figur 42See Figure 42
Standard- Einstellung der Zeitdauer sowie Lautstärke der akustischen Signale zur basalen Stimulation.Standard setting of the duration and volume of the acoustic signals for basal stimulation.
C. Einstellung des VibrationseffektesC. Adjusting the vibration effect
Siehe Figur 16See Figure 16
Individuelle oder Standard- Einstellung des Vibrationseffektes zum Erhalt der Tiefensensibilität, Vibrationskissen werden jeweils im Bereich der Handinnensei- te (palmar) sowie der Fußrücken (dorsal) - z.B. mittels Klettverschluss - angebracht. Die Technik der Vibration entspricht der von z.B. Mobiltelefonen.Individual or standard adjustment of the vibration effect to obtain the depth sensitivity, vibration pads are in each case in the area of the palmar and the dorsal -. by Velcro - attached. The technique of vibration corresponds to that of e.g. Mobile phones.
Siehe Figur 43See Figure 43
Individuelle Einstellung des Vibrationseffektes im Bereich der Hände und Fußrücken.Individual adjustment of the vibration effect in the area of the hands and back of the foot.
"Standard" bedeutet eine Mittelstellung der Intensität (point 5) aller Regionen,"Standard" means a middle position of the intensity (point 5) of all regions,
"stopp" bedeutet Stop der Vibration aller Bereiche,"stop" means stop the vibration of all areas,
"off bedeutet Stop der Einzelfunktion."off means stop the single function.
Siehe Figur 45:
Individuelle Zeiteinstellung des Vibrationseffektes im Bereich der Hände und Fußrücken.See Figure 45: Individual time adjustment of the vibration effect in the area of the hands and back of the foot.
Zum Aktivieren werden die hellblauen Buttons mittels Pen markiert.To activate the light blue buttons are marked by Pen.
Siehe Figur 46:See Figure 46:
Standardisierte Zeiteinstellung des Vibrationseffektes im Bereich der Hände und Fußrücken.Standardized time adjustment of the vibration effect on the hands and back of the foot.
D. Einstellung der Antidekubitus- FunktionD. Adjustment of the anti-decubitus function
Siehe Figur 47See Figure 47
Regionen der Dekubitus- Prophylaxe. Technisch handelt es sich um gekammerte Luftkissen, die jeweils mit wechselndem Druck gefüllt werden. Die Funktion wird durch Anklicken in den definierten Bereichen aktiviert und durch "o.k." bestätigt. Bei Aktivierung wechselt die Farbe des aπgeklickten Feldes. Bei "Standard" Wahl werden alle Regionen aktiviert.Regions of decubitus prophylaxis. Technically, these are chambered air cushions, each filled with alternating pressure. The function is activated by clicking in the defined areas and indicated by "o.k." approved. When activated, the color of the selected field changes. With "Standard" selection all regions are activated.
E. Einstellung des ThermosystemsE. Setting the thermo system
Siehe Figur 57See Figure 57
Thermosystem zur Regulation der Körpertemperatur. Technisch erfolgt eine Feed back- Einstellung über eine z.B. rektal eingelegte Thermosonde; das Thermosystem regelt die Körpertemperatur auf die vorgewählte Gradzahl.Thermosystem for the regulation of body temperature. Technically, a feedback setting is made via a e.g. rectally inserted thermoprobe; the thermo system regulates the body temperature to the preselected number of degrees.
Ohne Feed- back- Einstellung kann die Temperatur des Thermosystems über die Funktion "individual setup" manuell geregelt werden.Without feedback setting, the temperature of the thermo system can be controlled manually via the "individual setup" function.
Siehe Figur 48:See Figure 48:
Individuelle Einstellung der Temperatur des Thermosystems über einen mittels Pen zu bedienenden Schieberegler.Individual adjustment of the temperature of the thermo system via a pen to be operated slider.
Siehe Figur 49:
Standard-Individuelle Einstellung der Temperatur des Thermosystems über einen mittels Pen zu bedienenden Schieberegler. Standard- Einstellung des Thermosystems auf 37 Grad Celsius; bei Feed- back: Erreichen der 37 Grad Celsius Körpertemperatur, bei fehlendem Feed- back Thermosystem- Temperatur.See Figure 49: Standard Individual setting of the temperature of the thermo system via a pen-operated slider. Standard setting of the thermo system to 37 degrees Celsius; on feedback: reaching the body temperature of 37 degrees Celsius, with no feedback on the thermosystem temperature.
F. Current settingsF. Current settings
Siehe Figur 58See Figure 58
Aktuelle Einstellungen für Bewegung, akustische Signale, Vibrationseffekt, De- kubitus- Prophylaxe, Dokumentation des Notfall- Stops, Position und Gewicht.Current settings for movement, acoustic signals, vibration effect, decubitus prophylaxis, documentation of the emergency stop, position and weight.
"weight": aktuelles Gewicht"weight": current weight
G. SystemkontrolleG. System control
Siehe Figur 50See Figure 50
Übersicht über die Funktionen "system control". Hier sind alle erforderlichen files/ points of interest für die System Kontrolle enthalten, "stand by, shut down, new start" zusätzlich im "main menu" (siehe Figur2).Overview of the functions "system control". Here are all necessary files / points of interest for the system control included, "stand by, shut down, new start" additionally in the "main menu" (see figure 2).
Siehe Figur 22See Figure 22
Administrator- Controlling.Administrator controlling.
Siehe Figur 23See Figure 23
Registratur des Users. Die einzelnen User- Rechte sind zu definieren.Registry of the user. The individual user rights are to be defined.
H. Definierte FunktionenH. Defined functions
Die nachfolgenden definierten Bettpositionen werden bei Aktivierung durch Voi- ce- Funktionen begleitend ergänzt, die die jeweiligen Funktionen - wie z.B. Schock- Position, Notfall- Stop benennen.
Individuelle oder standardisierte Bewegungsfunktionen, Vibrationseffekte, akustische Signale und Antidekubitus- Effekte werden bei Wabl der nachfolgenden Positionen automatisch abgeschaltet.The following defined bed positions are complemented when activated by voce functions that name the respective functions - such as shock position, emergency stop. Individual or standardized motion functions, vibration effects, acoustic signals and anti-decubitus effects are automatically switched off when the following positions are selected.
Siehe Figur 24See Figure 24
Notfall- Stop aller Bewegungsfunktionen. Automatische Registierung der Zeit und Zeitdauer der Funktion.Emergency stop of all movement functions. Automatic registration of the time and duration of the function.
Siehe Figur 25See Figure 25
(Volumenmangel-) Schock- Position.(Volume deficit) shock position.
Siehe Figur 26See Figure 26
Herz- Position (z.B. bei Lungenödem, Herzinfarkt).Cardiac position (e.g., pulmonary edema, myocardial infarction).
Siehe Figur 27See Figure 27
Zerebrale- Position (zum Beispiel bei Schädel- Hirntrauma).Cerebral position (for example in cranial-brain trauma).
Siehe Figur 28See Figure 28
Sitzende Position (zum Beispiel bei beginnender Mobilisation). Akustische Sig- nalgebungen und Vibrationseffekte möglich.Seated position (for example, at the beginning of mobilization). Acoustic signals and vibration effects possible.
