Delhi master plan
- 1. SUBMITTED BY- GARIMA SINGH CLASS-B.ARCH 3 YEAR
- 2. ABOUT DELHI The capital city of India, is situated on the banks of Yamuna and extends over an area of 1483 sq. km . The city is bordered by Haryana on its north, west and south and Uttar Pradesh on its east. Delhi is the largest commercial center in the Northern India and the culture of Delhi has been influenced by its important history. It is approached through seven arched gateways, including the Delhi Gate in the south, the Ajmeri Gate in the east, and the Kashmere Gate in the north. Within the walls is a maze of congested narrow streets, alleys, busy bazaars, and some of the nation's most spectacular Indo-Muslim architectural features.
- 3. Climate and Geography The region has a tropical steppe climate. It is characterized with extremely hot and dry summers and chilling winters. Monthly temperatures range from 14.3° C in January (minimum 3°C) to 34.5°C in June (maximum 47°C). DEMOGRAPHICS Delhi holds the second position in the list of largest metropolises in India as per its population. As per the census 2011, the population of Delhi is 1,67,87,941 and its sex ratio is 866 females per 1000 males. The population density is 11,297 persons per sq .km There is no regional language of Delhi; like different cultures it has adapted languages from the rest of the nation. Languages commonly spoken are Hindi, Punjabi, Urdu and English.
- 4. Tourism Delhi is an international metropolis with excellent tourist spots, recreational facilities, and a history that goes back to antiquity. Economy Delhi has become a nucleus of trade, commerce and industry in the northern region. Government office complexes are a major source of employment and the city is also home to important medical, agricultural and educational institutions. It is often categorized as a "service town"; however, industry is rapidly expanding. The most important industrial sector in Delhi is however the tertiary sector. Most industries are located in the west, south and southeast of the city.
- 7. Delhi Master plan-2021 was drafted in end 2005. The Delhi Master Plan 2021 was finally notified on February 7, 2007, six years after it was due. The Plan acknowledges 7,000 objections/suggestions. Board of Enquiry, which met 17 times.
- 8. Physical characteristics and natural resources, City influence area & Settlement System Demography Economic base including employment in formal and informal sectors Housing and shelter Social infrastructures (health & education) Transport network (road, railway , water ways and airways) Utilities & services ( water supply , drainage and sewerage, solid waste management and energy) Land use Resource mobilization and Investment Plans. THE MAJOR CONTENTS OF THE MASTER PLAN
- 9. Government and Politics Delhi is an important cultural, commercial as well as political hub of India. At present, it has 11 districts. They are; Central Delhi, North Delhi, South Delhi, East Delhi, North East Delhi, South West Delhi, New Delhi, North West Delhi and West Delhi. Delhi is divided into three legislative; New Delhi Municipal Committee (NDMC), Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD) and Delhi Cantonment Board (DCB). The Supreme Court of India is located in Delhi, along with the regional Delhi High Court, the Magistrate Court, the Sessions Court for criminal cases and other Small Causes Courts for civil cases.
- 10. Transportation Delhi is well connected by air, road and railways to the rest of the country. The Indira Gandhi International Airport located in southwest of Delhi caters to domestic as well as international flights from all over the world. It is maintained by the GMR Group and is one of the busiest airports in South Asia. There are five major railway stations in Delhi: New Delhi Railway Station, Old Delhi Railway Station, Nizamuddin Railway Station, Anand Vihar Railway Terminal and Sarai Rohilla Railway Station. A suburban railway system also connects the city and neighbouring NCR regions.
- 11. Delhi is linked with five national highways; they are number 1, 2, 8, 10 and 24. In Delhi, Public transport vehicles are fuelled by Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and the state-owned Delhi Transport Corporation (DTC) is the major bus service provider. Taxis, radio cabs, auto rickshaws and cycle rickshaws are also easily available . The Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) has built a rapid transit system here. It serves the city and its neighbouring NCR regions like Gurgaon, Noida and Ghaziabad. The metro network consists of 6 lines and 142 stations. The total length of the lines is about 190 km. Delhi Metro will soon expand as more phases and lines are currently under-construction. Transportation
- 12. New Delhi Railway Station Old Delhi Railway Station Nizamuddin Railway Station Anand Vihar Railway Terminal and Sarai Rohilla Railway Station. A suburban railway system also connects the city and neighbouring NCR regions. There Are Five Major Railway Stations In Delhi:
- 13. As per 2001 Census, NCT of Delhi had a total population of 138 lakh. NCT Delhi is highly urbanized with 93.18% of its population living in urban areas as against the national average of 27.81%. During the course of implementation of the plan, attempt should be made to restrict the population of Delhi lower than 220 lakhs. This depends on the effective implementation of policies and proposals of Regional Plan 2021 by Govt. of NCT Delhi.