Siehe Figur 29See Figure 29
Rückenlagerung (zum Beispiel zum Betten des Patienten).Back support (for example, to bed the patient).
Siehe Figur 30See Figure 30
Schachtellage (zum Beispiel bei Bandscheibenprolaps).Box layer (for example in the case of disc prolapse).
Siehe Figur 31See Figure 31
Reanimations- Position. Begleitender Alarm sound.Automatischer Stop der Vibrationseffekte, der Antidekubitusfunktion sowie der akustischen Signale. Das Bett fährt automatisch in eine tiefere Position, die Ausgangsposition wechselt gleich-
zeitig in Rückenlage. Automatische Thermo- Funktion bei Reanimation: Kühlung auf 25 Grad Celsius.Resuscitation position. Accompanying alarm sound.Automatic stop of the vibration effects, the anti-decubitus function as well as the acoustic signals. The bed moves automatically to a lower position, the starting position changes early in supine position. Automatic thermal function during resuscitation: Cooling to 25 degrees Celsius.
"register": Abruf automatische Registrierung vom Zeitpunkt der Aktivierung der Funktion "reanimation function""register": retrieve automatic registration from the moment the activation of the function "reanimation function"
Siehe Figur 38See Figure 38
Registrierung der Reanimationsphase/ -position.Registration of the resuscitation phase / position.
I. GewichtsmessungI. Weight measurement
Siehe Figur 59See Figure 59
Gewichtsmessung. Digitale und graphische Darstellung, "select patients weight": Initiales Gewicht des Patienten.Weight measurement. Digital and graphical representation, "select patients weight": Initial weight of the patient.
"actual weight": zeigt das automatisch graphisch und digital per Datenspeicher registrierte aktuelle Gewicht des Patienten."actual weight": shows the current weight of the patient, which is automatically graphically and digitally registered via data memory.
Das aktuelle Datum (vgl. Figur 5) wird jeweils in der Fußzeile gezeigt und regist- riert. Diagramm "weight": das initiale Gewicht des Patienten wird in der Vektormitte gezeigt. Wird auf das Diagramm geklickt, wird automatisch das Datum zusätzlich angezeigt, "add diagram": Hinzufügen eines weiteren Diagrammes.The current date (see Figure 5) is shown and registered in the footer. Diagram "weight": the initial weight of the patient is shown in the vector center. If the diagram is clicked, the date will be displayed automatically, "add diagram": Add another diagram.
Siehe Figur 34See Figure 34
Fortlaufende tägliche automatische Gewichtsmessung und Registrierung. Nach- folgende Graphiken mit gleicher Darstellung ohne Limitierung.Continuous daily automatic weight measurement and registration. The following graphics with the same representation without limitation.
"overall view"; Das Diagramm zeigt die Gewichtsentwicklung in 1 Woche, 1 Monat und während der gesamten Zeit der Gewichtsmessung."overall view"; The graph shows weight gain at 1 week, 1 month, and throughout the weighting period.
J. Alarmfunktion: Lösen der FixationJ. Alarm function: release the fixation
Siehe Figur 20
Dokumentation des Verlustes der Fixation mit akustischem Alarm, "reset": Zeitdokumentation der Refixation. Die Extremitäten sowie der Rumpf werden mittels unterpolsterten Klettbändern an den beweglichen Modulen fixiert. Sensoren zeigen den mangelhaften Verschluss an.See Figure 20 Documentation of the loss of the fixation with acoustic alarm, "reset": time documentation of the refixation. The extremities and the trunk are fixed to the movable modules by means of padded velcro straps. Sensors indicate the defective closure.
Siehe Figur 60See Figure 60
ImpressunImpressun
2.2 Funktionsmodul2.2 Function module
Das Bett besteht aus 5 beweglichen Modulen (Fig.3):The bed consists of 5 movable modules (Fig.3):
1. Rumpf-I Kopfeinheit1. Hull-I head unit
2. je 2 Einheiten für die oberen Extremitäten2. 2 units each for the upper extremities
3. je 2 Einheiten für die unteren Extremitäten.3. 2 units each for the lower extremities.
Die Abmessungen des Bettes sind für Patienten mit einer Körperlänge bis 2.10m und einem Gewicht von 180kg ausgerichtet.The dimensions of the bed are designed for patients with a body length of up to 2.10m and a weight of 180kg.
siehe Figur 3see FIG. 3
Die 5 Grundmodule des MRBS. Jede Komponente besteht aus mehreren beweglichen schalenförmigen Einzelelementen, die aus leichtem, strapazierfähigem und leicht zu reinigendem Material bestehen. In Betracht kommt zum Beispiel Fiberglas. Metallische Grundsubstanzen sind nicht geeignet, um Röntgenaufnahmen zu ermöglichen.The 5 basic modules of the MRBS. Each component consists of several movable bowl-shaped individual elements made of lightweight, durable and easy-to-clean material. For example, fiberglass is considered. Metallic substances are not suitable for X-ray imaging.
Auf den Schalen werden die Einzelmodule für die Dekubitusprophylaxe aufgebracht (austauschbar, z.B. im Falle einer Reparatur). Für den Bezug der 5 Bettkomponenten stehen angefertigte StoffSpannüberzüge zur Verfügung. Die Fixierung der Extremitäten sowie des Rumpfes erfolgt mittels Klettverschlüssen, in denen Sensoren vorhanden sind, die einen mangelhaften Verschluss anzeigenOn the trays the individual modules for decubitus prophylaxis are applied (interchangeable, for example in case of repair). Fabric covers are available for the purchase of the 5 bed components. The fixation of the extremities and the trunk is done by means of Velcro fasteners in which sensors are present, indicating a poor closure
"'Loss of fixation alarm".
Siehe Figur 61"Loss of fixation alarm". See Figure 61
Modell für die beweglichen Einzelelemente der 5 Grundmodule. Die Schalen sind dabei allerdings nicht plan, sondern schalenförmig gebogen, um einem Herausfallen entgegenzuwirken. Unter den Schalen ist das zusammenhängende, com- putergesteuerte Bewegungssystem installiert, das aus den computergesteuerten Bewegungselementen für den Gelenkbereich und aus teleskopartig auszufahrenden metallischen Rohren besteht. Die Teleskop- Module für die 4 Extremitäten sind verschiebbar am zentralen (Rumpf-) Modul angebracht, so dass individuelle Körpergrößen berücksichtigt werden können.Model for the movable elements of the 5 basic modules. The shells are not flat, but curved bowl-shaped to counteract falling out. Under the shells, the coherent, computer-controlled movement system is installed, consisting of the computer-controlled movement elements for the joint area and of telescopically extending metallic tubes. The telescopic modules for the 4 extremities are slidably attached to the central (trunk) module so that individual body sizes can be taken into account.
Siehe Figur 4See Figure 4
Schemata für die beweglichen einzelnen Schalenelemente der 5 Grundmodule.Schemes for the movable individual shell elements of the 5 basic modules.
1 : Schale aus ultraleichtem Material (z.B. Glasfaser)1: shell of ultralight material (e.g., fiberglass)
2: Antidekubitus- Element2: anti-decubitus element
3: Thermosystem3: thermosystem
4: Wasserdichte Matratzenauflage, beziehbar4: Waterproof mattress pad, available
5: Teleskoparmsystem.5: Telescopic arm system.
Die Einheit aus Teleskop- Rohr- sowie Scharniersystem und Schalenelementen wird auf einem Grundmodul montiert, dass das Bett leicht beweglich resp. fahrbar macht und das computergesteuert höhenreguliert werden kann. Für die Fertigung von Röntgenaufnahmen der Lunge wird eine Kassettenhalterung in Standardgröße, verschieblich, unter dem Thoraxmodul installiert. Für die Fertigung von Röntgenaufnahmen des Abdomens (Bauchraumes) existiert eine analoge Halterung in Höhe des Bauchmoduls. Weitere Halterungen werden zum Einschieben einer Schale im Kopfbereich für die Haarwäsche und eines Toilet- teneimers angebracht. Die verwendeten leichten und gleichzeitig mechanisch hoch belastbaren Materialien des Bettsystems gewährleisten ein leichtes Rangieren des Bettes zum Transport. Seitlich angebrachte Schienen ermöglichen das
Anbringen von Infusionspumpen sowie am Kopfende eines mobilen Sauerstoffgerätes. Eine integrierte Waage ermöglicht die tägliche, computergestützte Dokumentation des GewichtsThe unit of telescopic tube and hinge system and shell elements is mounted on a base module that the bed easily movable resp. mobile and can be controlled by computerized height. For the production of X-ray images of the lung, a standard-sized cassette holder, slidable, is installed under the thorax module. For the production of radiographs of the abdomen (abdominal cavity) there is an analogous support at the level of the abdominal module. Additional brackets are used to insert a shell in the head area for hair washing and a toilet bin. The light and at the same time mechanically strong materials used in the bed system ensure easy maneuvering of the bed for transport. Laterally mounted rails make this possible Attachment of infusion pumps and at the head of a mobile oxygen device. An integrated scale allows daily, computer-aided weight documentation
2.3 Indikationen und Kontraindikationen zum Einsatz des Medical robot bed Systems2.3 Indications and contraindications to the use of the Medical robot bed system
2.31 Indikationen2.31 indications
1. Generell: Langzeitbeatmete Patienten aller medizinischen Fachdisziplinen im Alter zwischen 15 und 90 Jahren1. General: Long-term ventilation patients of all medical disciplines between the ages of 15 and 90 years
2. Neurologische Patienten zur Frührehabilitation (2. Bettversion mit reduzierten Funktionen möglich)2. Neurological patients for early rehabilitation (2nd bed version with reduced functions possible)
3. Unfall- und neurochirurgische Patienten zur Frührehabilitation3. Accident and neurosurgical patients for early rehabilitation
4. Häusliche Versorgung von Patienten mit chronisch- neurologischen Erkrankungen4. Domestic care of patients with chronic neurological diseases
5. Pflegeheimversorgung von immobilen Patienten mit internistischen neurologi- sehen Grunderkrankungen (z.B. Wach- Komapatienten)5. Nursing home care of immobile patients with underlying neurological disorders (eg, waking coma patients)
2.3.2 Kontraindikationen2.3.2 contraindications
Zur Zeit keine bekannt.Currently no known.
Der Erhalt resp. die Stabilisierung der Vitalfunktionen hat in jedem Fall Priorität. Der Umfang der Bewegungen in zeitlicher Dauer und Bewegungsausmaß richtet sich nach den Grunderkrankungen, den Herz-/ Kreislaufreaktionen, der respiratorischen Situation sowie den Erfordernissen nach einer Operation (z.B. erforderliche Ruhigstellung einer Extremität nach osteosynthetischer Versorgung einer Fraktur).The receipt resp. the stabilization of vital functions has priority in every case. The extent of the movements in terms of time duration and extent of movement depends on the underlying diseases, the cardiovascular reactions, the respiratory situation and the requirements for an operation (for example, required immobilization of a limb after osteosynthesis of a fracture).
2.4 Verschiedene technische Versionen des MRBS
Je nach Einsatz des Bettsystems stehen verschiedene technische Versionen als Modifikationen der Vollversion zur Verfügung.2.4 Various technical versions of the MRBS Depending on the use of the bed system, various technical versions are available as modifications of the full version.
Beispiele:Examples:
A. Intensivmedizin: VollversionA. Intensive Medicine: Full Version
B. Neurologische Frührehabilitation: Vollversion ohne "thermo System"B. Neurological early rehabilitation: full version without "thermo system"
C. Häusliche Versorgung: Vollversion ohne "acustic Signals", "Vibration", "thermo System", "weight".C. Domestic Supply: Full version without "acustic signal", "vibration", "thermo system", "weight".
D. Pflegeheimversorgung: Vollversion ohne "acustic Signals", 'Vibration", "thermo System.D. Nursing home care: Full version without "acoustic signal", "vibration", "thermo system.
Im Folgenden werden weitere detailierte Ausführungsformen beschrieben.In the following, further detailed embodiments will be described.
Continous moving intensive care bed (CMICB)Continuous moving intensive care bed (CMICB)
Krankenaktemedical record
Computermodulcomputer module
Mit der Computereinheit verfügt das Bett über ein ausfallsicheres Computermo- dul mit einem ergonomisch leicht zu bedienenden Ein- und Ausgabepanel. Darüber erfolgen das Systemsetup, die Userverwaltung und die Verwaltung der patientenspezifischen Basisdaten und Bewegungsvorgaben, d.h. alle Parameter der Bewegungs- und Signalfunktionen.With the computer unit, the bed has a fail-safe computer module with an ergonomically easy-to-use input and output panel. The system setup, the user administration and the administration of the patient-specific basic data and movement specifications, i. E. all parameters of the motion and signal functions.
Die Computereinheit steuert nach Aktivierung die entsprechenden Bewegungsund signalgebenden Funktionen des Bettes. Dabei laufen auch Kontrollioforma- tionen - z.B. Daten des Bettes, Gewichtsmessungen und Ergebnisdaten über die durchgeführten Bewegungen - an diese Computereinheit zurück. Außerdem ist eine Verbindung zu den anderen Computereinheiten Überwachungsmonitoren vorgesehen, die die aktuellen Überwachungsdaten der Intensivpatienten - wie beispielsweise Blutdruck und Herzfrequenz oder Sauerstoffsattignng -liefern, um
im Notfall unverzüglich und automatisch einen sofortigen Stillstand der Bewegung und eine Positionierung in Notfallage gewährleisten zu können. Zentral können die Daten des CMSI- Systems angesclossen werden werden; alternativ kann auch ein Drucker an den CMSI- Rechner angeschlossen werden.After activation, the computer unit controls the corresponding movement and signaling functions of the bed. At the same time, control information - eg data from the bed, weight measurements and result data on the movements performed - are returned to this computer unit. In addition, a connection to the other computer units is provided to surveillance monitors which provide the current monitoring data of the intensive care patients, such as blood pressure and heart rate or oxygen saturation to be able to immediately and automatically ensure an immediate stoppage of movement and positioning in an emergency situation in the event of an emergency. The data of the CMSI system can be accessed centrally; Alternatively, a printer can be connected to the CMSI computer.