- 14. METROPOLITAN TRANSPORT AUTHORITY ROADS -Delhi is planned on a ring – radial pattern with a hierarchical road network. Broadly, the road network is designed for regional, intra – city and local traffic. 1. National Highways- The recommended minimum right of way (ROW) is 90 meters, wherever possible. However, within the city it shall not be less than 60meters. All the National Highways within the NCTD are to be access controlled upto the Outer Ring Road. 2. Arterial Roads -These include primary roads with access control and other primary roads. i) Primary Roads: Vehicular routes carrying heavy volumes of traffic will generally have free flow conditions. There will be access control on these roads. The recommended ROW in existing urban area is 60-80 mts.
- 15. 3. Sub Arterial Roads -These include primary and secondary collector streets. (i) Primary Collector: These roads will connect major arterial roads and inter residential district collectors. The recommended ROW in existing urban area is 30-40 mts. and minimum 45 mts Local Streets -These are intended for neighbourhood (or local) use on which through traffic is to be discouraged. The suggested ROW is 12 to 20 mts. METROPOLITAN TRANSPORT AUTHORITY
- 16. LAND DISTRIBUTION Residential : 50-55 % Commercial : 2-5% Industrial use : 10-12% Public and semi public – 8-10 % Open spaces parks – 10-15 % playgrounds • Communication – 15-18% Other special uses – about 5 %
- 17. Housing need is for 24 lakh new houses till 2021 for population of 23 Million. For 24 lakh houses, we need proportionate no. of shops. Provide them at the time we plan for the residential complex. This concept should be built at the planning stage so that shops and other commercial establishments can come up along with houses. HOUSING
- 18. There is a very feeble act in the master plan: The master plan suggests the following densities for various categories. ◦ Slum housing (up to 30 sq.m)-600 DUs/Ha ◦ Category I (above30-upto40sq.m.)-500 DUs/ Ha ◦ Category II (above40-upto80sq.m.)-250 DUs/ Ha ◦ Category III (above80sqm) - 175 DUs/Ha ◦ The Master plan has varying density like 30sqm i.e. 600 dwelling units per Hectare its impossible to achieve that. HOUSING
- 19. MIXED LANDUSE PROBLEMS The constant presence of outsiders/shoppers with no local loyalty will erode residential quality and endanger the women, the children and the aged The water supply & power situations would be worsen. Vehicular movement with increased parking & goods supply would create chaos with housing areas SOLUTIONS Segregating entry points into housing and shopping areas as an exclusive public Domain for residential use which alone provide safety. Parking of housing should be separated and commercial parking should be severely Restricted. This would not only reduce vehicular nuisance , noise and dust pollution But would also indirectly control the size of commercial activity. Water, Electricity sewerage and solid waste disposal etc would require increased
- 20. Vision 2021 is to make Delhi a global metropolis and a WORLD CLASS city. What the term “world class” means is undefined except somewhat commitment “where all the people would be engaged in productive work witha better quality of life, living in a sustainable environment”. Though, this statement should logically apply to all settlements and societies, whether “world class”or not.
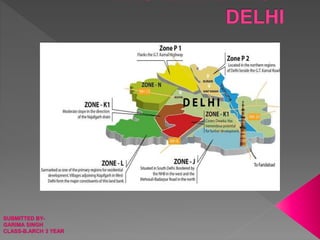
- 23. Zone- A (Old City) INTRODUCTION: As per the Master Plan for Delhi- 2021, notified on 07.02.07 the National Capital Territory of Delhi has been divided into 15 zones from A to H and J to P, of which 8 Zones are in the urban area, one in Riverbed and remaining 6 in the rural area. The zones K & P are subdivided into two part zones. The designated Special Area in MPD 2021 comprises of zone A (Walled city).Zone A (Other than Walled City) and Zone B. OTHER THAN WALLED CITY (Sub-Zone A-1 to A-12). Other than Walled City area also has a special character and therefore a separate zonal plan has been prepared. The area of the Zone is 559.13 hacts. and the population is 2.44 lacs as per MPD 2001.