Rechnercomputer
Grundmodul der Computereinheit ist ein Rechner mit einer Hard disk- Speicherkapazität zur Datendokumentation (zum Beispiel einer Krankenakte) aller gewählten Grund- und Einzelfunktionen im zeitlichen Verlauf. Die Größe der Festplatte richtet sich nach dem Volumen der zu installierenden Software und einer zu errechnenden Speicherkapazität für Daten des CMSI- Systems in einem Einsatzzeitraum von 6 Monaten.Basic module of the computer unit is a computer with a hard disk storage capacity for data documentation (for example, a medical record) of all selected basic and individual functions over time. The size of the hard disk depends on the volume of the software to be installed and a storage capacity to be calculated for data of the CMSI system in a usage period of 6 months.
Weitere Dokumentationen für die Krankenakte sind in den Einzelfunktionen enthalten.Further documentation for the medical record is contained in the individual functions.
Siehe Figur 32See Figure 32
Registrierung der Reanimationsphase/-position.Registration of the resuscitation phase / position.
Siehe Figur 59See Figure 59
Gewichtsmessung. Digitale und graphische Darstellung,Weight measurement. Digital and graphical representation,
"select patients weight": Initiales Gewicht des Patienten."select patients weight": Initial weight of the patient.
"actual weight": zeigt das automatisch graphisch und digital per Datenspeicher registrierte aktuelle Gewicht des Patienten."actual weight": shows the current weight of the patient, which is automatically graphically and digitally registered via data memory.
Das aktuelle Datum (siehe Figur 5) wird jeweils in der Fußzeile gezeigt und registriert.The current date (see FIG. 5) is shown and registered in the footer.
Diagramm "weight": das initiale Gewicht des Patienten wird in der Vektormitte gezeigt.
Wird auf das Diagramm geklickt, wird automatisch das Datum zusätzlich angezeigt.Diagram "weight": the initial weight of the patient is shown in the vector center. If the diagram is clicked, the date will be displayed automatically.
"add diagrarn": Hinzufügen eines weiteren Diagrammes."add diagrarn": Add another diagram.
Siehe Figur 35See Figure 35
Fortlaufende tägliche automatische Gewichtsmessung und Registrierung. Nachfolgende Graphiken mit gleicher Darstellung ohne Limitierung, "overall view": Das Diagramm zeigt die Gewichtsentwicklung in 1 Woche, 1 Monat und während der gesamten Zeit der Gewichtsmessung.Continuous daily automatic weight measurement and registration. The following graphics with the same representation without limitation, "overall view": The diagram shows the weight development in 1 week, 1 month and during the entire time of the weight measurement.
Ausgestaltung zur Verabreichung von spitzen oder stumpfen Klopf-, Streichel-, Bürst- oder Druckreizen an unterschiedlichen Körperstellen.Embodiment for the administration of pointed or blunt tapping, stroking, brushing or pressure stimuli at different body sites.
Die Steuerungselemente für die taktile Reizgebung sind explizit beschrieben: differenziert wird zwischen einem "Standard setup" und einem "Individual setup".The control elements for tactile stimulation are described explicitly: a distinction is made between a "standard setup" and an "individual setup".
Siehe Figuren 46, 43 und 45.See Figures 46, 43 and 45.
Lüftungseinheitventilation unit
Das Monitorbild zeigt die Steuerfunktion "thermo System".The monitor picture shows the control function "thermo system".
Siehe Figur 62See Figure 62
Siehe Figur 57See Figure 57
Thermosystem zur Regulation der Körpertemperatur.Thermosystem for the regulation of body temperature.
Technisch erfolgt eine Feed back- Einstellung über eine z.B. rektal eingelegte Thermosonde; das Thermosystem regelt die Körpertemperatur auf die vorgewählte Gradzahl.Technically, a feedback setting is made via a e.g. rectally inserted thermoprobe; the thermo system regulates the body temperature to the preselected number of degrees.
Ohne Feed- back- Einstellung kann die Temperatur des Thermosystems über die Funktion "individual setup" manuell geregelt werden.
Siehe Figur 48Without feedback setting, the temperature of the thermo system can be controlled manually via the "individual setup" function. See Figure 48
Individuelle Einstellung der Temperatur des Thermosystems über einen mittels Pen zu bedienenden Schieberegler.Individual adjustment of the temperature of the thermo system via a pen to be operated slider.
Siehe Figur 49See Figure 49
Standard- Einstellung des Thermosystems auf 37 Grad Celsius; bei Feed- back: Erreichen der 37 Grad Celsius Körperkerntemperatur, bei fehlendem Feed- back Thennosystem- Temperatur.Standard setting of the thermo system to 37 degrees Celsius; with feedback: reaching the 37 degrees Celsius body core temperature, in the absence of feedback Thennosystem- temperature.
Siehe Figur 4See Figure 4
Schemata für die beweglichen einzelnen Schalenelemente der 5 Grundmodule.Schemes for the movable individual shell elements of the 5 basic modules.
1 : Schale aus ultraleichtem Material (z.B. Glasfaser) 2: Antidekubitus- Element 3: Thermosystem1: shell of ultralight material (e.g., fiberglass) 2: anti-decubitus element 3: thermosystem
4: Wasserdichte Matratzenauflage, beziehbar 5: Teleskoparmsystem.4: Waterproof mattress pad, available 5: Telescopic arm system.
Entscheidend für die Technik des Thermosystems sind die Patienten- bezogenen individuellen Regulationsmöglichkeiten.Decisive for the technique of the thermosystem are the patient-related individual regulation possibilities.
In dem erfindungsgemäßen System werden bevorzugt englischsprachige Begriffe verwendet (wie in den Screenshots beispielhaft dargestellt), mit den folgenden Übersetzungen:In the system according to the invention preferably English-language terms are used (as exemplified in the screenshots), with the following translations:
Claims
1. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ), umfassend ein Bettgestell (2), das bewegbare Teile aufweist, mindestens eine Antriebseinheit (3) für das Bewegung der bewegbarenA controllable hospital bed (1), comprising a bed frame (2) having movable parts, at least one drive unit (3) for the movement of the movable
Teile und/oder zum Fahren der bewegbaren Teile in bestimmte Positionen, mindestens eine Steuereinheit (4) zum Steuern der mindestens einen Antriebseinheit (3) und mindestens eine Speichereinheit (5) zur Speicherung einer Vielzahl von bestimmten Positionen und Funktionen, wobei die bestimmten Positionen eine Schockposition, eine Herzposition, eine Zerebralposition, eine Sitzposition, eine Rückenposition, eine Wiederbelebungsposition und/oder eine horizontale Position umfassen, wobei die Funktionen ein kontinuierliches Bewegen von Extremitäten und/oder eines Rumpfes, eine Vibrationsfunktion, eine Druckgeschwürprophylaxefunktion, eine Auswahl von verschiedenen Positionen mittels einer schnellen und direkten Einstellung und/oder eine Gewichtskontrollfunktion umfassen, wobei die Steuereinheit (4) eine Mehrzahl der bestimmten Positionen und Funktionen bereitstellt und wobei die Positionen und die Funktionen individuell konfigurierbar sind und in der Speichereinheit (5) abgelegt werden.Parts and / or for driving the movable parts in certain positions, at least one control unit (4) for controlling the at least one drive unit (3) and at least one memory unit (5) for storing a plurality of specific positions and functions, wherein the determined positions Shock position, a heart position, a cerebral position, a sitting position, a back position, a resuscitation position and / or a horizontal position, the functions include a continuous movement of extremities and / or a trunk, a vibration function, pressure ulcer prophylactic function, a selection of different positions a fast and direct adjustment and / or a weight control function, wherein the control unit (4) provides a plurality of the determined positions and functions and wherein the positions and the functions are individually configurable and stored in the memory unit (5).