- 24. WALLED CITY: (Sub- Zones A-13 to A-27 & Sub-zone C-1 Part) Walled City, an Old built up and historic area, has a special character and therefore, zonal Plan for the same has been prepared separately.
- 25. Zone 'C', is also known as 'Civil Lines Zone' and it is located towards North, covering an area of 3959 hac. and consists of 21 Sub-Zones The Boundaries Of The Zone- C Are As Under: North-East Part Ring Road, Outer Ring Road, Zone O (River Yamuna). N.H.-1 & P-II (North Delhi) adjoining Sub-zone C-21. North-West Zone P-H (Narela) & Zone P-II (North Delhi) South-East Old City (Zone-A) South-West Delhi Amritsar Railway Line, Zone-H (North West Delhi-l) Zone-C is identifiable with its prestigious Delhi University. Northerm Ridge, ISBT (Kashmiri Gate) and Tis Hazari Courts.
- 26. ZONAL (DIVISIONAL PLAN FOR ZONE 'D' (NEW DELHI) Under the Master Plan for Delhi- 2001, promulgated on 1.8.1990, the Union Territory of Delhi is divided into 15 Zones, out of which 8 zones are in Urban Delhi (A to H), 6 are in Urban Extension and Rural Areas (J to N and P) and one is for river and river front area (0). A zone could be divided into sub-zones. Zone 'D' is mainly comprised of Lutyens Garden City and extensions This zone is situated betvween river Yamuna on one side and the ridge on the other and comprises of important central areas of Delhi. MPD-2001 proposals have also underlined the import- ance of this Division as the most beautiful and planned national Capital area of New Delhi
- 27. INTRODUCTION - The NCT of Delhi has been divided in 15 nos. planning zones (division) designated from 'A' to 'P" (except Zone-l) in the Master Plan for Delhi 2021. Planning Zone comprises of an area of 8797 hects (approx.) It is surrounded on the three sides by the State of Uttar Pradesh and on the fourth side by river Yamuna. This Zone has been developing since pre independence era and through the MPD-1962, MPD 2001 and now MPD 2021. As such the zone has heterogeneous character where the unplanned areas and planned areas developed under the norms of various plans co- exist.
- 28. Zone- F In the context of Urban Delhi, Zone-F is identifiable with it's low density green character. This zone is mainly comprised of planned, well maintained posh residential localities. This also included rehabilitation colonies and Government housing areas. This Zone is situated in the south of Zone-D.
- 29. Zone 'G' is located in the West Delhi covering an area of about 11,865 Ha. And consists of 18 sub- zone (17 old as per MPD 1962 and 1 New). The zone is surrounded by Delhi Rohtak Railway Line in the North. Delhi Rewari railway line in the South- East, Pankha road in the South-West and Agricultural Green- Belt/Rural Area in the West.
- 30. Zone H' is also known as North West Delhi-l and it covers an area of 5677 Hac Zone H is distinctly characterized by well planned residential localities. This zone is situated between two major railway lines viz railway line to Ambala in the North East and the other tRohtak in the South West Prestigious TV Tower. Delhi Haat, developed parks, DDA Sports Centres with Internaltional Standards and protected forest area namely Shalimar Bagh are some of the significant features in this zone. Rohini Project Ph- l/II(Pant) forms part of this zone mosly in zones H-7, 8 & 9.
- 31. Planning Zone-J located in the South Delhi, is bounded by Mehrauli , Badarpur road in the. North, National Highway No.8 in the West, and National Capital Territory of Delhi boundary in the South and East. The total area of the zone as per MPD-2021 is about 15,178 Ha., out of which around 6,200 Ha. comprises of the 'Regional Park/ Ridge There are 30 villages/census towns falling in the zone.