2. Steuerbares Krankenbett nach Anspruch 1 , wobei das Bettgestell (2) ein erstes bewegbares Teil zum Halten und Bewegen eines Kopf- und Rumpfbereiches eines Patienten und ein zweites, drittes, viertes und fünftes bewegbares Teil zum Halten und Bewegen jeweils einer Extremität des Patienten aufweist.A steerable bedside according to claim 1, wherein the bed frame (2) comprises a first movable part for holding and moving a head and trunk area of a patient, and second, third, fourth and fifth movable parts for holding and moving, respectively, a limb of the patient ,
3. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei das steuerbare Krankenbett mindestens eine Sensoreinheit aufweist.3. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein the controllable hospital bed has at least one sensor unit.
4. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei das steuerbare Krankenbett ein akustisches System zur Ausgabe akustischer Reize aufweist. 4. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein the controllable hospital bed has an acoustic system for the output of acoustic stimuli.
5. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei das Krankenbett ein Thermosystem zur Regulierung einer Körpertemperatur aufweist.5. A controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein the hospital bed has a thermo-system for regulating a body temperature.
6. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei die mindestens eine Antriebseinheit (3) elektrisch und oder hydraulisch ausgestaltet ist.6. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein the at least one drive unit (3) is configured electrically and or hydraulically.
7. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei das steuerbare Krankenbett (1) eine Alarmfunktion bereitstellt.7. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein the taxable hospital bed (1) provides an alarm function.
8. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei die Steuereinheit (4) über einen Berührungsbildschirm (7) bedienbar ist.8. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein the control unit (4) via a touch screen (7) is operable.
9. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei das steuerbare Krankenbett (1) mindestens eine Kommunikationsschnittstelle (8) aufweist.9. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein the controllable hospital bed (1) has at least one communication interface (8).
10. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei die Antriebseinheiten (3) individuell gesteuert werden können.10. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein the drive units (3) can be controlled individually.
11. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei die Steuereinheit (4) eine Timingfunktion bereitstellt.11. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein the control unit (4) provides a timing function.
12. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, wobei in einem Rumpfbereich des steuerbaren Krankenbettes (1 ) Materialien verwendet werden, die eine Röntgenmessung im Wesentlichen nicht beeinträchtigen.12. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, wherein in a trunk area of the controllable hospital bed (1) materials are used, which do not affect an X-ray measurement substantially.
13. Verfahren zur Steuerung eines steuerbaren Krankenbettes (1) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche, umfassend mindestens einen der folgenden Schritte:13. A method for controlling a controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of the preceding claims, comprising at least one of the following steps:
Fahren des steuerbaren Krankenbetts (1 ) in eine ausgewählte Position, nachdem die ausgewählte Position konfiguriert und ausgewählt ist, Durchführen einer ausgewählten Funktion des steuerbaren Krankenbettes (1 ), nachdem die ausgewählte Funktion konfiguriert und ausgewählt ist, undDriving the steerable hospital bed (1) to a selected position after the selected position is configured and selected; Performing a selected function of the steerable hospital bed (1) after the selected function is configured and selected, and
Durchführen von Kontrollfunktionen und Bereitstellen eines Alarmssig- nals, wobei die Positionen und die Funktionen individuell konfigurierbar sind und in einer Speichereinheit (5) abgelegt werden.Performing control functions and providing an alarm signal, wherein the positions and the functions are individually configurable and stored in a memory unit (5).
14. Computerprogrammprodukt, das eine Steuerung für ein steuerbares Kran- kenbett (1 ) nach einem der vorherigen Ansprüche implementiert.14. A computer program product implementing a control for a steerable hospital bed (1) according to any preceding claim.
15. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1) für die Lagerung, Pflege, Therapie und Rehabilitation von, und der Prävention von Immobilitätsschäden bei, eingeschränkt mobilen oder immobilen Patienten, umfassend ein Bettgestell (2), das bewegbare oder auswechselbare Teile oder Module aufweist, mindestens eine Antriebseinheit (3) für die Bewegung oder für die Einstellung der bewegbaren Teile oder Module und/oder zum Fahren der bewegbaren Teile oder Module in von der Speichereinheit (5) gespeicherte oder in mittels der Steuereinheit (4) individuell eingestellte Positionen oder Bewegungsabläufe oder für sensorische Reize, mindestens eine Steuereinheit (4) mit Schnittstellen oder Reglern zum Steuern der mindestens einen Antriebseinheit (3), der eingestellten Positionen, der individuellen Bewegungsabläufe, der Lüftungs- und Klimatisierungseinheit (6), der sensorischen (taktilen, olefaktorischen oder akustischen) Reize und mindestens eine Speichereinheit (5) mit Schnittstellen oder Reglern zurA controllable hospital bed (1) for the storage, care, therapy and rehabilitation of, and the prevention of immobility in, limited mobile or immobile patients, comprising a bed frame (2) having movable or interchangeable parts or modules, at least one drive unit (3) for the movement or adjustment of the movable parts or modules and / or for driving the movable parts or modules in positions or movements stored by the storage unit (5) or individually set by the control unit (4) or for sensory stimuli at least one control unit (4) with interfaces or regulators for controlling the at least one drive unit (3), the set positions, the individual movement sequences, the ventilation and air conditioning unit (6), the sensory (tactile, olefaktorischen or acoustic) stimuli and at least a memory unit (5) with interfaces or regulators for
Eingabe, Speicherung, Verarbeitung, Übertragung und Wiedergabe (i) von Daten für (aa) Lagerungs- oder Bewegungstherapien, (bb) sensorische (taktile, olfaktorische oder akustische) Reize, (cc) Temperatur- und Belüftungseinstellungen und/oder (ii) von zur Dokumentation (Krankenakte) anfallenden Daten und/oder (iii) von einer Vielzahl von vorgespeicherten Grundpositionen und Grundfunktionen, eine Lüftungs- und Klimatisierungseinheit (6) zur Bereitstellung von benötigter Wärme, Kälte und BelüftungInputting, storing, processing, transmitting and reproducing (i) data for (aa) storage or movement therapies, (bb) sensory (tactile, olfactory or acoustic) stimuli, (cc) temperature and ventilation settings, and / or (ii) for the documentation (medical records) resulting data and / or (iii) from a variety of pre-stored basic positions and basic functions, a ventilation and air conditioning unit (6) for providing required heat, cold and ventilation
Vibrationsmodule mit unterschiedlichen Befestigungselementeπ zur Verabreichung von Vibrationsreizen an unterschiedlichen Körperstellen, Sensorikmodule mit unterschiedlichen Befestigungselementen zur Verabreichung von spitzen oder stumpfen Klopf-, Streichel-, Bürst- oder Druckreizen an unterschiedlichen Körperstellen, olefaktorische Module zur Aufnahme oder Erzeugung oder Wiedergabe von Gerüchen und deren Verabreichung an den Patienten, akustische Module zur Aufnahme oder Erzeugung oder Wiedergabe von menschlichen und tierischen Stimmen, von Musik, von natürlichen oder von künstlichen - auch mechanischen - Geräuschen,Vibrating modules with different Befestigungselementeπ for administering vibration stimuli at different body sites, sensor modules with different fasteners for the administration of sharp or blunt Knock-, stroking, brushing or pressure stimuli at different body sites, olefaktorische modules for recording or generating or reproducing odors and their administration the patient, acoustic modules for recording or producing or reproducing human and animal voices, music, natural or artificial - even mechanical - noises,
wobei die Steuereinheit (4) und die Speichereinheit (5) ausfallsicher gestaltet sind und durch geeignete Individualisierungsmaßnahmen (wie z.B. durch PIN- Eingabe und/oder durch Iris-Scan und/oder durch Haut-Scan und/oder durch RFID-tag und/oder durch Magnetstreifenkarte und/oder durch andere Maßnahmen) gegen unerwünschte Manipulation oder gegen unbeabsichtigte Änderung der getroffenen Einstellung sicherbar sind und/oder eine Verbindung zu nicht zum Krankenbett gehörenden intensivmedizinischen Überwachungssystemen und deren Alarmfunktionen haben können um im Alarmfall eine sofortige Abschaltung der kinetischen Module des Krankenbetts sicherzustellen, wobei die bestimmten Positionen des Krankenbetts eine Schockposition, eine Herzposition, eine Zerebralposition, eine Sitzposition, eine Schachtellage- rung/Rückenposition, eine Wiederbelebungsposition und/oder eine horizontale Position umfassen, wobei die individuell einstellbaren Funktionen ein kontinuierliches oder periodisches Bewegen mit unterschiedlicher Geschwindigkeit, Intensität, unterschiedlichen Radien von jeweils auswählbaren Extremitäten und/oder des Rump- fes, eine Vibrationsfunktion, das therapeutische Einspielen und Steuern von sensorischen sowie taktilen Reizen, eine für Körperabschnitte unterschiedlich einstellbare Temperierung und Belüftung des Patienten, eine Auswahl von ver- schiedenen Positionen mittels einer schnellen und direkten Einstellung und/oder eine Gewichtskontrollfunktion umfassen, wobei das olefaktorische Modul Möglichkeiten zur Aufnahme, Erzeugung, Wiedergabe und Verstärkung von Gerüchen und deren Zuleitung in den Ge- sichts- und/oder Mund- und/oder Nasenbereich des Patienten umfassen kann; wobei das Sensorikmodul für taktile Reize unter anderem (i) vakuum- und/oder druckluftgesteuerte und/oder rnagnetgesteuerte und/oder elektromotorgesteuerte Antriebsteile mit einheitlicher Aufnahme und/oder (ii) unterschiedliche Therapiestücke für verschiedene Therapieformen die jeweils in die einheitli- che Aufnahme passen und/oder (iii) auf der Patientenseite der Therapiestücke unterschiedlich geformte und aus therapeutisch sinnvollen Materialien bestehende Oberflächen für Vibrationen und/oder für Druckreize und/oder für Streichelreize und/oder für Klopfreize und/oder für Nadelreize und/oder für Bürstenreize haben kann und/oder (iv) mittels unterschiedlichen Befestigungsgeschirren an verschiedenen Körperstellen und/oder mit geeigneten Befestigungsvorrichtungen an geeignete Stellen des Krankenbetts angebracht werden kann; wobei das akustische Modul einen Datenspeicher und ein Aufnahme- /Abspielgerät und Verstärker und/oder Lautsprecher und/oder Kopfhörer für Geräusche (einschließlich Eignung für menschliche oder tierische Stimmen, für natürliche oder künstliche Geräusche sowie für Musik) umfassen kann. wobei die Steuereinheit (4) eine Mehrzahl der bestimmten Positionen und Funktionen bereitstellt und wobei die Positionen und die Funktionen individuell konfigurierbar sind und in der sicherbaren Speichereinheit (5) abgelegt werden.wherein the control unit (4) and the memory unit (5) are designed to be fail-safe and by suitable customization measures (such as PIN input and / or by iris scan and / or skin scan and / or by RFID tag and / or by magnetic stripe card and / or by other measures) against unwanted manipulation or against unintentional change of the adopted setting are securable and / or a connection to non-hospital bed intensive care monitoring systems and their alarm functions may have to ensure an immediate shutdown of the kinetic modules of the hospital bed in case of alarm wherein the determined positions of the hospital bed comprise a shock position, a cardiac position, a cerebral position, a sitting position, a box position / back position, a resuscitation position and / or a horizontal position, wherein the individually adjustable functions include a continuous or periodic movement egen with different speed, intensity, different radii of each selectable limbs and / or the hull, a vibration function, the therapeutic import and control of sensory and tactile stimuli, a different body sections for adjustable temperature and ventilation of the patient, a selection of ver - various positions by means of a quick and direct adjustment and / or a weight control function, the olefaktorische module possibilities for recording, generating, reproducing and amplifying odors and their supply to the face and / or mouth and / or nose area of the patient may include; wherein the sensor module for tactile stimuli inter alia (i) vacuum and / or compressed air controlled and / or magneto-controlled and / or electric motor-driven drive parts with uniform recording and / or (ii) different therapy pieces for different forms of therapy each fit into the uniform recording and / or (iii) on the patient side of the therapy pieces differently shaped and made of therapeutically useful materials existing surfaces for vibration and / or for pressure stimuli and / or for petting and / or for knocking and / or for needle stimuli and / or for brush stimuli and / / or (iv) can be attached to appropriate locations of the hospital bed by means of different attachment harnesses at different body locations and / or with suitable attachment devices; wherein the acoustic module may comprise a data memory and a recording / playback device and amplifiers and / or loudspeakers and / or headphones (including suitability for human or animal voices, for natural or artificial sounds as well as for music). wherein the control unit (4) provides a plurality of the determined positions and functions, and wherein the positions and the functions are individually configurable and stored in the securable storage unit (5).