- 34. L Zone of Delhi is all set to be the smart city that uses digital technologies to enhance performance and well being to reduce costs and resources consumption and also to engage more effectively and actively with its residents. It will have, among other facilities, 100% power, 100% web connectivity, 24x7 water supply and high frequency mass transport L – Zone Neighboring Dwarka on one side & Gurgaon on the other. The Zone covers an area of around 23 thousand Hectares
- 35. The Zone L of West Delhi is contemplated to be a major hub for population in the near future. The zone covers an area formulate policies and norms have been recognized in the Master Plan. Also, land measuring about 53.6 ha is to be kept of 22,979 hectares and is located in the South West Delhi, hence is closest to South Delhi
- 37. Zone 'N mainly comprises of the proposed Urban Extn./green belt and forms part of urb- anis able area under the Master Plan of Delhi (MPD-2021) North West part of Delhi and mainly constitutes of rural settlements and the industrial area of Bawana. It is connected by railway line towards Rohtak. The zone is situated on the Urban Extension Road I is passing through this zone.
- 38. As per MPD 2021 notified on 7.2.2007, the National Capital Territory of Delhi has been divided into fifteen zones (Divisions) designated 'A' to 'P" (except zone 'l'), eight in urban Delhi (A' to H), six in Urban Extension (J' to 'N' & P') and one for River a Yamuna/River front which has been designated as Zone 'O 1.2 The River Yamuna/ River front, Zone 'O' has special characteristics and ecological significance for which various studies have been conducted from time to time. As such, the Zonal Development Plan of Zone 'O' is conceived to set the strategies for rejuvenation of river Yamuna and eco-friendly development.
- 39. The P-I Zone is located in North West Delhi. The total area of the zone is 9,866 hectares of which 7,365 can be developed. The remaining 2,501 hectares is under the green belt as per MPD 2021 land use plan. It is proposed for a population of 16.2 lakh including that of the existing settlements. The existing railway line has been proposed as the major mass transit movement corridor for this zone. The residential areas are proposed to be located on both sides of the railway line within a distance of 3-4 Kms. An integrated system of green linkages and circulation network will connect residential areas with work centres and various social cultural facilities. Residential land use shall make up 42.98% of the total land area for P-I Zone and when fully developed will provide housing facilities to over 3.6 Lakh families from all socio-economic backgrounds
- 40. Zone P-II is the code name of DDA new housing hub provisioned under Delhi Master Plan 2021. The zone has been divided into 13 Sectors and has already been approved and notified by the Government of India as well as DDA under Sub Section (2) of Section 9 under Delhi Development Act 1957. Skyscrapers complete with helipads to help residents reach their workplaces in a matter of minutes, new apartments for 4.22 lakh families — for every category in space- starved Delhi, a leisure valley, river-front boulevard, city park, museum, art galleries, open-air theatres and large stretches of greens interspersed with water bodies and much more.
- 41. South Delhi - South Delhi is an administrative district of the National Capital Territory of Delhi in India. It is bounded by the Yamuna River to the east, the districts of New Delhi to the north, Faridabad District of Haryana state to the southeast, Gurgaon District of Haryana to the southwest, and South West Delhi to the west SOUTH DELHI-I
- 42. oSouth Delhi is an administrative district of the National Capital Territory of Delhi in India. o It is bounded by the Yamuna River to the east, the districts of New Delhi to the north, Faridabad District of Haryana state to the southeast, Gurgaon District of Haryana to the southwest, and South West Delhi to the west SOUTH DELHI-I
- 43. LISTED BELOW ARE VARIOUS AREAS UNDER SOUTH NEW DELHI: Kalkaji Chanakyapuri Defense Colony RK Puram Greater Kailash Lajpat Nagar Nehru Place Vasant Kunj South Extension Green Park Hauz Khas Panchsheel Enclave CR Park Sarojini Nagar Mehrauli Friends Colony Safdarjung
- 44. South New Delhi is bordered in the north by the districts of New Delhi, the Yamuna river to the east, Gurgaon district of Haryana to the southwest, Faridabad District of Haryana to the southeast and South West Delhi to the west. Ideally located this part of the city boasts of well-developed infrastructure, uninterrupted electricity and abundant water supply. South Delhi is one of the most high class areas in the city. South Delhi shelters some of the finest hotels, stores, tourist spots, infrastructures, historical monuments, nightclubs and restaurants. LISTED BELOW ARE VARIOUS AREAS UNDER SOUTH NEW DELHI:
- 45. South Delhi is huge in terms of area and it covers places such as Greater Kailash, Vasant Kunj, Lajpat Nagar, Safdarjung and Mehrauli. These are significant locations in New Delhi since they have both residential and commercial value. Chanakyapuri in South New Delhi is home to all the international embassies in India. Purana Qila, Qutub Minar and Humayun Tomb. Other tourist attractions in South New Delhi include Chattarpur Mandir, Lotus Temple, Lodi Garden and Kalindi Kunj. A FEW OF THE WELL-KNOWN MONUMENTS THAT YOU WILL FIND IN THIS AREA ARE
- 46. Given below are the important universities and academic institutions located in South New Delhi Jawahar Lal Nehru University Indian Institute of Technology Delhi National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) Delhi University, South Campus. EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS IN SOUTH NEW DELHI
- 47. Lajpat Nagar If you are a shopaholic then Lajpat Nagar is the best place for us. An entire area dedicated to numerous open markets, retail outlets and fashionable stores Lajpat Nagar provides large stocks of merchandize at cheap rates. Although it is a commercial region of South Delhi Lajpat Nagar is also home to some of the finest residential properties in Delhi. Nehru Place Nehru Place is one of the largest financial, commercial and business centers in South Delhi. It is also known as the information technology hub of New Delhi. It serves as the headquarters of a host of Indian firms. Incase you are a techie and desire to get the latest computer accessories at absolutely affordable rates then this is the ideal destination for you. Nehru Place is also has many restaurants to pamper your taste buds.