16. Steuerbares Krankenbett nach Anspruch 15, wobei das Bettgestell (2) ein erstes bewegbares Teil zum Halten und Bewegen eines Kopf- und Rumpfbereiches eines Patienten und ein zweites, drittes, viertes und fünftes jeweils ein- oder mehrgliedriges, bewegbares Teil zum Halten und Bewegen jeweils einer Extremität des Patienten aufweist und/oder (i) diese Teile entsprechend der Körpergröße des jeweiligen Patienten verstellbar sind und/oder (ii) diese Teile eine Bewegung der jeweiligen Körperteile (Rumpfteil, Kopf-/Halsbereich, Extremität) (aa) in verstellbaren Radien und/oder (bb) mit verstellbarer Frequenz und/oder (cc) in verstellbaren Ebenen und/oder (dd) in gestreckter Bewegung und/oder (ee) in beu- gender und streckender Bewegung und/oder (ff) in einer Kombination aus mehreren Bewegungsarten in verschiedenen Radien und/oder auf verschiedenen Ebenen und/oder in verschiedener Frequenz und/oder (gg) mit einem einstellbaren Maximalwiederstand (maximale Bewegungskraft) zum bewegten Körperteil zu- lässt.A steerable bedside according to claim 15, wherein the bed frame (2) comprises a first movable member for holding and moving a head and trunk region of a patient and a second, third, fourth and fifth movable member for holding and moving one or more members each having a limb of the patient and / or (i) these parts are adjustable according to the height of the respective patient and / or (ii) these parts movement of the respective body parts (torso, head / neck area, limb) (aa) in adjustable Radii and / or (bb) with adjustable frequency and / or (cc) in adjustable planes and / or (dd) in extended motion and / or (ee) in bulk gender and stretching movement and / or (ff) in a combination of several types of movement in different radii and / or on different levels and / or in different frequencies and / or (gg) with an adjustable maximum resistance (maximum movement force) to the moving body part. leaves.
17. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach Ansprüche 15 oder 16, wobei das steuerbare Krankenbett mindestens eine Sensoreinheit aufweist.17. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to claims 15 or 16, wherein the controllable hospital bed has at least one sensor unit.
18. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 17, wobei das steuerbare Krankenbett ein akustisches System zur Ausgabe akustischer Reize aufweist.18. A controllable hospital bed (1) according to any one of claims 15 to 17, wherein the controllable hospital bed has an acoustic system for the output of acoustic stimuli.
19. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 18, wobei das Krankenbett ein Thermosystem zur Regulierung einer Körpertemperatur und zur Belüftung der Haut mit lokal unterschiedlichen Klimazonen für verschiedene Körperteile aufweist.The controllable hospital bed (1) according to any one of claims 15 to 18, wherein the hospital bed has a thermosystem for regulating a body temperature and for ventilating the skin with locally different climatic zones for different body parts.
20. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 19, wobei die mindestens eine Antriebseinheit (3) elektrisch und oder pneumatisch und oder hydraulisch ausgestaltet ist.20. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of claims 15 to 19, wherein the at least one drive unit (3) is configured electrically and or pneumatically and or hydraulically.
21. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 20, wobei das steuerbare Krankenbett (1 ) eine eigene Alarmfunktion bereitstellt und/oder Alarmfunktionen von angeschlossenen intensivmedizinischen Überwachungssystemen erkennen und/oder darauf reagieren kann.21. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to any one of claims 15 to 20, wherein the controllable hospital bed (1) provides its own alarm function and / or recognize alarm functions of connected intensive care monitoring systems and / or can respond.
22. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 21 , wobei die Steuereinheit (4) über einen Berührungsbildschirm (7) und/oder über eine angeschlossene Eingabeeinheit (wie zum Beispiel ein Laptop) bedienbar ist. 22. A controllable hospital bed (1) according to any one of claims 15 to 21, wherein the control unit (4) via a touch screen (7) and / or via a connected input unit (such as a laptop) is operable.
23. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 22, wobei das steuerbare Krankenbett (1 ) mindestens eine Kommunikationsschnittstelle zur Einstellung oder Datenübertragung (8) aufweist.23. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of claims 15 to 22, wherein the controllable hospital bed (1) has at least one communication interface for setting or data transmission (8).
24. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 23, wobei die Antriebseinheiten (3) und/oder die Funktionen individuell gesteuert werden können.24. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of claims 15 to 23, wherein the drive units (3) and / or the functions can be controlled individually.
25. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 24, wobei die Steuereinheit (4) eine Timingfunktion (Zeitschaltuhr) für das Anfahren und Beenden von einzelnen Funktionen zu unterschiedlichen Zeiten und/oder zur generellen Unterscheidung zwischen Tagesprogramm und Nachtprogramm bereitstellt.25. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to any one of claims 15 to 24, wherein the control unit (4) provides a timing function (timer) for starting and stopping individual functions at different times and / or for the general distinction between daily program and night program.
26. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 25, wobei im unteren Rumpfbereich ein Liegekissenmodul gegen ein seitlich oder nach unten herausnehmbares Modul zur Aufnahme von Ausscheidungen eines Patienten getauscht werden kann.26. A controllable hospital bed (1) according to any one of claims 15 to 25, wherein in the lower trunk area, a mattress module can be exchanged for a laterally or downwardly removable module for receiving excretions of a patient.
27. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 26, wobei im Kopfbereich ein Liegekissenmodul gegen ein seitlich oder nach unten herausnehmbares Modul mit Schale und/oder Tropfgitter für Haarwäsche getauscht werden kann.27. Controllable hospital bed (1) according to any one of claims 15 to 26, wherein in the head area a mattress module can be exchanged for a laterally or downwardly removable module with shell and / or drip grid for shampooing.
28. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 27, wobei für die Auflagebereiche des Rumpfes und der Extremitäten des Patienten für das steuerbare Krankenbett (1 ) Materialien verwendet werden, die eine Röntgenmes- sung im Wesentlichen nicht beeinträchtigen und/oder bei dem im Thoraxbereich sowie im Abdomenbereich des Patienten Liegekissenmodul(e) gegen seitlich oder nach unten herausnehmbare Module mit Röntgenfilmkassette getauscht werden können. 28. A controllable hospital bed (1) according to any one of claims 15 to 27, wherein for the support areas of the torso and the extremities of the patient for the controllable hospital bed (1) materials are used, which does not substantially affect an X-ray measurement and / or at in the thorax region and in the abdomen region of the patient lying cushion module (s) can be exchanged for laterally or downwardly removable modules with X-ray film cassette.
29. Steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 28, wobei die Konstruktion und der Aufbau des steuerbaren Krankenbettes (1 ) die Abmessungen einfacher Krankenbetten nicht wesentlich überschreiten und die verwendeten Materialien das Gewicht des steuerbaren Krankenbettes gegenüber dem übli- chen Gewicht einfacher Krankenbetten nicht mehr als verdoppeln.29. A controllable hospital bed (1) according to any one of claims 15 to 28, wherein the construction and structure of the controllable hospital bed (1) does not significantly exceed the dimensions of simple hospital beds and the materials used simplify the weight of the controllable hospital bed compared to the usual weight easier Do not double hospital beds more than double.
30. Verfahren zur Steuerung eines steuerbaren Krankenbettes (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 29, umfassend mindestens einen der folgenden Schritte:30. A method for controlling a controllable hospital bed (1) according to one of claims 15 to 29, comprising at least one of the following steps:
Fahren des steuerbaren Krankenbetts (1) in eine ausgewählte Position, nachdem die ausgewählte Position konfiguriert und ausgewählt ist,Driving the steerable hospital bed (1) to a selected position after the selected position is configured and selected;
Durchführen einer ausgewählten Funktion des steuerbaren Krankenbettes (1 ), nachdem die ausgewählte Funktion individuell konfiguriert und ausgewählt ist, undPerforming a selected function of the steerable hospital bed (1) after the selected function is individually configured and selected, and
Durchführen von Kontrollfunktionen und Bereitstellen eines Alarmsig- nals,Performing control functions and providing an alarm signal,
- Absicherung der vorgenommenen Einstellungen gegen ungewollte Verstellung oder gegen unerwünschte Manipulation durch nicht autorisierte Personen. wobei die Positionen und die Funktionen individuell konfigurierbar sind und in einer Speichereinheit (5) sowohl zur Dokumentation, als auch zur Wiederholung abgelegt werden.- Protection of the settings made against unintentional adjustment or against unwanted manipulation by unauthorized persons. wherein the positions and the functions are individually configurable and stored in a memory unit (5) both for documentation and for repetition.
31. Computerprogrammprodukt, das eine Steuerung für ein steuerbares Krankenbett (1 ) nach einem der Ansprüche 15 bis 30 implementiert. A computer program product implementing a steerable bed control (1) as claimed in any one of claims 15 to 30.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP09737887.1A EP2273962B1 (en) | 2008-04-29 | 2009-04-29 | Controllable hospital bed |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE200810021503 DE102008021503B4 (en) | 2008-04-29 | 2008-04-29 | Controllable bedside, control method and computer program product |
| DE102008021503.1 | 2008-04-29 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2009132843A1 true WO2009132843A1 (en) | 2009-11-05 |
Family
ID=40814774
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/EP2009/003114 WO2009132843A1 (en) | 2008-04-29 | 2009-04-29 | Controllable hospital bed |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2273962B1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE102008021503B4 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2009132843A1 (en) |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE8304560U1 (en) | 1983-02-18 | 1983-06-09 | Ciecierski, Wolf, 8403 Bad Abbach | Adjustable lounger |
| DE19603318A1 (en) | 1996-01-31 | 1997-08-14 | Dewert Antriebs Systemtech | Control system for electric motor-operated adjustment devices for hospital beds |
| DE10001687A1 (en) | 2000-01-11 | 2001-07-12 | Albrecht Hoerlin | Bed for treatment of bedsores, with bed frame mounted on at least three hydraulic cylinders which can be pressurized |
| US6351678B1 (en) * | 1997-11-07 | 2002-02-26 | Hill-Rom Services, Inc. | Medical equipment controller |
| US20030052787A1 (en) * | 2001-08-03 | 2003-03-20 | Zerhusen Robert Mark | Patient point-of-care computer system |
| EP1486191A1 (en) * | 2002-02-22 | 2004-12-15 | Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. | Movable bed |
| EP1669049A1 (en) * | 2004-12-07 | 2006-06-14 | Hill-Rom Services, Inc. | Touch screen control for lateral rotation of a hospital bed mattress |
| WO2006061834A2 (en) | 2004-12-07 | 2006-06-15 | Tylerton International Inc. | Device and method for training, rehabilitation and/or support |
| US20060123546A1 (en) * | 2004-12-10 | 2006-06-15 | Horton William C | Dynamic surgical table system |
| US20060168729A1 (en) * | 1995-08-04 | 2006-08-03 | Weismiller Matthew W | Hospital bed and mattress having extendable foot section |
-
2008
- 2008-04-29 DE DE200810021503 patent/DE102008021503B4/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2009
- 2009-04-29 WO PCT/EP2009/003114 patent/WO2009132843A1/en active Application Filing
- 2009-04-29 EP EP09737887.1A patent/EP2273962B1/en not_active Not-in-force
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE8304560U1 (en) | 1983-02-18 | 1983-06-09 | Ciecierski, Wolf, 8403 Bad Abbach | Adjustable lounger |
| US20060168729A1 (en) * | 1995-08-04 | 2006-08-03 | Weismiller Matthew W | Hospital bed and mattress having extendable foot section |
| DE19603318A1 (en) | 1996-01-31 | 1997-08-14 | Dewert Antriebs Systemtech | Control system for electric motor-operated adjustment devices for hospital beds |
| US6351678B1 (en) * | 1997-11-07 | 2002-02-26 | Hill-Rom Services, Inc. | Medical equipment controller |
| DE10001687A1 (en) | 2000-01-11 | 2001-07-12 | Albrecht Hoerlin | Bed for treatment of bedsores, with bed frame mounted on at least three hydraulic cylinders which can be pressurized |
| US20030052787A1 (en) * | 2001-08-03 | 2003-03-20 | Zerhusen Robert Mark | Patient point-of-care computer system |
| EP1486191A1 (en) * | 2002-02-22 | 2004-12-15 | Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. | Movable bed |
| EP1669049A1 (en) * | 2004-12-07 | 2006-06-14 | Hill-Rom Services, Inc. | Touch screen control for lateral rotation of a hospital bed mattress |
| WO2006061834A2 (en) | 2004-12-07 | 2006-06-15 | Tylerton International Inc. | Device and method for training, rehabilitation and/or support |
| US20060123546A1 (en) * | 2004-12-10 | 2006-06-15 | Horton William C | Dynamic surgical table system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2273962B1 (en) | 2013-10-09 |
| DE102008021503B4 (en) | 2013-01-03 |
| EP2273962A1 (en) | 2011-01-19 |
| DE102008021503A1 (en) | 2009-11-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN204909915U (en) | Intelligence air conditioner massage mattress | |
| US20080132383A1 (en) | Device And Method For Training, Rehabilitation And/Or Support | |
| Elliott et al. | Rehabilitation interventions for vegetative and minimally conscious patients | |
| EP3202450B1 (en) | Device for generating sensory stimuli for a child | |
| CN204709198U (en) | Orthopedic chair | |
| CN103750968A (en) | Two-axis automatic hospital bed | |
| McCorkle | Chiropractic: a deviant theory of disease and treatment in contemporary western culture | |
| Ghersi et al. | From modern push-button hospital-beds to 20th century mechatronic beds: a review | |
| Haber | Technology in aging | |
| WO2021038105A1 (en) | Reclining unit for caring for a premature baby, in particular for an incubator | |
| Crews et al. | Motor-evoked potentials following imagery and limb disuse | |
| DE202019002177U1 (en) | Data processing system for an electric motor driven ambulance or Mobilisationsrollstuhl | |
| WO2009132843A1 (en) | Controllable hospital bed | |
| WO2019206954A1 (en) | Multi-sensor therapeutic/diagnostic system for monitoring orthopedic training and athletic performance | |
| Foster et al. | Behavior Following Acute Myocardial Infraction | |
| Bazzo et al. | Imagine this! Infinite uses of guided imagery in women’s health | |
| CN104510203A (en) | Music somatosensory relaxing chair | |
| Pawlitza | Design of a Multifunctional and Modular Bed System | |
| Jones | Doctors' health and wellbeing: Tasty toasties provide a much needed frontline boost | |
| Tobis | Physical medicine and rehabilitation management in aphasia | |
| Crisci et al. | Old patients: unethical thoughts | |
| CN104510580B (en) | Medical patient turning-over side-lying fixing device | |
| Kovach et al. | Understanding Huntington's disease: An overview of symptomatology and nursing care | |
| Raynolds | Teaching parents home care after surgery for scoliosis | |
| CN113576783A (en) | Multi-functional intelligent nursing bed based on internet technique |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09737887 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE1 | Request for preliminary examination filed after expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009737887 Country of ref document: EP |