- 48. Greater Kailash An apt place for the middle class Greater Kailash is characterized by stylish apartments, busy markets and lively crowds. There are a number of retail chains and showrooms in this area. Greater Kailash has two divisions - Greater Kailash I and Greater Kailash II. There are a number of elegant nightlife venues and restaurants in this area as well. Chanakyapuri Chanakyapuri is considered among the prime localities in South Delhi. A prime residential place of most of the elites in the city Chanakpuri is home to numerous foreign embassies. A part from the many embassies you can also find important education centers, architectural monuments and a number of luxury hotels in this area. It is conveniently located at the heart of the city and the distance from the IGI Airport is around 14 km.
- 49. WATER Sustainable development of water resources in Delhi. Water Treatment Plants Capacity 2001 (in mgd) Capacity* 2021 (in mgd) 1. Chandrawal & II 90 100 2. Wazirabd 120 130 3. Haiderpur I & II 200 216 4. Bhagirathi 100 110 5. Dwarka – 40 6. Sonia Vihar – 140 7. Nangloi 40 40 8. Bawana – 20 9. Okhla - 20 10 . Ranney wells at Okhla 100 12 11 . Palla and other ground water sources – 91 Total 650 919
- 50. The existing capacity of sewerage system in Delhi is grossly inadequate, as only about 55% of the population is covered under organised conventional sewerage system and about 15% under on-site sanitation systems. Rest of the population does not have proper access to sanitation facilities. The increasing pollution in the river Yamuna is also a major indicator of lack of sewerage treatment facilities. Planning of the city must incorporate land at appropriate location for STP’s, sewerage pumping stations, CETP’s etc. Recycling plants of treated waste water and a plan for recycling of treated waste water to meet nonpotable water needs. Common effluent treatment plants (CETP’s) with supportive distributive infrastructure i.e. conveyance system has to be laid to carry treated wastewater from STP’s to the areas for alternative uses. Decentralised STP’s with smaller capacities are to be provided at the subcity level (10 lakh population). Possibility of recovering energy/ gas SEWERAGE
- 51. Drainage has two aspects: flood protection and storm water discharge, which are interrelated. The storm water and flood protection in Delhi are not local but have regional bearing including areas of Haryana and Rajasthan. The main drainage system of Delhi is such that all water collected through main drains, link drains and small rivulets is discharged into Yamuna. On the basis of topographical characteristics and existing drainage network, NCT of Delhi has been divided into five drainage basins namely Najafgarh, Alipur, Shahdara, Khushak nallah and Mehrauli. DRAINAGE
- 52. Delhi’s requirement of power in the year 2021 as tentatively estimated by Delhi Transco Ltd, is 8800 mw based on 16th Electricity Power Survey of India, CEA. To meet this demand, the concerned agencies need to augment the power supply and improve the transmission and distribution system. A 400 kv ring is being set up around Delhi to draw power from northern regional grid. The additional power requirement would be met from local generation and allocated share from the grid system. The projected arrangement for both local generation and central allocation is given in Table 14.5. The actual requirement should be monitored and arranged as per seasonal demand. POWER
- 54. THANK YOU